GAMES101作业2+提高题
声明:使用的是vs2022版,以下内容如有问题,感谢各位大佬指正!
作业要求:

作业目的:在屏幕上画出一个实心的三角形(深度测试)
我们需要做的:
关键词:包围盒;插值计算;深度测试;判断点是否在三角形内;光栅化;
1.粘贴自己第一次代码
Eigen::Matrix4f get_projection_matrix(float eye_fov, float aspect_ratio,float zNear, float zFar)
{
// Students will implement this function
Eigen::Matrix4f projection = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
// TODO: Implement this function
// Create the projection matrix for the given parameters.
// Then return it.
//粘贴第一次作业
float n = zNear;
float f = zFar;
Eigen::Matrix4f M_persp2Ortho;
M_persp2Ortho << n, 0, 0, 0,
0, n, 0, 0,
0, 0, n + f, -n * f,
0, 0, 1, 0;
float fov = eye_fov * MY_PI / 180.0;
float t = -n * tan(fov / 2.);//解决原三角倒着的方法,将t换为-t
float b = -t;
float r = aspect_ratio * t;
float l = -r;
Eigen::Matrix4f M_ortho, trans, scale;
trans << 1, 0, 0, -(r + l) / 2,
0, 1, 0, -(t + b) / 2,
0, 0, 1, -(n + f) / 2,
0, 0, 0, 1;
scale << 2 / (r - l), 0, 0, 0,
0, 2 / (t - b), 0, 0,
0, 0, 2 / (n - f), 0,
0, 0, 0, 1;
M_ortho = scale * trans;
projection = M_ortho * M_persp2Ortho;
return projection;
}
2.rasterize_triangle(): 执行三角形栅格化算法
分三步:
1.写三角形包围盒,计算三角形在屏幕空间的边界值
void rst::rasterizer::rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t)
{
auto v = t.toVector4();//v 是三角形三个顶点的齐次坐标(x,y,z,w)
// TODO : Find out the bounding box of current triangle.
//包围盒(计算三角形在屏幕空间中的边界值)AABB
float min_x = width;
float max_x = 0;
float min_y = height;
float max_y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
min_x = std::min(v[i].x(), min_x);
max_x = std::max(v[i].x(), max_x);
min_y = std::min(v[i].y(), min_y);
max_y = std::max(v[i].y(), max_y);
}
2.判断采样点是否在三角形内,计算采样点的重心坐标,然后透视矫正插值计算深度和颜色
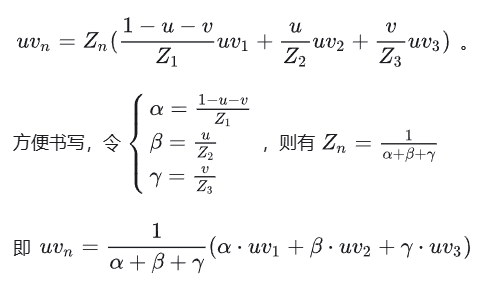

// iterate through the pixel and find if the current pixel is inside the triangle
//遍历像素,找出当前像素是否在三角形内
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
//如果是这样,请使用以下代码获取插值z值。
//auto[alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
//float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
//float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
//z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
for (int y = min_y; y < max_y; y++)
{
for (int x = min_x; x < max_x; x++)
{
//遍历边界框内的所有像素,检查中心点是否在三角形内
if (insideTriangle(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, t.v))//使用 (x + 0.5, y + 0.5) 作为像素中心点
{
//透视矫正插值计算深度和颜色
auto [alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, t.v);//计算该点的重心坐标
// 计算:1/(α + β + γ)
float w_reciprocal = 1.0 / (alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
// 计算:α(z₀/w₀) + β(z₁/w₁) + γ(z₂/w₂)
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
// 相乘,得到最终插值结果
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
3.深度测试与像素更新
// TODO : set the current pixel (use the set_pixel function) to the color of the triangle (use getColor function) if it should be painted.
int index = get_index(x, y);
if (z_interpolated < depth_buf[index])
{
Eigen::Vector3f p;
p << x, y, z_interpolated;
set_pixel(p, t.getColor());
depth_buf[index] = z_interpolated;
}
}
}
}
}
2.rasterize_triangle():的完整代码
void rst::rasterizer::rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t)
{
auto v = t.toVector4();//v 是三角形三个顶点的齐次坐标(x,y,z,w)
// TODO : Find out the bounding box of current triangle.
//包围盒(计算三角形在屏幕空间中的边界值)AABB
float min_x = width;
float max_x = 0;
float min_y = height;
float max_y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
min_x = std::min(v[i].x(), min_x);
max_x = std::max(v[i].x(), max_x);
min_y = std::min(v[i].y(), min_y);
max_y = std::max(v[i].y(), max_y);
}
// iterate through the pixel and find if the current pixel is inside the triangle
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
//auto[alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
//float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
//float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
//z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
for (int y = min_y; y < max_y; y++)
{
for (int x = min_x; x < max_x; x++)
{
//遍历边界框内的所有像素,检查中心点是否在三角形内
if (insideTriangle(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, t.v))//使用 (x + 0.5, y + 0.5) 作为像素中心点
{
//透视矫正插值计算深度和颜色
auto [alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, t.v);//计算该点的重心坐标
// 计算:1/(α + β + γ)
float w_reciprocal = 1.0 / (alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
// 计算:α(z₀/w₀) + β(z₁/w₁) + γ(z₂/w₂)
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
// 相乘,得到最终插值结果
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
// TODO : set the current pixel (use the set_pixel function) to the color of the triangle (use getColor function) if it should be painted.
// 深度测试与像素更新
int index = get_index(x, y);//将坐标转化为索引
if (z_interpolated < depth_buf[index]) //将当前像素的深度值和缓冲区中的进行比较
{
//z 值越小越近
//如果当前像素更近,就更新颜色和深度缓冲区
Eigen::Vector3f p;
p << x, y, z_interpolated;
//更新帧缓冲区的颜色
set_pixel(p, t.getColor());
//更新深度缓冲区的值
depth_buf[index] = z_interpolated;
}
}
}
}
}
3.测试点是否在三角形内(叉积)Cross product
static bool insideTriangle(float x, float y, const Vector3f* _v)
{
// TODO : Implement this function to check if the point (x, y) is inside the triangle represented by _v[0], _v[1], _v[2]
int flag = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Eigen::Vector3f p0 = { x,y,0 }; //待检测点
Eigen::Vector3f p1 = _v[i]; //当前边的起点
Eigen::Vector3f p2 = _v[(i + 1) % 3]; //当前边的终点
Eigen::Vector3f v1 = p1 - p0; //从待检测点到边起点的向量
Eigen::Vector3f v2 = p1 - p2; //边的方向向量
float cp = v1.cross(v2).z(); //计算叉积的z分量
if (cp == 0) continue; // 点在边上,继续检查下一条边
int sign = cp < 0 ? 0 : 1; // 获取叉积的符号(0为负,1为正)
if (flag == -1) flag = sign; // 记录第一个非零叉积的符号
if (flag != sign)return false; // 符号不一致,点在三角形外部
}
return true; // 所有边的叉积符号一致,点在三角形内部
}
最后运行,得到这幅图

[提高项 5 分] :
用 super-sampling 处理 Anti-aliasing : 你可能会注意到,当我们放大图像时,图像边缘会有锯齿感。我们可以用 super-sampling来解决这个问题,即对每个像素进行 2 * 2 采样,并比较前后的结果 (这里并不需要考虑像素与像素间的样本复用)。需要注意的点有,对于像素内的每一个样本都需要维护它自己的深度值,即每一个像素都需要维护一个 samplelist。最后,如果你实现正确的话,你得到的三角形不应该有不正常的黑边。
超采样抗锯齿 (SSAA) 的核心思想是:
- 以更高的分辨率渲染场景(例如每个像素分成 2×2=4 个子像素)
- 对每个子像素执行完整的光栅化和深度测试
- 将多个子像素的颜色值平均,得到最终像素颜色
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1912986768225047690
1.修改光栅化器类(rasterizer.hpp)—增加ssaa的缓冲区和索引
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> frame_buf;
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> frame_buf_ssaa;//超采样颜色缓冲区
std::vector<float> depth_buf;
std::vector<float> depth_buf_ssaa;//超采样深度缓冲区
int get_index(int x, int y);
int ssaa_factor = 2;//超采样系数(2*2超采样)
int get_ssaa_index(int x, int y);//索引
void downsampling();
int width, height;
2.修改 rasterizer.cpp
修改函数rasterizer
rst::rasterizer::rasterizer(int w, int h) : width(w), height(h)//初始化缓冲区
{
frame_buf.resize(w * h);
depth_buf.resize(w * h);
frame_buf_ssaa.resize(w * ssaa_factor * h * ssaa_factor);// 超采样颜色缓冲区
depth_buf_ssaa.resize(w * ssaa_factor * h * ssaa_factor);// 超采样深度缓冲区
}
修改清除函数clear
void rst::rasterizer::clear(rst::Buffers buff)
{
//清除颜色缓冲区,避免上一帧的残留颜色影响当前帧
if ((buff & rst::Buffers::Color) == rst::Buffers::Color)
{
std::fill(frame_buf.begin(), frame_buf.end(), Eigen::Vector3f{0, 0, 0});//重置为黑色
std::fill(frame_buf_ssaa.begin(), frame_buf_ssaa.end(), Eigen::Vector3f{ 0, 0, 0 });
}
//清除深度缓冲区,确保所有新的几何体都能正确进行深度比较
if ((buff & rst::Buffers::Depth) == rst::Buffers::Depth)
{
//初始化为无穷大确保所有新的片段都会通过测试
std::fill(depth_buf.begin(), depth_buf.end(), std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity());
std::fill(depth_buf_ssaa.begin(), depth_buf_ssaa.end(), std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity());
}
}
增加ssaa索引函数get_ssaa_index,将坐标(x,y)转换为线性索引
int rst::rasterizer::get_index(int x, int y)
{
return (height-1-y)*width + x;
}
int rst::rasterizer::get_ssaa_index(int x, int y) // 增加索引函数get_ssaa_index
{
return (height * ssaa_factor - 1 - y) * width * ssaa_factor + x;
//height * ssaa_factor - 1 - y:计算高分辨率下的目标行
//* width * ssaa_factor:每行的元素数(考虑超采样系数)
//+ x:当前行内的列偏移
}
修改光栅化三角形函数rasterize_triangle
未使用SSAA时的代码,不做修改
void rst::rasterizer::rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t)
{
//未使用SSAA时的代码,不做修改
auto v = t.toVector4();//v 是三角形三个顶点的齐次坐标(x,y,z,w)
// TODO : Find out the bounding box of current triangle.
//包围盒(计算三角形在屏幕空间中的边界值)AABB
float min_x = width;
float max_x = 0;
float min_y = height;
float max_y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
min_x = std::min(v[i].x(), min_x);
max_x = std::max(v[i].x(), max_x);
min_y = std::min(v[i].y(), min_y);
max_y = std::max(v[i].y(), max_y);
}
// iterate through the pixel and find if the current pixel is inside the triangle
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
//auto[alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
//float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
//float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
//z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
for (int y = min_y; y < max_y; y++)
{
for (int x = min_x; x < max_x; x++)
{
//遍历边界框内的所有像素,检查中心点是否在三角形内
if (insideTriangle(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, t.v))//使用 (x + 0.5, y + 0.5) 作为像素中心点
{
//透视矫正插值计算深度和颜色
auto [alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x + 0.5, y + 0.5, t.v);//计算该点的重心坐标
// 计算:1/(α + β + γ)
float w_reciprocal = 1.0 / (alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
// 计算: = α(z₀/w₀) + β(z₁/w₁) + γ(z₂/w₂)
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
// 相乘,得到最终插值结果
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
// TODO : set the current pixel (use the set_pixel function) to the color of the triangle (use getColor function) if it should be painted.
// 深度测试与像素更新
int index = get_index(x, y);//将坐标转化为索引
if (z_interpolated < depth_buf[index]) //将当前像素的深度值和缓冲区中的进行比较
{
//z 值越小越近
//如果当前像素更近,就更新颜色和深度缓冲区
Eigen::Vector3f p;
p << x, y, z_interpolated;
//更新帧缓冲区的颜色
set_pixel(p, t.getColor());
//更新深度缓冲区的值
depth_buf[index] = z_interpolated;
}
}
}
}
增加的ssaa部分
//将普通分辨率的边界框转换为超采样分辨率
float ss_min_x = min_x * ssaa_factor;
float ss_max_x = max_x * ssaa_factor;
float ss_min_y = min_y * ssaa_factor;
float ss_max_y = max_y * ssaa_factor;
//计算超采样空间中的整数边界,并确保不超出缓冲区范围
int ss_xmin = std::max(0, static_cast<int>(std::floor(ss_min_x)));
int ss_xmax = std::min(width * ssaa_factor - 1, static_cast<int>(std::ceil(ss_max_x)));
int ss_ymin = std::max(0, static_cast<int>(std::floor(ss_min_y)));
int ss_ymax = std::min(height * ssaa_factor - 1, static_cast<int>(std::ceil(ss_max_y)));
// 遍历超采样分辨率下的像素
for (int y = ss_ymin; y <= ss_ymax; ++y)
{
for (int x = ss_xmin; x <= ss_xmax; ++x)
{
// 转换为原始坐标系的坐标 (0.5是样本点偏移量)
float pixel_x = x / static_cast<float>(ssaa_factor) + 0.5f;
float pixel_y = y / static_cast<float>(ssaa_factor) + 0.5f;
// 检查当前超采样点是否在三角形内
if (insideTriangle(pixel_x, pixel_y, t.v))
{
auto [alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(pixel_x, pixel_y, t.v);
float w_reciprocal = 1.0 / (alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
int ss_index = get_ssaa_index(x, y);
// 深度测试
if (z_interpolated < depth_buf_ssaa[ss_index])
{
// 更新超采样缓冲区的颜色和深度
depth_buf_ssaa[ss_index] = z_interpolated;
frame_buf_ssaa[ss_index] = t.getColor();
}
}
}
}
}
增加降采样 (Downsampling):将多个子像素的颜色值平均,得到最终像素颜色
void rst::rasterizer::downsampling()
{
if (ssaa_factor == 1) // 特殊情况:如果SSAA系数为1,直接复制缓冲区(无需降采样)
{
std::copy(frame_buf_ssaa.begin(), frame_buf_ssaa.end(), frame_buf.begin());
return;
}
// 遍历每个原始像素
for (int y = 0; y < height; ++y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; ++x)
{
Eigen::Vector3f avg_color(0, 0, 0);
// 遍历当前像素对应的所有子像素
for (int dy = 0; dy < ssaa_factor; ++dy)
{
for (int dx = 0; dx < ssaa_factor; ++dx)
{
// 计算子像素在超采样缓冲区中的坐标
int ss_x = x * ssaa_factor + dx;
int ss_y = y * ssaa_factor + dy;
// 获取子像素的颜色并累加
int ss_index = get_ssaa_index(ss_x, ss_y);
avg_color += frame_buf_ssaa[ss_index];
}
}
// 计算平均值
avg_color /= (ssaa_factor * ssaa_factor);
// 将平均颜色写入最终帧缓冲区
int index = get_index(x, y);
frame_buf[index] = avg_color;
}
}
}
修改绘制函数draw
void rst::rasterizer::draw(pos_buf_id pos_buffer, ind_buf_id ind_buffer, col_buf_id col_buffer, Primitive type)
{
auto& buf = pos_buf[pos_buffer.pos_id]; // 顶点位置缓冲区
auto& ind = ind_buf[ind_buffer.ind_id]; // 索引缓冲区
auto& col = col_buf[col_buffer.col_id]; // 颜色缓冲区
// 计算视口变换参数
float f1 = (50 - 0.1) / 2.0; // 近平面和远平面的中间值
float f2 = (50 + 0.1) / 2.0; // 近平面和远平面的平均值
Eigen::Matrix4f mvp = projection * view * model;
for (auto& i : ind)
{
Triangle t;
// 1. 应用MVP变换
Eigen::Vector4f v[] = {
mvp * to_vec4(buf[i[0]], 1.0f),
mvp * to_vec4(buf[i[1]], 1.0f),
mvp * to_vec4(buf[i[2]], 1.0f)
};
// 2. 齐次除法(从裁剪空间到NDC)
for (auto& vec : v) {
vec /= vec.w();
}
// 3. 视口变换(从NDC到屏幕坐标)
for (auto & vert : v)
{
vert.x() = 0.5*width*(vert.x()+1.0);
vert.y() = 0.5*height*(vert.y()+1.0);
vert.z() = vert.z() * f1 + f2;
}
// 4. 设置三角形顶点
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
t.setVertex(i, v[i].head<3>());
t.setVertex(i, v[i].head<3>());
t.setVertex(i, v[i].head<3>());
}
// 5. 设置三角形颜色
auto col_x = col[i[0]];
auto col_y = col[i[1]];
auto col_z = col[i[2]];
t.setColor(0, col_x[0], col_x[1], col_x[2]);
t.setColor(1, col_y[0], col_y[1], col_y[2]);
t.setColor(2, col_z[0], col_z[1], col_z[2]);
// 6. 光栅化三角形
rasterize_triangle(t);
}
//7. 执行降采样
downsampling();
}
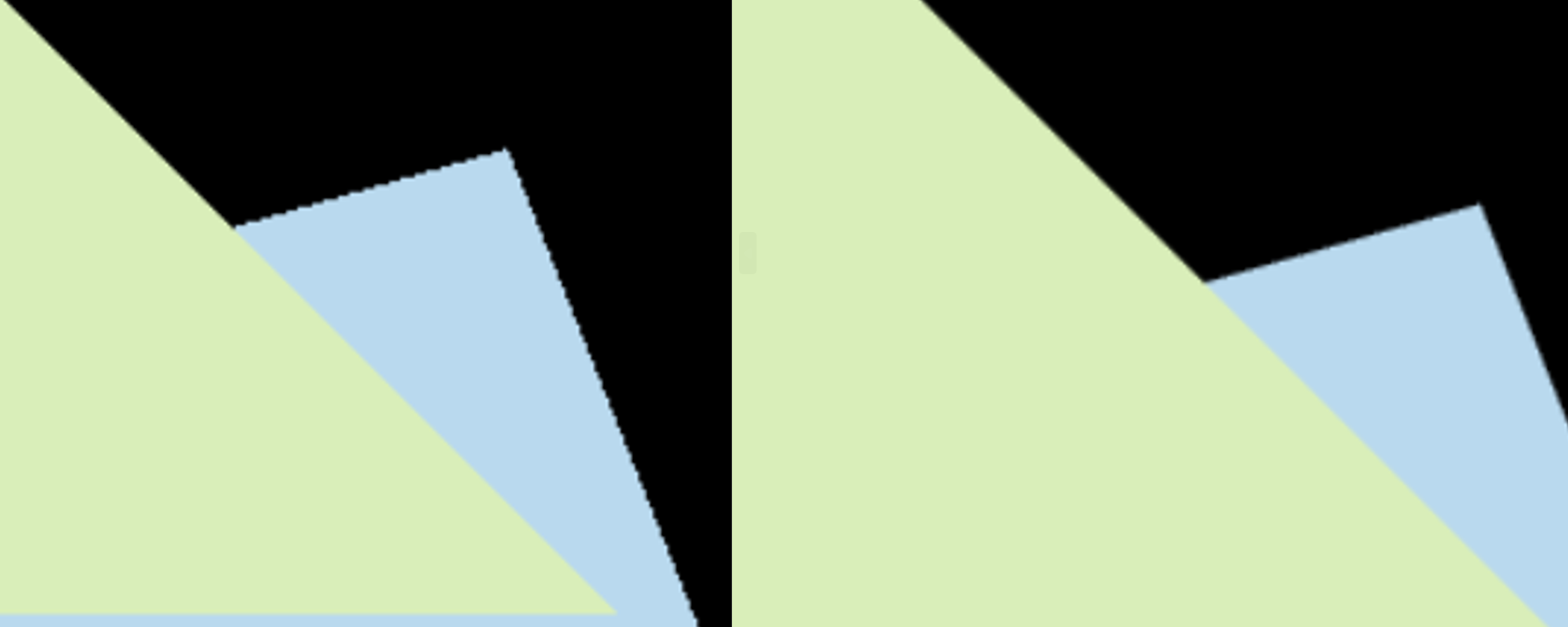


左图是未使用ssaa,右图是使用了ssaa,还是比较明显的




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号