第三次实验
实验任务1
1.
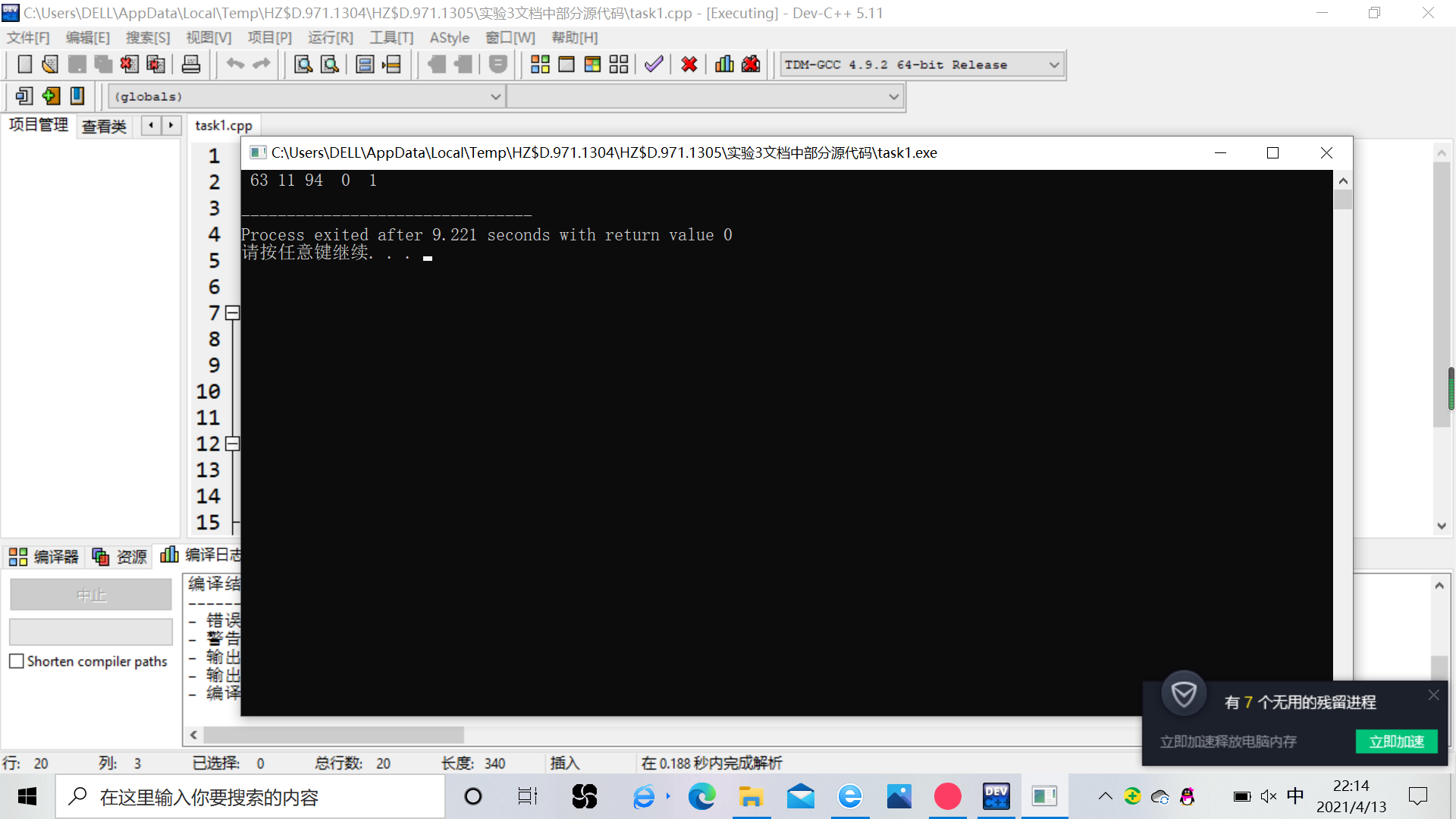
// 生成N个0~99之间的随机整数,并打印输出 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #define N 5 int main() { int x, n; srand(time(0)); // 以当前系统时间作为随机种子 for(n=1; n<=N; n++) { x = rand() % 100; // 生成一个0~99之间的随机整数 printf("%3d", x); } printf("\n"); return 0; }
2.
实验任务2
1.
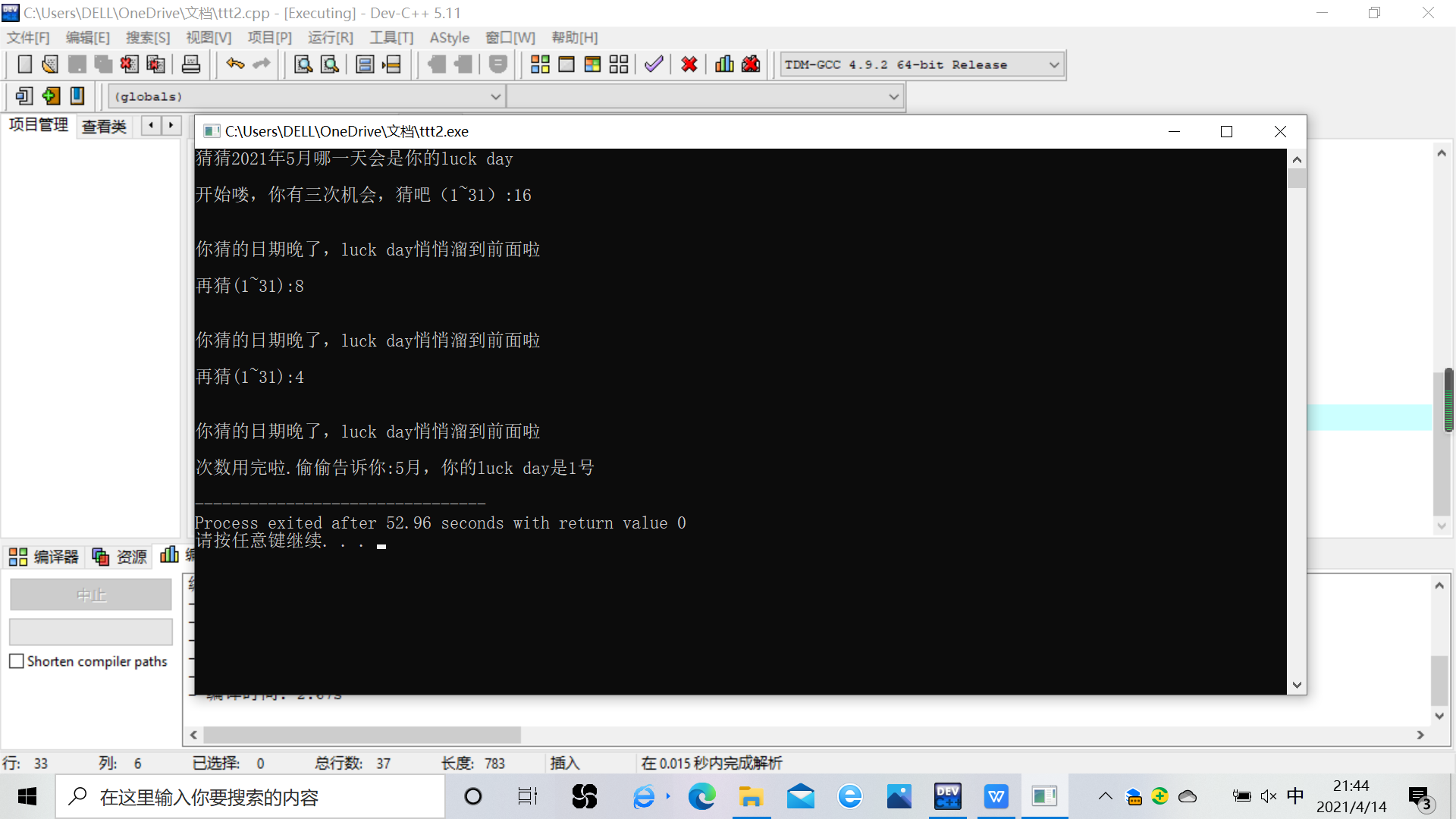
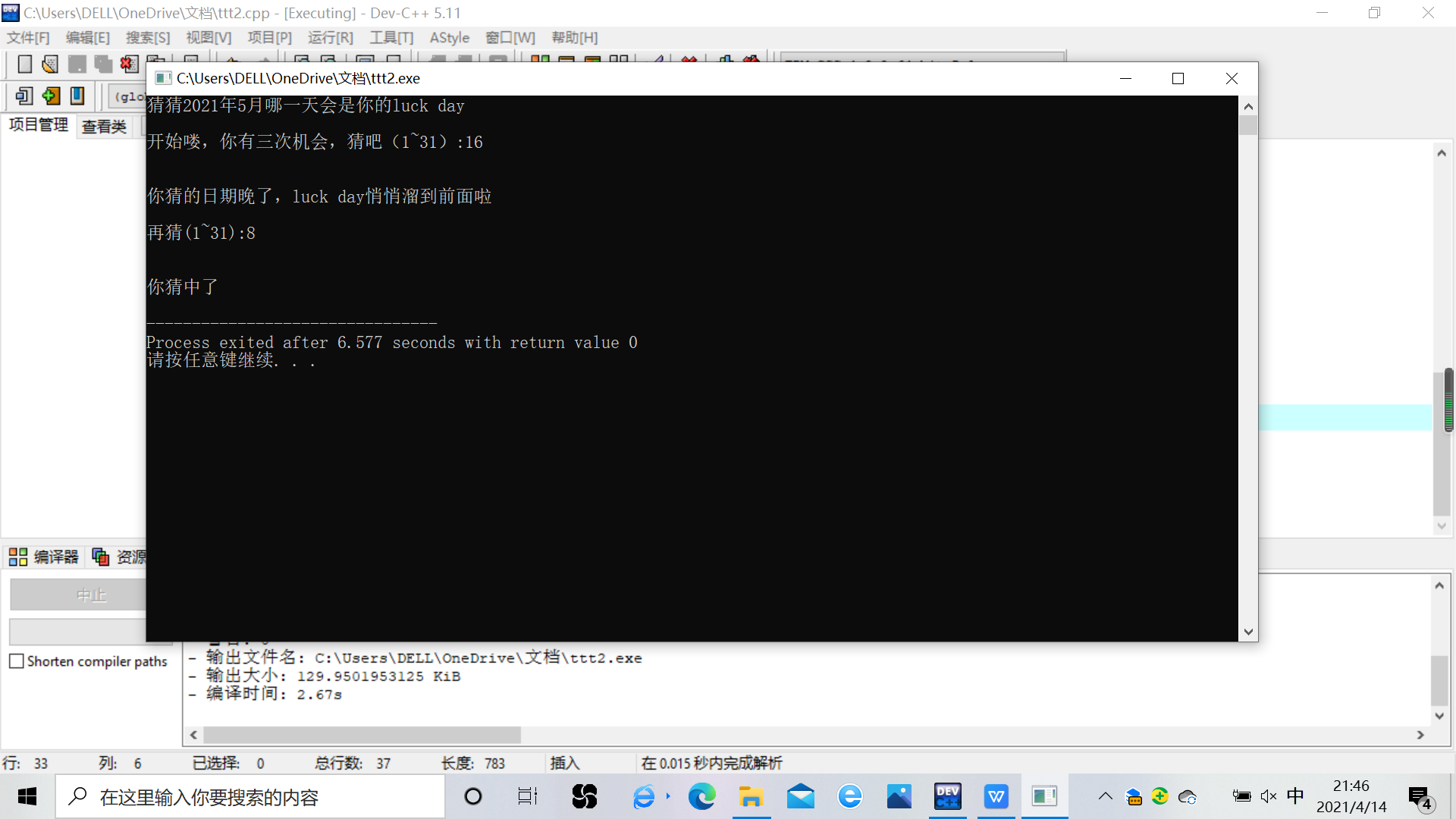
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main() { int x,y,i; printf("猜猜2021年5月哪一天会是你的luck day\n\n"); srand(time(0)); // 以当前系统时间作为随机种子 x = rand() % 31; // 生成一个0~99之间的随机整数 x++; printf("开始喽,你有三次机会,猜吧(1~31):"); for(i=1;i<=3;i++){ if(i>1){ printf("\n"); printf("再猜(1~31):"); } scanf("%d",&y); printf("\n"); if(y>x){ printf("\n"); printf("你猜的日期晚了,luck day悄悄溜到前面啦\n"); } else if(y<x){ printf("\n"); printf("你猜的日期早了,luck day还没到呢\n"); } else if(y=x){ printf("\n"); printf("你猜中了\n"); return 0; } } printf("\n"); printf("次数用完啦.偷偷告诉你:5月,你的luck day是%d号\n", x); return 0; }
2.
实验任务3
1.
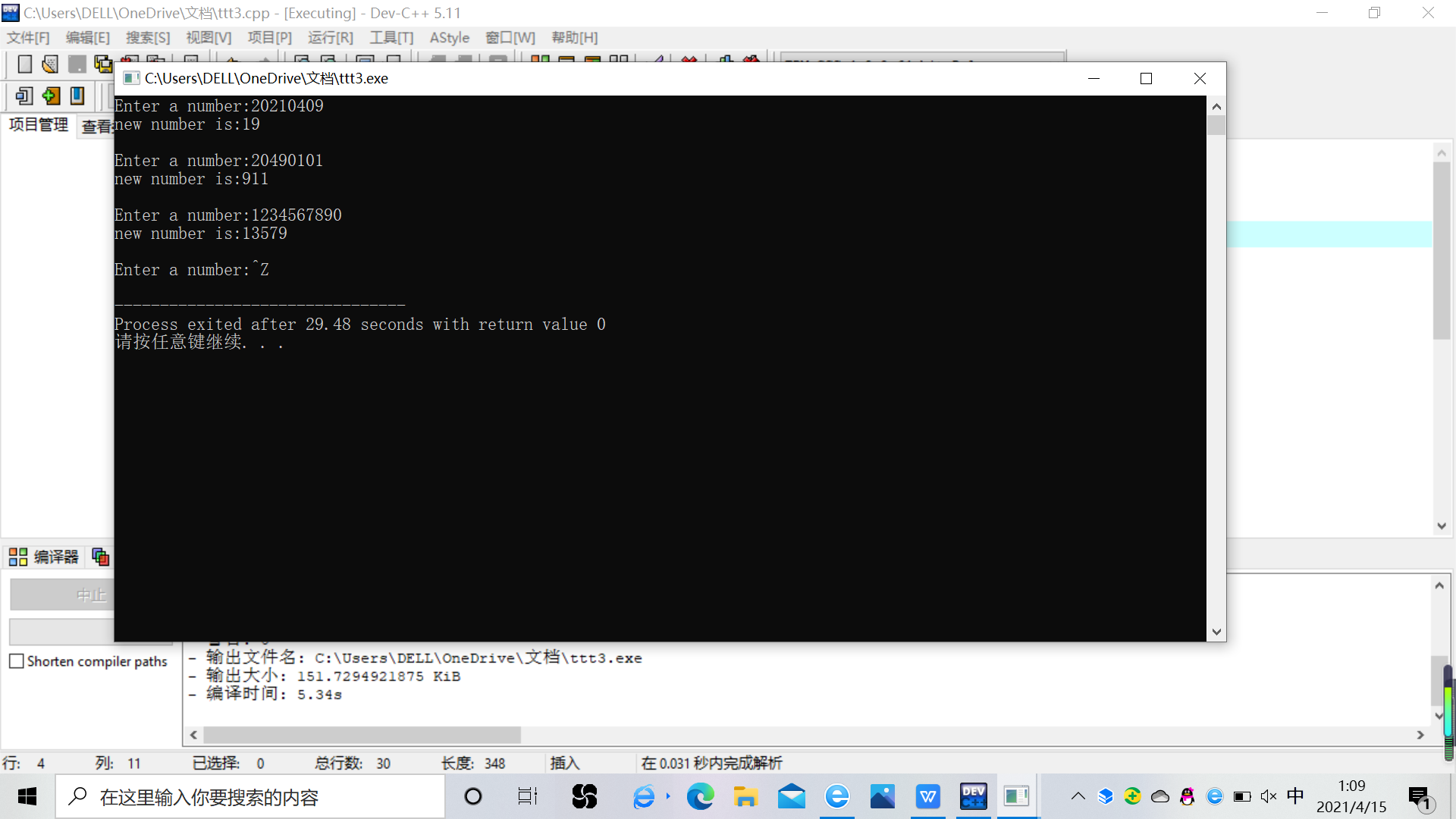
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int main(){ long s; int n,x,i; while(printf("Enter a number:"),scanf("%ld",&s)!=EOF){ x=0; i=0; while(s!=0){ n=s%10; s=s/10; if(n%2!=0){ x=x+n*pow(10,i); i++; } } printf("new number is:%d\n\n",x); } return 0; }
2.
实验任务4
1.
// 一元二次方程求解(函数实现方式) // 重复执行, 直到按下Ctrl+Z结束 #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> // 函数声明 void solve(double a, double b, double c); // 主函数 int main() { double a, b, c; printf("Enter a, b, c: "); while(scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &a, &b, &c) != EOF) { solve(a, b, c); // 函数调用 printf("Enter a, b, c: "); } return 0; } // 函数定义 // 功能:求解一元二次方程,打印输出结果 // 形式参数:a,b,c为一元二次方程系数 void solve(double a, double b, double c) { double x1, x2; double delta, real, imag; if(a == 0) printf("not quadratic equation.\n"); else { delta = b*b - 4*a*c; if(delta >= 0) { x1 = (-b + sqrt(delta)) / (2*a); x2 = (-b - sqrt(delta)) / (2*a); printf("x1 = %.2f, x2 = %.2f\n", x1, x2); } else { real = -b/(2*a); imag = sqrt(-delta) / (2*a); printf("x1 = %.2f + %.2fi, x2 = %.2f - %.2fi\n", real, imag, real, imag); } } }
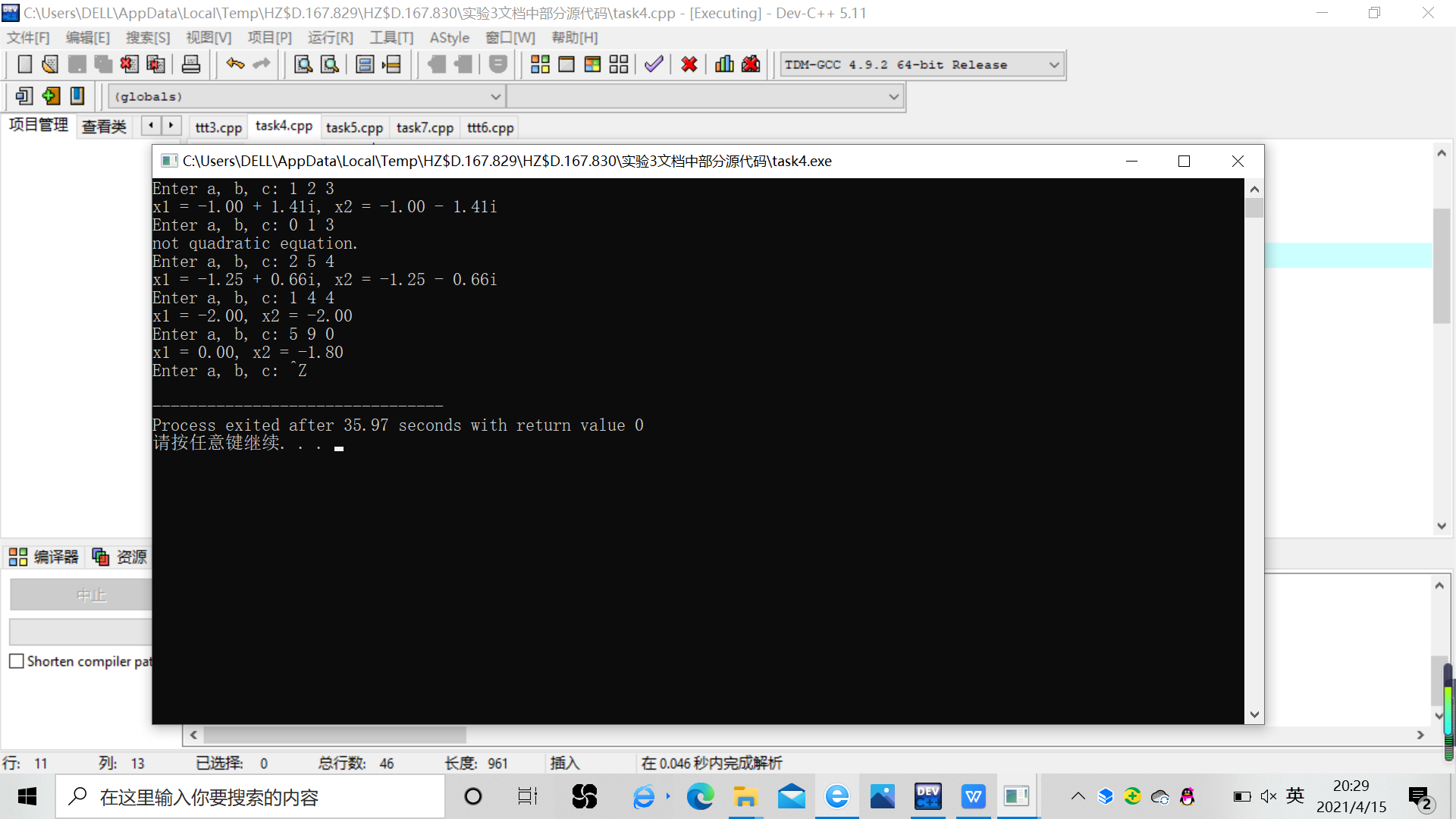
2.否。因为:一元二次方程一旦有根,就会有两个根。而两个结果无法以函数返回值的方式返回给主调函数。
实验任务5
1.
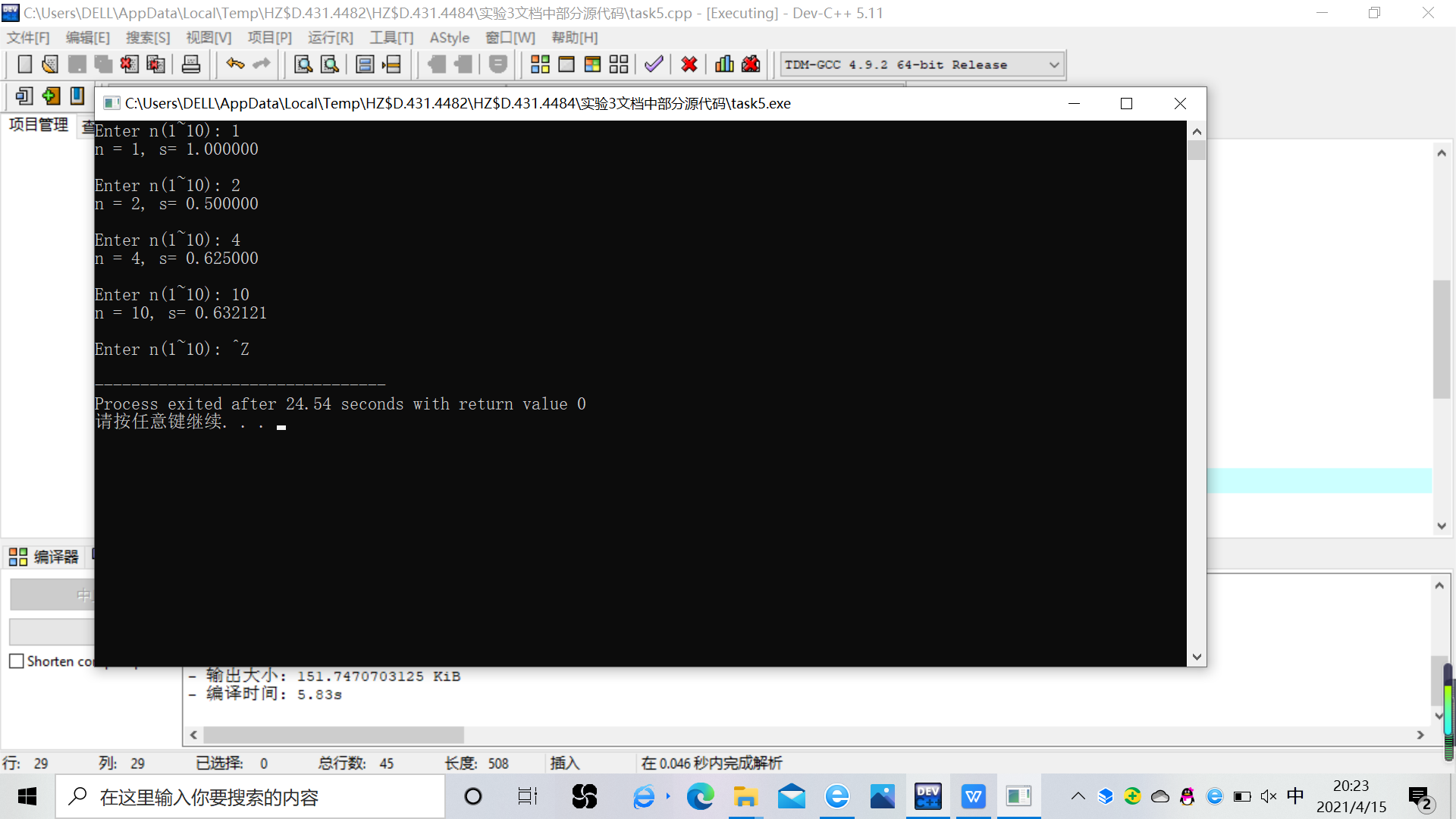
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> double fun(int n); // 函数声明 int main() { int n; double s; printf("Enter n(1~10): "); while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { s = fun(n); // 函数调用 printf("n = %d, s= %f\n\n", n, s); printf("Enter n(1~10): "); } return 0; } // 函数定义 double fun(int n) { int m,i,j; double s; s=0; for(i=1;i<=n;i++){ m=1; for(j=1;j<=i;j++){ m=m*j; } s=s+pow(-1,i-1)*(1.0/m); } return s; }
2.
实验任务6
1.
#include <stdio.h> #include<math.h> int isPrime(int x); int main (){ int n,t; t=0; for(n=100;n<=200;n++){ if(isPrime(n)){ t++; printf("%4d",n); if(t%5==0){ printf("\n"); } } } printf("\n\n"); printf("100~200之间素数个数为:%d",t); } int isPrime(int x){ int k; for(k=2;k<=sqrt(x);k++){ if(x%k==0){ return 0; } } return 1; }
2.

实验总结
1.for循环的使用,函数的定义以及调用,一元二次方程的解法。
2.我感觉实验三要比前两次难好多好多。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号