读书报告
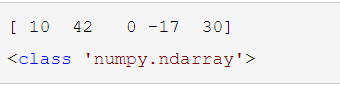
import numpy as np ls1 = [10, 42, 0, -17, 30] nd1 =np.array(ls1) print(nd1) print(type(nd1))
import scipy import numpy as np from scipy import linalg mat_ = np.array([[2,3,1],[4,9,10],[10,5,6]]) #创建矩阵 print(mat_) #>[[ 2 3 1],[ 4 9 10],[10 5 6]] linalg.det(mat_) #矩阵的行列式 inv_mat = linalg.inv(mat_) #矩阵的逆 print(inv_mat) #>[[ 0.02409639 -0.07831325 0.12650602] #[ 0.45783133 0.01204819 -0.09638554] #[-0.42168675 0.12048193 0.03614458]]
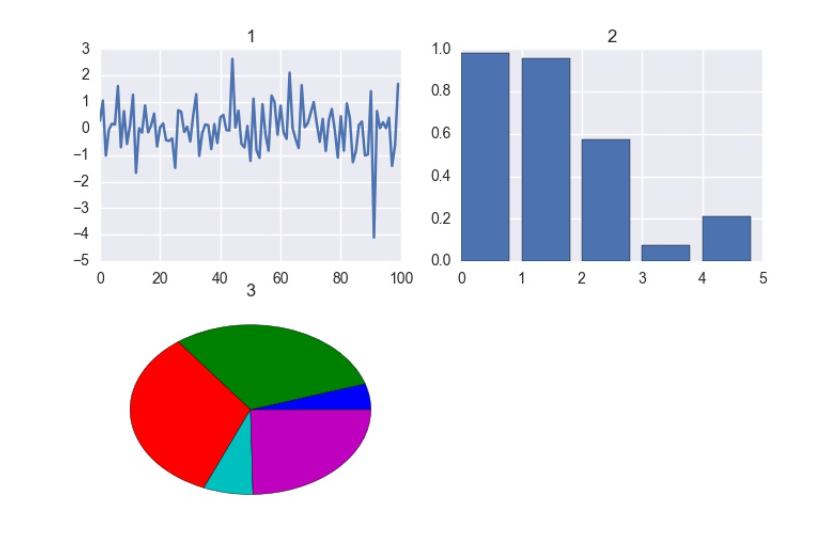
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1)
y = np.random.randn(100)
plt.plot(y);
ax.set_title('1')
y = np.random.rand(5)
x = np.arange(5)
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 2)
plt.bar(x, y)
ax.set_title('2');
y = np.random.rand(5)
y = y / np.sum(y)
y[y < .05] = .05
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3)
plt.pie(y)
ax.set_title('3')
plt.draw()
plt.show()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号