集合框架_DAY17
1:五种数据结构:
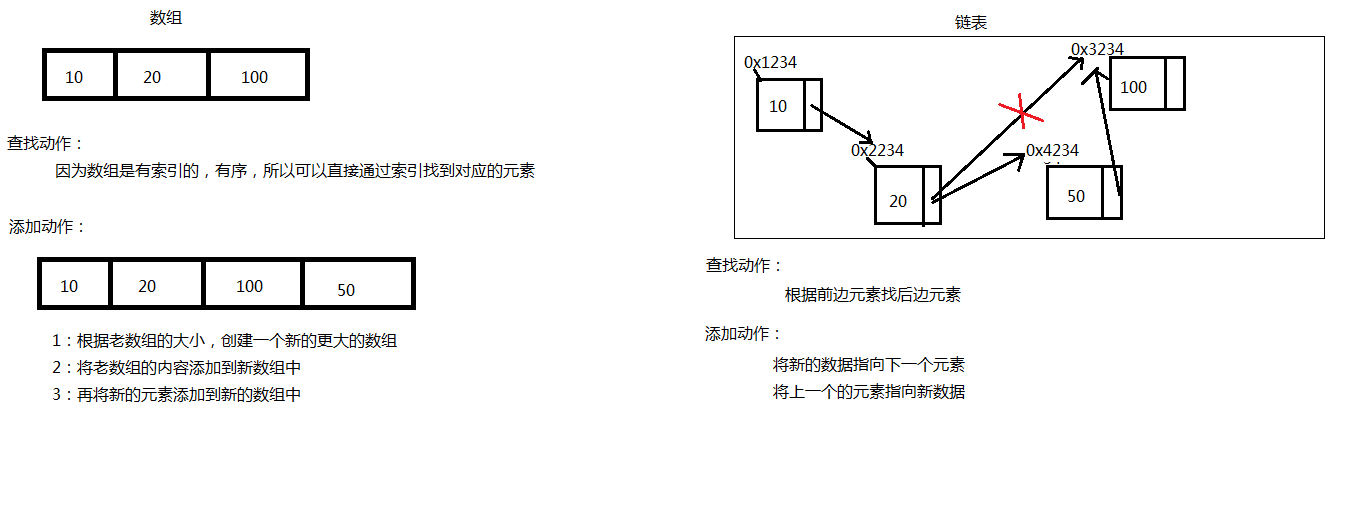
数组:长度固定,有序,查找方便
链表:添加删除方便
栈:先进后出
队列:先进先出
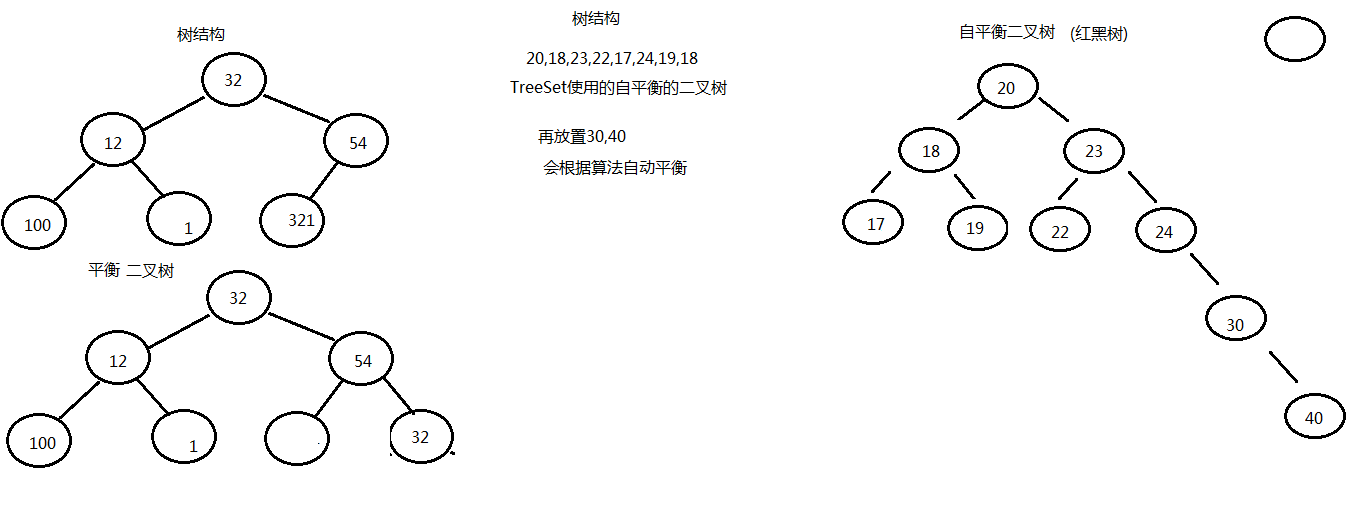
树结构:完成排序动作
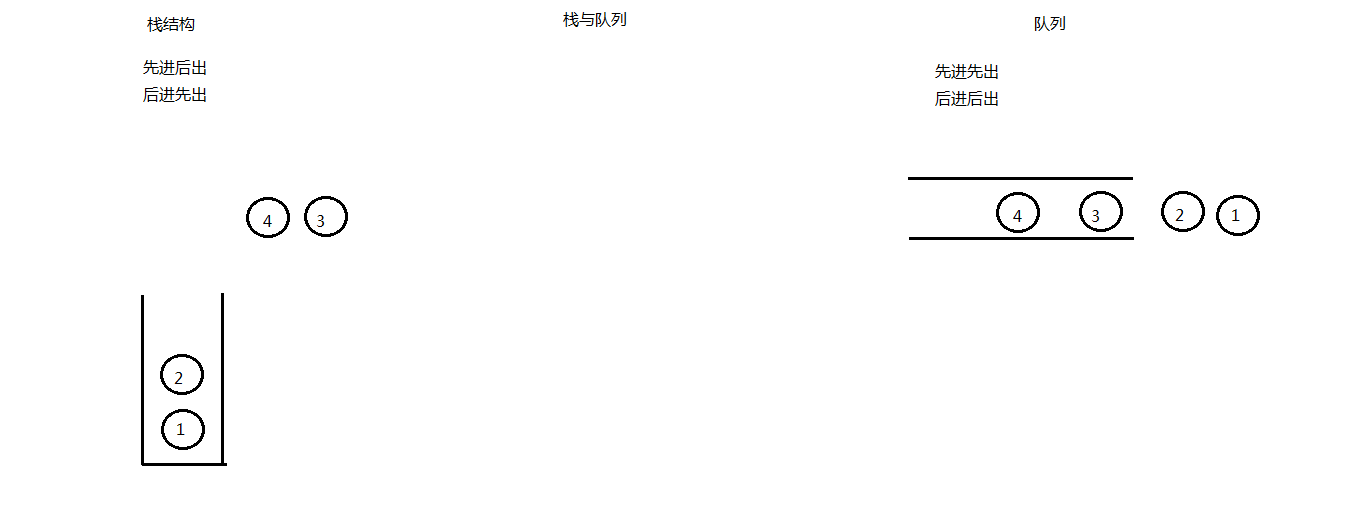
2:泛型(了解)
(1)是一种把明确数据类型的工作推迟到创建对象或者调用方法的时候采取明确的特殊的类型,将运行时的异常转到编译时的异常。
(2)格式:
<数据类型>
注 默认情况下,泛型是Object类型。
(3)好处:(理解)
A:优化了程序的设计。
B:把运行期的问题提前到了编译期。
D:避免了强制类型转换。
(4)泛型体现:
A:泛型类 :把泛型定义在类上 (见例题2)
B:泛型接口:把泛型定义在接口上
方式一:在类实现接口时定义范型(见例题3)
方式二:在类实现接口时任然不明确范型类型,在创建对象时明确范型类型(见例题3)
C:泛型方法 :把泛型定义在方法上(见例题4)
(5)泛型通配符,表示任意类型<?>。
<?>与<T>的差别:
通配符修饰的泛型不能直接使用而<T>可以使用
通配符修饰相当于声明了一种变量,它可以作为参数在方法中传递,如collection的containsAll方法(见例题5)
使用<?>可以完成类型限定,可参见TreeSet构造方法
TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) , 限定类型上限 (见例题6)
TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) , 限定类型下限
3:静态导入
import 包.包.类.静态成员(见例题 7)
4:可变参数
格式:方法名(参数类型... 变量名)(见例题8)
本质:将参数转成数组再进行操作
注意事项:
可变参数与数组类型不能重载,因为二者本质上是一样的;
可变参数必须放在最后。
5:Stack类(底部存储结构是堆栈)
Stack类的主要方法:
push():加入一个元素
pop():弹出一个元素(堆栈少一个元素)
peak():取出一个元素(堆栈中的元素不会少)
6:Arrays与Collections
数组与集合工具类
附:
1、完成ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet、TreeSet的泛型使用。

import java.util.*; public class GenericsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("-----------ArrayList----------------"); ArrayList<String> arrayList=new ArrayList<>(); String string1="唐嫣"; String string2="糖糖"; String string3="唐老鸭"; arrayList.add(string1); arrayList.add(string2); arrayList.add(string3); //arrayList.add(2); 只能加String for(String string:arrayList){ System.out.println(string); } Iterator<String> iterator= arrayList.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } System.out.println("---------------LinkedList---------------"); LinkedList<String> linkedList=new LinkedList<String>(); linkedList.add(string1); linkedList.add(string2); linkedList.add(string3); //linkedList.add(2); 只能加String for(String string:linkedList){ System.out.println(string); } System.out.println("---------------HashSet---------------"); HashSet<String> hashSet=new HashSet<String>(); hashSet.add(string1); hashSet.add(string2); hashSet.add(string3); for(String string:hashSet){ System.out.println(string); } System.out.println("---------------TreeSet---------------"); TreeSet<String> treeSet=new TreeSet<String>(); treeSet.add("1string"); treeSet.add("2string"); treeSet.add("3string"); treeSet.add("4花花"); treeSet.add("5绿绿"); for(String string:treeSet){ System.out.println(string);//TreeSet类实现了Comparable接口,里面的元素实现了自然排序 } } }
2、自定义范型类的使用

public class defGeneTest { public static void main(String[] args) { DedineGenerics<String> dedineGenerics=new DedineGenerics<String>(); dedineGenerics.setObj("自定义范型"); String obj=dedineGenerics.getObj(); System.out.println(obj); } }

public class DedineGenerics<T> { private T obj; public T getObj() { return obj; } public void setObj(T obj) { this.obj = obj; } }
3、范型接口的两种使用方式
方式1:在类实现接口时定义范型

public interface MyInterface<T> { public abstract void method(T t); }

public class MyClass implements MyInterface<String> { @Override public void method(String t) { System.out.println(t); } }

public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //不带泛型的类,直接创建对象即可。 MyClass myClass = new MyClass(); myClass.method("我爱中华,莫谈国事!"); } }
方式2:在类实现接口时任然不明确范型类型,在创建对象时明确范型类型

//定义了MyClass2类,定义该类时,不明确接口的泛型类型,从而使该类也变成了泛型类。 public class MyClass2<T> implements MyInterface<T>{ @Override public void method(T t) { System.out.println(t); } }

public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //泛型类创建对象时,需要指定泛型类型。 MyClass2<Person> myClass2 = new MyClass2<Person>(); myClass2.method(new Person("唐嫣",28)); } }
4、把泛型定义在方法上

public class Demo<T> { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo<Person> p = new Demo<Person>(); p.method(new Person("唐嫣", 28)); p.method2(new Person("唐唐",26)); p.method2("唐嫣"); } public void method(T t){ System.out.println(t); } public <E> void method2(E e){ System.out.println(e); } }
5、通配符修饰相当于声明了一种变量,它可以作为参数在方法中传递,如collection的containsAll方法

public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<String>(); collection.add("唐嫣"); collection.add("唐三彩"); collection.add("唐伯虎"); collection.add("唐人街"); Collection<Person> collection2 = new ArrayList<Person>(); collection2.add(new Person("唐嫣",28)); collection2.add(new Person("baby",30)); collection2.add(new Person("杨颖",26)); collection.containsAll(collection2); } }
6、使用<?>可以完成类型限定,可参见TreeSet构造方法 TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) , 限定类型上限

public class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { //public TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) // Collection<Person> c = new ArrayList<Person>(); 存Person类型不可以 Collection<Cat> c = new ArrayList<Cat>(); //Cat类是Animal的子类,可以存 TreeSet<Animal> animals = new TreeSet<Animal>(c); } }
7、静态导入

import static java.lang.System.out; import static java.lang.Math.PI; import static java.lang.Math.random; public class Demo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("hello"); System.out.println("hello"); System.out.println("hello"); out.print("hello"); out.print("hello"); out.print("hello"); double random = Math.random(); out.println(PI); out.println(random()); } }
8、可变参数

/* * 可变参数: 即参数可变,可以传入任意个数的参数,只要数据类型相同,这些参数会自动存储到数组当中,只需要操作数组即可。 * 格式:函数名(参数类型... 数组名) * * 注意事项: * 可变参数与数组类型不能重载,因为二者本质上是一样的。 * 可变参数必须放在最后 */ public class Demo6 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getSum(1, 2)); System.out.println(getSum("的调用", 2,3)); System.out.println(getSum(1, 2, 3)); System.out.println(getSum(1, 2, 3,4,5,6,7,8,9)); } // // 计算两个数字的和 // public static int getSum(int a, int b) { // return a + b; // } // // // 计算三个数字的和 // public static int getSum(int a, int b, int c) { // return a + b + c; // } // 计算N个数字的和 public static int getSum(int... numbers) { System.out.println("可变参数方法"); int sum = 0; for (int i : numbers) { sum += i; } return sum; } public static int getSum(String b,int... numbers) { System.out.println("可变参数方法"+b); int sum = 0; for (int i : numbers) { sum += i; } return sum; } //可变参数与数组类型不能重载,因为二者本质上是一样的。 // public static int getSum(int[] numbers) { // System.out.println("可变参数方法"); // int sum = 0; // for (int i : numbers) { // sum += i; // } // return sum; // } }
9、完成单列集合嵌套任意其他集合。如ArrayList当中元素为HashSet等

import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashSet; /* * 完成单列集合嵌套任意其他集合。如ArrayList当中元素为HashSet等。 */ public class CollectionNesting { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<HashSet> arrayList=new ArrayList<HashSet>(); HashSet<String> hashSet1=new HashSet<String>(); hashSet1.add("宝宝"); hashSet1.add("乖乖"); hashSet1.add("亲爱的"); hashSet1.add("花花"); HashSet<String> hashSet2=new HashSet<String>(); hashSet2.add("宝宝"); hashSet2.add("乖乖"); hashSet2.add("亲爱的"); hashSet2.add("花花"); HashSet<String> hashSet3=new HashSet<String>(); hashSet3.add("宝宝"); hashSet3.add("乖乖"); hashSet3.add("亲爱的"); hashSet3.add("花花"); arrayList.add(hashSet1); arrayList.add(hashSet2); arrayList.add(hashSet3); System.out.println(arrayList); } }
10、产生10个1-20之间的随机数要求随机数不能重复案例。

public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = 1; i <=20 ; i++) { arrayList.add(i); } Collections.shuffle(arrayList);//随机打乱顺序,取前10个 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Integer integer = arrayList.get(i); System.out.print(integer+" "); } } }
11、键盘录入多个数据在控制台输出最大值案例
方法1:

/** *键盘录入多个数据在控制台输出最大值案例 */ public class shuffle { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("请输入任意个数,以输入0结束:"); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); //创建集合 List list = new ArrayList(); //向集合里添加元素 while(true) { int num=in.nextInt(); if(num !=0){ list.add(num); }else{ break; } } //打印集合 System.out.println("您输入的数是:"); System.out.println(list); //求集合里的最大值 int maxNum = (int)Collections.max(list); //输出最大值 System.out.println("最大值是:"+maxNum); } }
方法2:

import java.util.*; /** *键盘录入多个数据在控制台输出最大值案例 */ public class shuffle { public static void main(String[] args) { //键盘录入 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); String str=sc.nextLine(); //建TreeSet集合 TreeSet treeSet=new TreeSet(); //切割字符串成字符串数组 String[] strings=str.trim().split(" +"); //字符串数组转Integer类型数组,并且存在集合中 for (String string:strings){ Integer integer=Integer.parseInt(string); treeSet.add(integer); } //排序过后的treeSet System.out.println(treeSet); //输出做大值 int max=(int)treeSet.last(); System.out.println(max); } }
12、键盘录入多个数据,按数据从小到大的顺序打印到控制台

import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.Scanner; /** * 键盘录入多个数据,按数据从小到大的顺序打印到控制台 */ public class InputNumSort { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("请输入任意个数,以输入0结束:"); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); //创建集合 List list = new ArrayList(); //向集合里添加元素 while(true) { int num=in.nextInt(); if(num !=0){ list.add(num); }else{ break; } } //打印集合 System.out.println("您输入的数是:"); for(Object num:list){ System.out.print(num+" "); } //从大到小的顺序排序 Collections.sort(list); System.out.println(); //排序后的集合输出到控制台 System.out.println("排序后的数是:"); for(Object num:list){ System.out.print(num+" "); } } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号