Java 单例模式
饿汉式,DCL懒汉式,深究
饿汉式
public class Hungry {
//可能会浪费空间
private byte[] data1 = new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data2 = new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data3 = new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data4 = new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data5 = new byte[1024*1024];
private Hungry(){}
public final static Hungry HUNGRY = new Hungry();
public static Hungry getInstance(){
return HUNGRY;
}
}
DCL懒汉式
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
//懒汉式单例
public class LazyMan {
private static boolean shijie = false;
private LazyMan(){
synchronized(LazyMan.class) {
if(shijie == false){
shijie = true;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射破坏异常");
}
}
}
//加入volatile 可以禁止指令重排序
private static volatile LazyMan instance= null;
//双重检锁模式的 懒汉式单例 DCL 懒汉式 (double check lock 双端检锁机制)
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
if(instance == null) {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if(instance == null){
instance = new LazyMan();//"new LazyMan()" 不是一个原子性操作,是分三步走的
/*
* 1、分配内存空间
* 2、执行构造方法,初始化对象
* 3、把这个对象指向这个空间
*
* 正常是 123;若是发生指令重排,就有可能变成 132
* 假如有 A、B 两个线程,当A线程执行完1和3的时候,B线程进来了;
* 由于A线程执行完1和3时,已经用空对象先把内存空间给占用了(执行到2时,再去指向初始化对象);
* 因此,B线程在判断 instance==null 时,instance已经不等于null。
* 会直接 return instance,此时 instance 还没完成构造,内存空间还是一片虚无,就有可能会产生一些问题。
* 132 A
* B
*
* */
}
}
}
return instance;
}
//反射
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//LazyMan instance = LazyMan.getInstance();
Field shijie = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredField("shijie");
shijie.setAccessible(true);
Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
LazyMan instance = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
shijie.set(instance,false);
LazyMan instance2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance.hashCode());
System.out.println(instance2.hashCode());
}
//多线程并发
/*public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
LazyMan.getInstance();
}).start();
}
}*/
}
静态内部类
//静态内部类
public class Holder {
private Holder(){}
public static Holder getInstance(){
return InnerClass.HOLDER;
}
public static class InnerClass{
private final static Holder HOLDER = new Holder();
}
}
因为反射的存在,使得单例不安全
枚举
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public enum EnumSingle {
INSTANCE;
public EnumSingle getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
EnumSingle instance1 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE;
//Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
//NoSuchMethodException: temp.single.EnumSingle.<init>()
Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
//IllegalArgumentException: Cannot reflectively create enum objects
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
EnumSingle instance2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance1.hashCode());
System.out.println(instance2.hashCode());
}
}
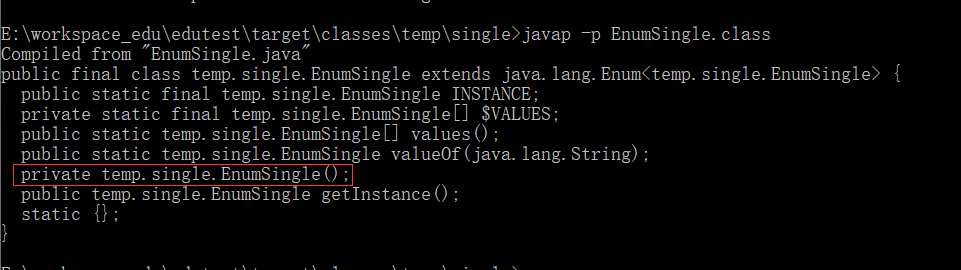
枚举类型的最终反编译源码:
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public enum EnumSingle {
INSTANCE;
public EnumSingle getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
EnumSingle instance1 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE;
//Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
//NoSuchMethodException: temp.single.EnumSingle.<init>()
Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
//IllegalArgumentException: Cannot reflectively create enum objects
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
EnumSingle instance2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance1.hashCode());
System.out.println(instance2.hashCode());
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号