MAT分析
MAT分析前置步骤
前置步骤:生成堆转储文件(Heap Dump):
jmap -dump:live,format=b,file=heap.hprof <PID>
MAT分析步骤
-
下载 Eclipse Memory Analyzer (MAT)
- 下载地址:Eclipse Memory Analyzer (MAT)下载地址
- 选择适合你系统的版本(需注意 Java 版本兼容性):
- MAT 1.11+ 需要 Java 11+。
- MAT 1.9.x 支持 Java 8。
-
解压下载的 ZIP 文件到任意目录(无需安装)
-
启动 MAT:
- Windows:双击
MemoryAnalyzer.exe。 - Linux/macOS:运行
./MemoryAnalyzer。
- Windows:双击
-
使用 MAT 分析堆转储,打开堆转储文件
-
启动 MAT,点击 File → Open Heap Dump,选择
heap.hprof。 -
MAT 会解析文件并生成报告首页。
-
-
查看内存泄漏报告(Leak Suspects)
- MAT 首页会直接显示 疑似内存泄漏(Leak Suspects):点击 Details 查看对象引用链,定位占用内存最多的对象。
-
手动分析对象
-
- 直方图(Histogram):
-
点击工具栏 Histogram。
-
输入类名(如
String)查看实例数量和总大小。 -
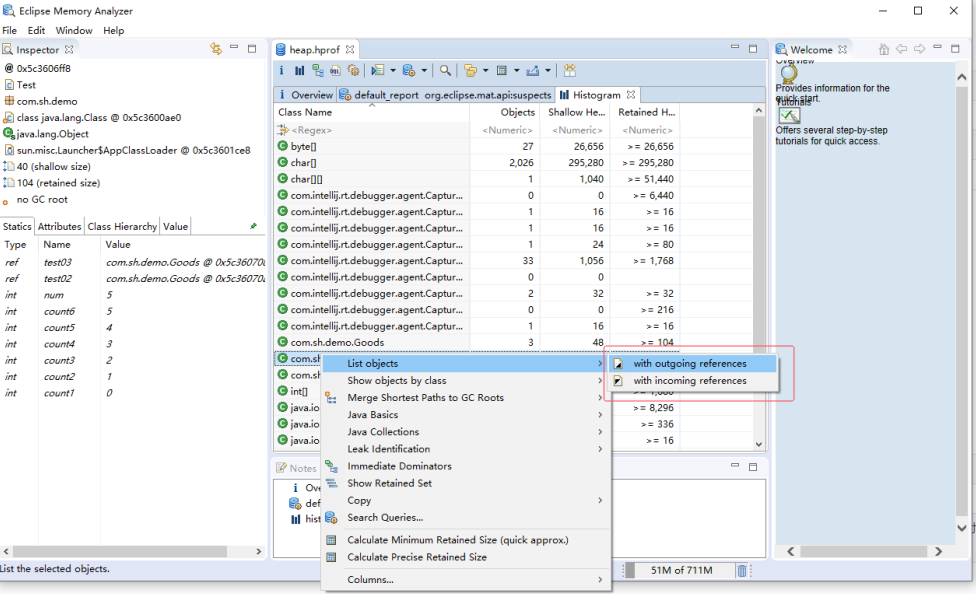
右键 → List objects → with incoming references 查看谁引用了这些对象。
-
支配树(Dominator Tree):
- 点击 Dominator Tree。显示对象支配关系,快速找到内存占用最大的对象。
-
- 线程分析(Thread Overview):
- 点击 Thread Overview 查看线程栈和线程局部变量。
- 查找静态变量
- 在 Histogram 中搜索目标类(如
MyClass)。 - 右键 → List objects → with incoming references。
- 展开
Class Loader→Static Fields查看静态变量。
- 在 Histogram 中搜索目标类(如
实战示例:
-
实例变量 → 堆(对象实例内)
-
静态变量 → Class 对象(堆)
代码:
package com.sh.demo;
public class Test {
public static int count1 = 0;
public static int count2 = 1;
public static int count3 = 2;
public static final int count4 = 3;
public static final int count5 = 4;
public static final int count6 = 5;
public static final int num = 5;
public int num1 = 5;
public int num2 = 6;
public Goods test01 = new Goods();
public static Goods test02 = new Goods();
public static final Goods test03 = new Goods();
}
图解:
静态属性:Class 对象(堆)中
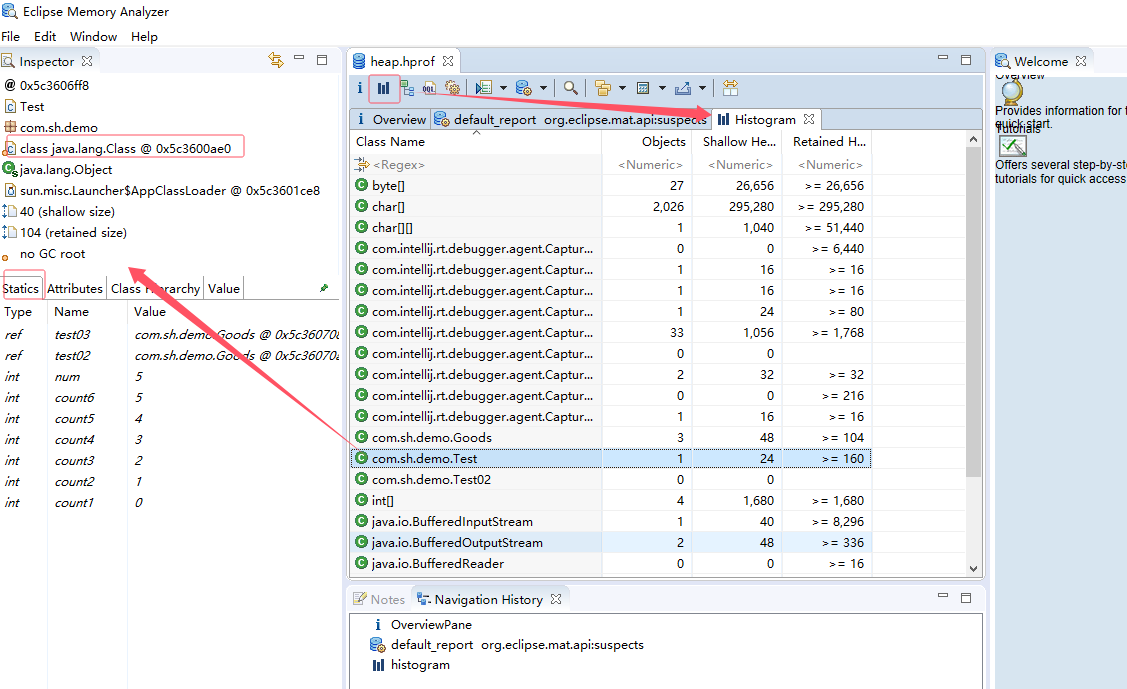
非静态属性:在实例对象中
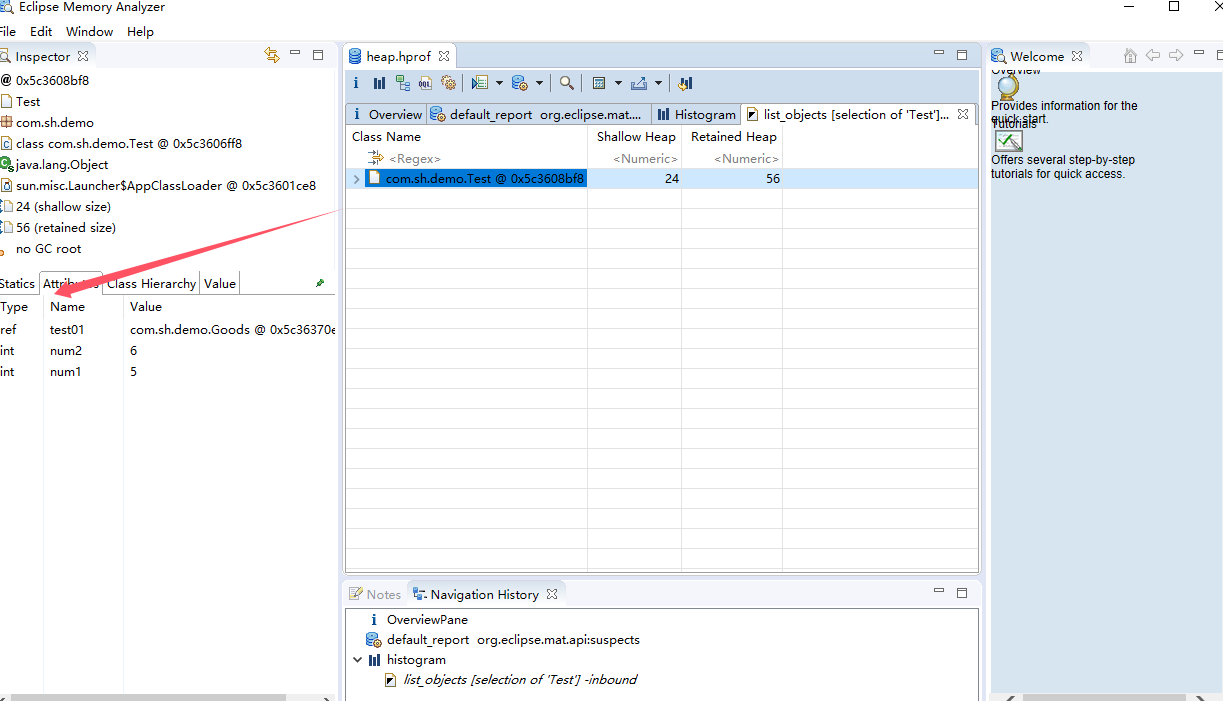
额外知识点补充
with outgoing references 和 with incoming references
| 功能 | 方向 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| with outgoing references | 对象 → 外部 | 查看当前对象 引用了哪些其他对象(即它持有的字段或集合中的对象)。 |
| with incoming references | 外部 → 对象 | 查看当前对象 被哪些其他对象引用(即谁持有它的引用,可能导致内存泄漏)。 |
Path to GC Roots |
外部 → 对象 | 显示到 GC Roots 的完整引用链(更精确的泄漏分析)。 |
Shallow Heap 的定义
- Shallow Heap 表示对象 本身 在堆内存中占用的空间,仅计算:
- 对象头(Object Header)
- 基本类型字段(如
int,boolean) - 引用类型字段(如
String,List,但仅计算引用指针,不计算引用对象的大小)
- 不包含:
- 该对象引用的其他对象的大小(这些属于 Retained Heap)。
- 静态变量(存储在 Class 对象中)。
Shallow Heap vs Retained Heap
| 指标 | 计算范围 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| Shallow Heap | 仅对象自身内存(头+字段) | 分析对象的基础内存占用。 |
| Retained Heap | 对象自身 + 所有递归引用的对象(即该对象被回收时能释放的总内存) | 分析内存泄漏的关键指标(如谁持有了大量不可回收的对象)。 |

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号