python super()函数
描述:
super()函数用于调用父类(超类)的一个方法。
super()函数是用来解决多重继承问题的,直接用类名调用父类方法在使用单继承的时候没有问题,但是如果使用多继承,会涉及到查找顺序(MRO)、重复调用(钻石继承)等种种问题。
MRO就是类等方法解析顺序表,其实也就是继承父类方法时的顺序表。
语法:
以下是super()方法的语法:
super(type[object-or-type])
参数:
- type --类
- object-or-type --类,一般是self
实例:
1 class FooParent(object): 2 def __init__(self): 3 self.parent = 'I\'m the parent.' 4 print('Parent') 5 6 def bar(self,message): 7 print("%s from Parent" % message) 8 9 class FooChild(FooParent): 10 def __init__(self): 11 # super() 首先找到 FooChild 的父类(就是类 FooParent),然后把类 FooChild 的对象转换为类 FooParent 的对象 12 super().__init__() 13 print('Child') 14 15 def bar(self,message): 16 super().bar(message) 17 print('Child bar function') 18 print(self.parent) 19 20 if __name__ == '__main__': 21 fooChild = FooChild() 22 fooChild.bar('helloworld')
我们在学习python类的时候,总会碰见书上的类中有__init__()这样一个函数,其实它就是python的构造方法。
构造方法类似于init()这种初始化方法,来初始化新创建对象的状态,在一个对象被创建以后立即调用,比如实例话一个类:
f = FooBar f.init()
使用构造方法就能让它简化成如下形式:
f = FooBar()
栗子:
class FooBar:
def __init__(self):
self.somevar = 42
>>>f = FooBar()
>>>f.somevar
我们会发现在初始化FooBar中的somevar的值为42之后,实例化直接就能够调用somevar的值;如果说你没有用构造方法初始化值的话,就不能够调用。
在明白了构造方法之后,我们来点进阶的问题,那就是构造方法中的初始值无法继承的问题。
栗子:
1 class Bird: 2 def __init__(self): 3 self.hungry = True 4 def eat(self): 5 if self.hungry: 6 print('Ahahahah') 7 else: 8 print('No thanks!') 9 10 class SongBird(Bird): 11 def __init__(self): 12 self.sound = 'Squawk' 13 def sing(self): 14 print(self.sound) 15 16 if __name__ == '__main__': 17 sb = SongBird() 18 sb.sing() # 能正常输出 19 sb.eat() # 报错,因为 songgird 中没有 hungry 特性
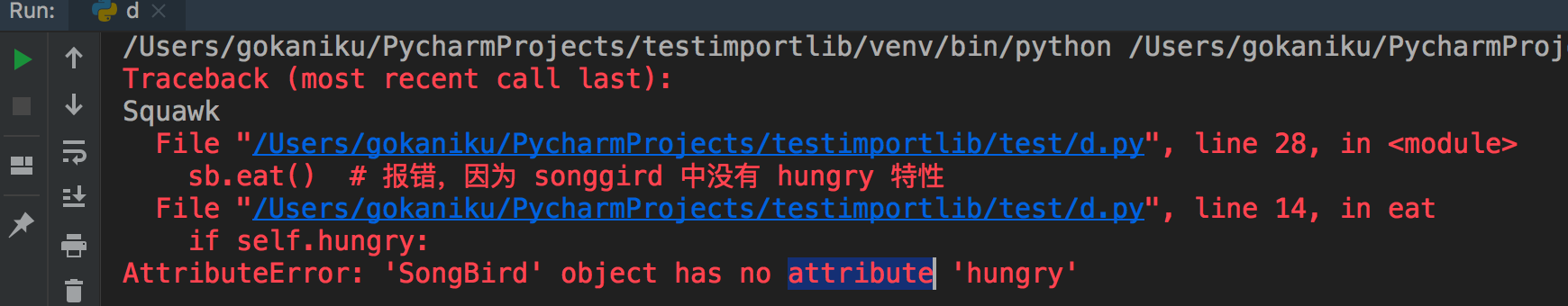
解决的办法有两种:
1、调用未绑定的超类构造方法(多用于旧版python)
1 class SongBird(Bird): 2 def __init__(self): 3 Bird.__init__(self) 4 self.sound = 'Squawk' 5 def sing(self): 6 print(self.sound)
原理:在调用了一个实例的方法时,该方法的self参数会自动绑定到实例上(称为绑定方法);如果直接调用类的方法(比如Bird.__init__),那么就没有实例会被绑定,可以自由提供需要的self参数(未绑定方法)
2、使用super函数(只在新式类中使用)
1 class SongBird(Bird): 2 def __init__(self): 3 super().__init__() 4 self.sound = 'Squawk' 5 def sing(self): 6 print(self.sound)
原理:它会查找所有的超类,以及超类的超类,直到找到所需的特性为止。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号