结对编程-小学四则运算
结对编程——小学四则运算
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
|
|
这个作业要求在哪里 |
|
|
这个作业的目标 |
1、尝试结对编程 |
一、合作者
|
姓名 |
学号 |
|
郑佳媚 |
3221005071 |
|
张萱文 |
3221005070 |
|
github |
二、PSP表格
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
30 |
30 |
|
Development |
开发 |
120 |
150 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
30 |
25 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
30 |
35 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
30 |
25 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
15 |
15 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 |
50 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
400 |
480 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
20 |
15 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 |
70 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
80 |
75 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
25 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
30 |
20 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
30 |
|
合计 |
895 |
1015 |
三、效能分析
性能分析图
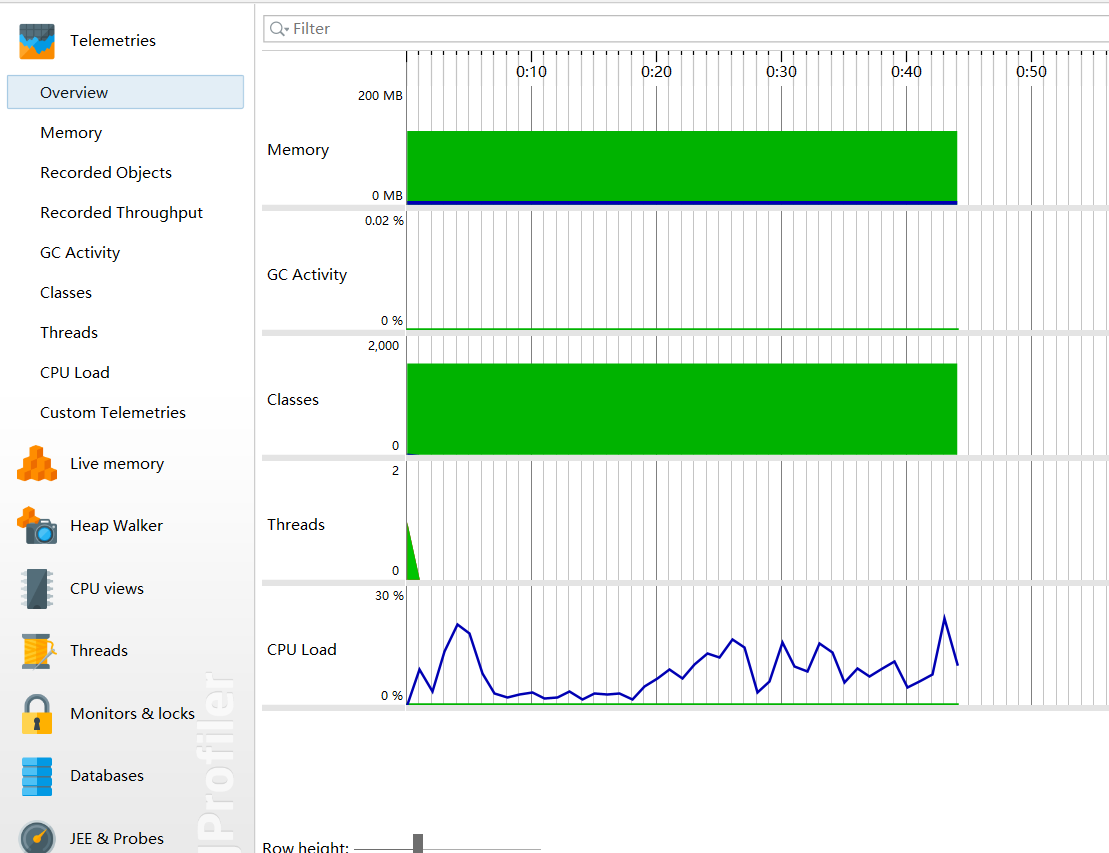
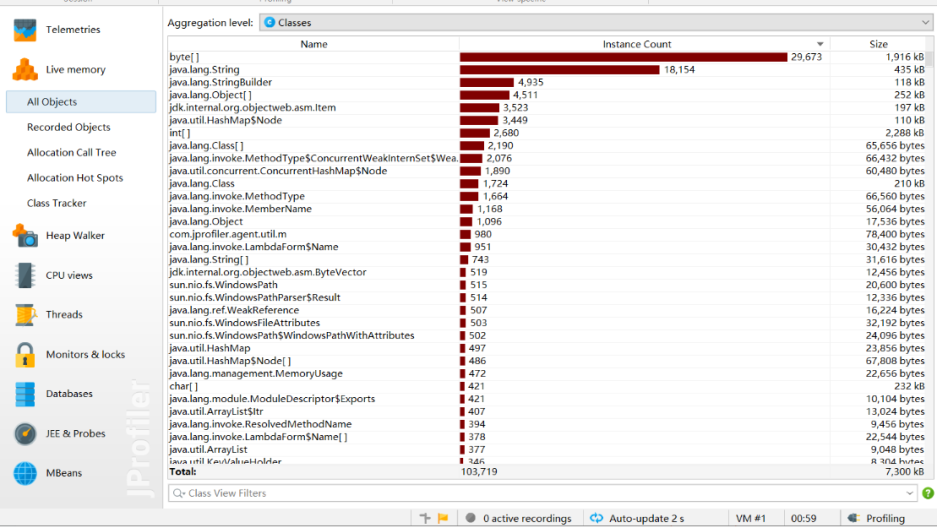
四、设计实现过程
1、代码组织
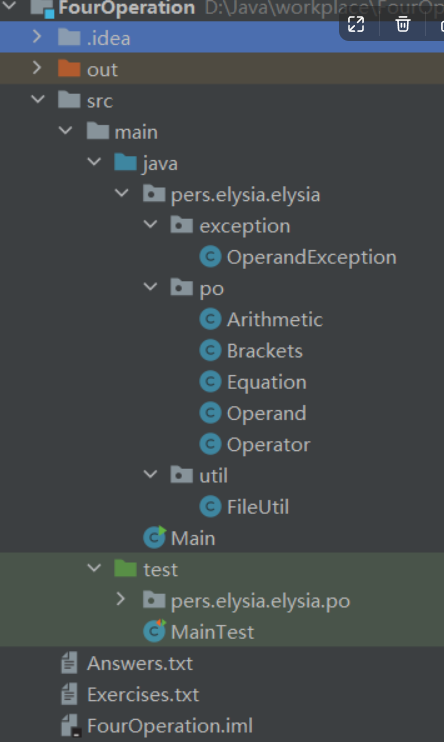
五、代码说明
// 说明:用于过滤重复的表达式
// 思路:按顺序层层筛选,由于转换成后缀表达式,不用考虑括号
// a. 先去除运算过程含负数的
// b. 先比较结果
// c. 比较表达式是否一样
// d. 再比较包含的运算符是否相同
// e. 比较第一次运算的两数是否只是交换位置
public static List<Equation> filter(List<Equation> list){
for(int i=0;i < list.size();i++){
Equation equation = list.get(i);
//如果运算过程含负数,则跳过
if(equation.isOf()){
list.remove(equation);
//remove会整体前移
i--;
continue;
}
//和整个list比较
//标签方便下面层层嵌套能直接goto出来
flag:
for(int o=0;o< list.size();o++){
Equation toCompare = list.get(o);
//删除后有空位,要跳过
if(toCompare == null){
continue;
}
//遇到自己就跳过
if(equation == toCompare){
continue;
}
//先比较结果
if(Math.abs(equation.getResult() - toCompare.getResult()) < 0.000001) {
//结果相同,看是否完全一样
if(equation.equals(toCompare)){
list.remove(equation);
//remove会整体前移
i--;
break flag;
}
//再比较运算符
List<Arithmetic> postfix1 = equation.getPostfix();
List<Arithmetic> postfix2 = toCompare.getPostfix();
List<Operator> operators1 = equation.getOperators();
List<Operator> operators2 = toCompare.getOperators();
//有不同运算符就保留
if(operators1.size() != operators2.size()){
break flag;
}
for(int j=0;j<operators1.size();j++){
if(operators1.get(j) != operators2.get(j)){
break flag;
}
}
//运算符相同,只比较第一次计算的两数字是否交换位置
//找到第一个运算符,取前两个数字
List<Operand> operands1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Operand> operands2 = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j=0;j<postfix1.size();j++){
if(postfix1.get(j) instanceof Operator){
operands1.add((Operand) postfix1.get(j-1));
operands1.add((Operand) postfix1.get(j-2));
break;
}
}
for(int j=0;j<postfix1.size();j++){
if(postfix2.get(j) instanceof Operator){
operands2.add((Operand) postfix2.get(j-1));
operands2.add((Operand) postfix2.get(j-2));
break;
}
}
//比较两对数字
if((operands1.get(0).equals(operands2.get(0)) || operands1.get(0).equals(operands2.get(1)))
&& (operands1.get(1).equals(operands2.get(0)) || operands1.get(1).equals(operands2.get(1)))){
list.remove(equation);
//remove会整体前移
i--;
break flag;
}else{
//两对数字不相同,保留
break flag;
}
}else{
//结果不一样,保留
break flag;
}
}
}
return list.stream().toList();
}
// generate()
// ● 说明:用于生成随机表达式
// ● 思路:通过传参确定此次生成中包含的操作数数量、运算符数量、括号数量、数的范围,然后随机new出各对象,交替拼接操作数和运算符,最后随机添加括号
public static Equation generate(int operandNo, int operatorNo, int bracketsNo
, int lowEnd, int upEnd){
Random r = new Random();
int scope = upEnd - lowEnd;
List<Arithmetic> arithmetics = new ArrayList<>();
List<Operand> operands = new ArrayList<>();
List<Operator> operators = new ArrayList<>();
List<Brackets> brackets = new ArrayList<>();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < operandNo; i++) {
// 操作数类型 自然数(0),真分数(1)
int type = r.nextInt(10)%2;
if(0 == type){
//生成随机整数
operands.add(new Operand(type, r.nextInt(scope) + lowEnd + ""));
}else if (1 == type){
//生成真分数
int denominator = r.nextInt(scope) + lowEnd + 1;
// 分子 > 0
int numerator = r.nextInt(denominator - 1) + 1;
String str = numerator + "/" + denominator;
operands.add(new Operand(type, str));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < operatorNo; i++) {
// 除去等号
int index = r.nextInt(4) + 1;
operators.add(Operator.getByIndex(index));
}
for (int i = 0; i < bracketsNo; i++) {
brackets.add(Brackets.getByIndex(0));
brackets.add(Brackets.getByIndex(1));
}
for (int i = 0; i < operands.size(); i++) {
if(operands.get(i) != null){
arithmetics.add(operands.get(i));
}
if(i == operands.size()-1){
break;
}
if(operators.get(i) != null) {
arithmetics.add(operators.get(i));
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
return new Equation(arithmetics);
}
// 1.扫描中缀表达式的每一个字符,将数字入列;
// 2.遇到运算符,栈空时直接进栈,栈顶非空时,运算符优先级大于栈顶元素才进栈,
// 否则栈顶元素退栈入列,当前运算符再进栈;
// 3.依次进行直至所有字符操作完毕
// 有括号:
// 1.扫描中缀表达式的每一个字符,将数字入列;
// 2.遇到运算符,栈空时直接进栈,栈顶非空时,运算符优先级大于栈顶元素才进栈,
// 否则栈顶元素退栈入列,当前运算符再进栈;
// 3.遇到左括号,直接进栈,左括号后面的运算符直接进栈,直至遇到右括号;
// 4.遇到右括号时,将栈顶元素依次退栈入列,直到遇到左括号,将左括号退栈,符号操作移动下一位
// 5.重复以上操作,直至所有字符操作完成。
public List<Arithmetic> infixToPostfix(){
Stack<Arithmetic> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Arithmetic> postfix = new ArrayList<>();
for(int start = 0; start < infix.size(); start++){
//如果是运算符
if(infix.get(start).priority > 0) {
//栈空 或 "(" 或 符号优先级>栈顶符号 且 不为")" 直接进栈
if (stack.isEmpty() || infix.get(start).priority == 3 ||
((infix.get(start).priority > stack.peek().priority) && infix.get(start).priority < 4)) {
stack.push(infix.get(start));
} else if (!stack.isEmpty() && infix.get(start).priority <= stack.peek().priority) {
//栈非空 且 符号优先级≤栈顶符号, 出栈; 直到 栈为空 或 遇到了"("
while (!stack.isEmpty() && infix.get(start).priority <= stack.peek().priority) {
if (stack.peek().priority == 3) {
stack.pop();
break;
}
postfix.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.push(infix.get(start));
} else if (infix.get(start).priority == 4) {
//")",依次出栈直到空栈或遇到第一个"(",此时"("出栈
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (stack.peek().priority == 3) {
stack.pop();
break;
}
postfix.add(stack.pop());
}
}
}else if(infix.get(start).priority == -1){
postfix.add(infix.get(start));
}
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
postfix.add(stack.pop());
}
return postfix;
}
六、测试运行
1、测试用例
生成算式

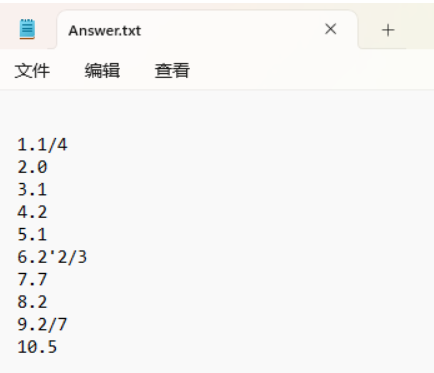
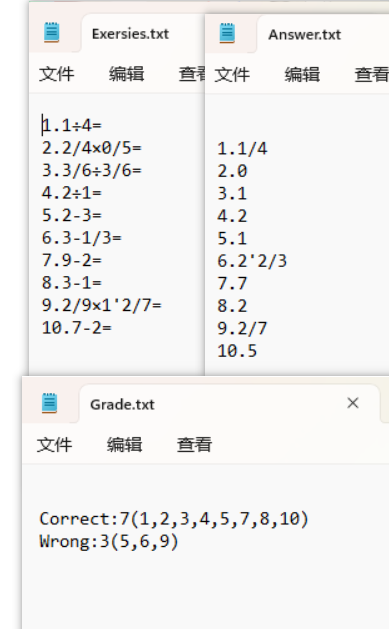
七、项目小结
在这次结对编程的体验中,我负责测试及博客的编写,队友负责写算法及性能分析。我们采用一个人编程,一个人监督并帮忙的模式;达到一定时间角色互换,思维互换,这样既不会思维僵硬,还能学到对方身上的优点,还可以解决不专注问题。如果一个人编程感觉枯燥,进行不下去了,另一个就积极与她沟通,并帮忙编程。一开始,效果并不理想,我们两个的代码思路有分歧,但是在后面的开发过程中,我们不断沟通,借鉴前人的经验,出现了问题,一起想办法解决,包容不同的思想,从中获取经验,开发效率得到很大提高。在这个过程中,我们收获的不仅是编程能力的提高,更是团队协作,沟通能力和表达能力的提高。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号