mysql学习三:查询表
一条完整的sql语句: select xxx from xxx where xxx group by xxx having xxx order by xxx limit xxx
以上语句的执行顺序:
1. from 将硬盘上的表文件加载到内存
2. where 将符合条件的数据进行过滤。生成一张新的临时表
3. group by 根据列中的数据种类,将当前临时表分成若干个新的临时表
4. having 过滤掉group by生成的不符合条件的临时表
5. select 对当前临时表进行整列读取
6. order by 对select生成的临时表,进行重新排序,生成新的临时表
7. limit 对最终生成的临时表的数据行,进行截取
跨表查询:
- 1.内连接,省略了inner,完整的应该是inner join。查询中的比较次数:表1记录 * 表2记录 * .... 表N
- 等值连接
# 查询员工所对应的部门名称:如果某员工没有部门或者某部门没有员工,则这两条记录都不会显示
select e.ename,d.dname from emp e join dept d on e.deptno=e.deptno; - 非等值连接
# 查出员薪水对应的薪水等级: select e.ename,e.sal,s.grade from emp e join salgrade s on e.sal between s.losal and s.hisal;
- 自连接,看一张表当作两张表看
# 查出员工对应的经理名字
select a.ename,b.ename from emp a join emp b on a.mgr=b.empo;
2. - 等值连接
- 外连接:A表和B表能够完全匹配的记录查询出来之外(内连接),将其中一张表的记录无条件的完全查询出来,对应表没有匹配的记录时,会自动模拟出null值与之匹配。外连接的查询结果条数 >= 内连接的查询结果条数。省略了outer,完整的为left | right outer join
-
- 左外连接/左连接:包含左边表的全部行(不管右边的表中是否存在与它们匹配的行),以及右边表中全部匹配的行。 示例:显示所有员工,及其部门;如果员工存在但对应的部门不存在,也要显示,部门显示为null。假设左表为员工表,右表为部门表,此时,需要用左外连接(左边的表全显示,右边的表符合条件的显示,不符合条件的显示null)。
# 左外连接:左边的行全部无条件显示 # 如果有一个员工,没有部门,则左外连接的查询结果会包含此员工,部门null select e.ename,d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
- 右外连接/右连接:包含右边表的全部行(不管左边的表中是否存在与它们匹配的行),以及左边表中全部匹配的行。 示例:显示所有部门,及其对应的员工;如果某部门存在但不存在员工,也要显示此部门,员工姓名显示为null。假设左表为员工表,右表为部门表,此时,需要用右外连接(右边的表全显示,左边的表符合条件的显示,不符合条件的显示为null)
# 右外连接:右边的行全部无条件显示 # 如果有一个部门,没有员工,则右外连接的查询结果会包含此部门,员工姓名为null select e.ename,d.name from emp e right join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
- 左外连接/左连接:包含左边表的全部行(不管右边的表中是否存在与它们匹配的行),以及右边表中全部匹配的行。 示例:显示所有员工,及其部门;如果员工存在但对应的部门不存在,也要显示,部门显示为null。假设左表为员工表,右表为部门表,此时,需要用左外连接(左边的表全显示,右边的表符合条件的显示,不符合条件的显示null)。
- 3.全连接:包含左、右两个表的全部行,不管另外一边的表中是否存在与它们匹配的行。
示例:查出员工的部门名称,员工的领导名称和薪水等级
select d.dname,e.ename,b.ename as leadername from emp e join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno join emp b on e.mgr=b.empno join salgrade s on e.sal between s.losal and s.hisal;
子查询:select语句嵌套select语句,称为子查询。
注意:select子句,可以出现在select、from、where关键字后面。
select .........(select 子查询)........ from .........(select 子查询)........ where .........(select 子查询)........
示例:找出薪水比公司平均薪水高的员工,要求显示员工名和薪水
select ename,sal from emp where sal > select avg(sal) as avgsal from emp;
查出部门的平均薪水,并显示平均薪水的薪水等级
select t.avgsal,s.grade from (select e.deptno,avg(e.sal) avgsal from emp group by e.deptno) t join salgrade s on t.avgsal between s.losal and s.hisal;
合并查询:union,合并相加结果集。
示例:查询出工作岗位为manager和salesman的员工
# 方法一: select ename,job from emp where job='manager' or job='salesman' # 方法二: select ename,job from emp where job in ('manager','salesman') # 方法三: select ename,job from emp where job='manager' union select ename,job from emp where job='salesman'
使用union的两个查询结果集的字段要相同。
创建学生表:
CREATE TABLE `db_student` ( `id` int(11) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `stuName` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `sex` varchar(2) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, `age` smallint(4) NOT NULL, `gradeName` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 1 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `db_student`.`student`(`id`, `stuName`, `sex`, `age`, `gradeName`) VALUES (1, '张三', '男', 21, '一年级'); INSERT INTO `db_student`.`student`(`id`, `stuName`, `sex`, `age`, `gradeName`) VALUES (2, '张x', '', 23, '一年级'); INSERT INTO `db_student`.`student`(`id`, `stuName`, `sex`, `age`, `gradeName`) VALUES (3, '张y', '男', 25, '三年级'); INSERT INTO `db_student`.`student`(`id`, `stuName`, `sex`, `age`, `gradeName`) VALUES (4, '张三', '男', 23, '一年级'); INSERT INTO `db_student`.`student`(`id`, `stuName`, `sex`, `age`, `gradeName`) VALUES (5, '张三', '男', 18, '一年级'); INSERT INTO `db_student`.`student`(`id`, `stuName`, `sex`, `age`, `gradeName`) VALUES (6, '刘一', '女', 23, '一年级'); INSERT INTO `db_student`.`student`(`id`, `stuName`, `sex`, `age`, `gradeName`) VALUES (10, '王九', '女', 22, '一年级');
一、单表查询:
1.
select distinct gradeName from db_student;
select * from db_student order by age asc; # 默认asc升序;降序desc
2.分组查询:
group by 字段名 [having 条件表达式] [with rollup]
- 单独使用(无意义)group by 字段名;
- 与group_concat()函数一起使用;
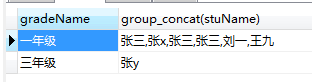
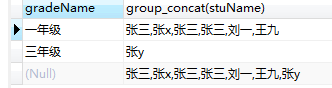
select gradeName, group_concat(stuName) from student group by gradeName;
![]()
根据分组结果(一年组、三年级),将每组中的stuName以逗号分隔组成一个字段返回group_concat(stuName)
- 与聚合函数一起使用;
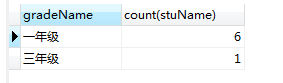
# 查看每个年级的学生总数 select gradeName,count(stuName) from student group by gradeName;
![]()
根据分组结果,统计每组中的学生总数count(stuName)
-
与having一起使用;
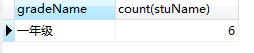
# 查看学生总数大于3的年级:首先根据年级分组,然后having过滤学生总数大于3 select gradeName,count(stuName) from student group by gradeName having count(stuName) > 3;
![]()
- 与with rollup一起使用(最后加入一个总和行)
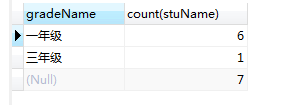
# with rollup:在最后一行,增加一个总和行 select gradeName,count(stuName) from student group by gradeName with rollup;
![]()
# with rollup:如果聚合函数的结果不是数值,是文字,则将所有文字连接起来,以逗号分隔 select gradeName,group_concat(stuName) from student group by gradeName with rollup;
![]()
limit:limit 起始位置,记录数
3、使用聚合函数:count、sum、avg、max、min 通常与group by联合使用
create table grade ( id int, stuName varchar(60), course varchar(60), score int );
insert into grade (id, stuName, course, score) values (1, '张三','语文', '91'); insert into grade (id, stuName, course, score) values (2, '张三','数学', '90'); insert into grade (id, stuName, course, score) values (3, '张三','英语', '87'); insert into grade (id, stuName, course, score) values (4, '李四','语文', '95'); insert into grade (id, stuName, course, score) values (5, '李四','数学', '80'); insert into grade (id, stuName, course, score) values (6, '李四','英语', '77'); insert into grade (id, stuName, course, score) values (7, '王五','语文', '81'); insert into grade (id, stuName, course, score) values (8, '王五','数学', '60'); insert into grade (id, stuName, course, score) values (9, '王五','英语', '50');
count:统计条数
select count(*) from grade; select count(*) as total from grade; # 9 # 统计每个学生考试的总科目 select stuName,count(*) as total from grade group by stuName;
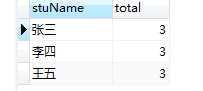
sum:求和
#求出张三的总分 select stuName, sum(score) from grade where stuName='张三';
#根据学生分组,查出每个学生的总分 select stuName, sum(score) from grade group by stuName;
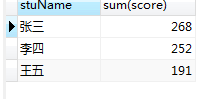
avg:求平均
#求出张三的平均成绩 select stuName, avg(score) from grade where stuName='张三'; #89.3
# 求出所有学生的平均成绩 select stuName, avg(score) from grade group by stuName;
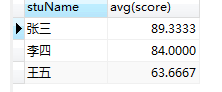
max:求最大值
#求出张三的最高成绩 select stuName, max(score) from grade where stuName='张三';
#求出每个学生的最高分 select stuName, max(score) from grade group by stuName;
min:求最小值
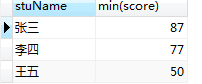
select stuName, min(score) from grade where stuName='张三';
#求出每个学生的最低分 select stuName, min(score) from grade group by stuName;
二、连接查询
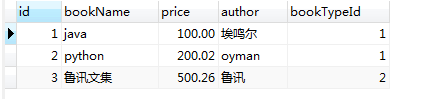
create table `book` ( `id` int(11) not null auto_increment, `bookName` varchar(20) default null, `price` decimal(6,2) default null, `author` varchar(20) default null, `bookTypeId` int(11) default null, primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb auto_increment=5 default charset=utf8;
create table `bookType` ( `id` int(11) not null auto_increment, `bookTypeName` varchar(20) default null, primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb auto_increment=5 default charset=utf8;
连接查询:是将两个或两个以上的表按照某个条件连接起来,从中选取需要的数据。
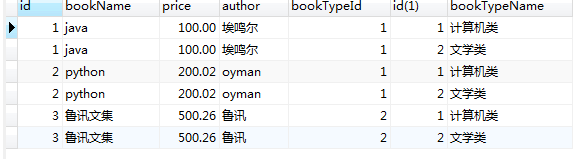
select * from book,bookType;
结果为:book的记录数 * bookType的记录数
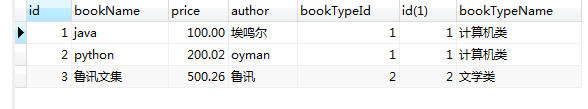
1.内连接查询:是一种最常用的连接查询,查询两张或多张表的信息
select * from book,bookType where book.bookTypeId=bookType.id;
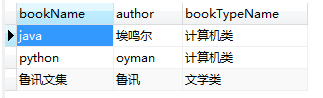
select b.bookName,b.author,bt.bookTypeName from book b,bookType bt where b.bookTypeId=bt.id;
2.外连接查询:联合多张表,查出一张表的所有信息,其它表的信息要看条件
select 字段列表 from 表1 left|right join 表2 on 表1.字段x=表2.字段x;
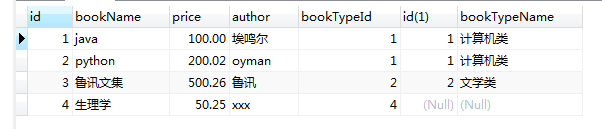
1)左连接:查出表1的所有记录,而表2中,只能查出匹配的记录;
select * from book b left join bookType bt on b.bookTypeId=bt.id;
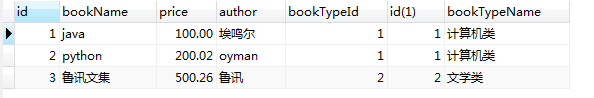
2)右连接:查出表2的所有记录,而表1中,只能查出匹配的记录;
select * from book b right join bookType bt on b.bookTypeId=bt.id;
三、子查询:子查询的结果,作为结果集或某一具体的值,用于条件判断
create table pricelevel ( id int, priceLevel int, price float, description varchar(300) )
insert into pricelevel (id, priceLevel, price, description) values ('1', '1', '90.00', '贵'),('2', '2','60.00','适中'),('3','3','20.00','便宜');
1.带in关键字的子查询:一个查询语句的条件可能落在另一个select语的查询结果中
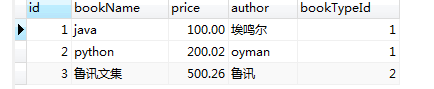
# 查询book表,要求book表中的bookType要在bookType表中 select id from bookType; select * from book where bookTypeId in (select id from bookType); select * from book where bookTypeId not in (select id from bookType);
子查询select id from bookType的查询结果:注意子查询中应该说明要查询的字段,否则无法得到集合
第二条语句的条件:即book表的bookTypeId的值 ,要在上面的子查询结果集中;相当于 bookTypeId in (1, 2)
第三条语句:bookTypeId的值,不在子查询的结果集中;相当于 bookTypeId not in (1, 2)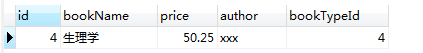
2.带比较运算符的子查询:子查询可以使用比较运算符
#查询比较贵的书:pricelevel表中priceLevel=1的是比较贵的,把它作为比较条件 select price from pricelevel where priceLevel=1; select * from book where price >= (select price from pricelevel where priceLevel=1);
子查询语句的查询结果:注意子查询的结果应该要说明要查询的字段,否则无法比较
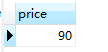
第二条语句:与子查询的结果,比较
3.带exists关键字的子查询:假如子查询,查询到记录,则进行外层查询;否则,不执行外层的查询
#查book表,假如booktype表中有数据,则查询book表 select * from booktype; select * from book where exists (select * from booktype); # 假如booktype表中没有数据,则查询book表 select * from booktype; select * from book where not exists (select * from booktype);
第一条语句:查询是有数据的
第二语句:exists (子查询,第一条语句是有数据的),返回True;则查询所有的book记录
第三条语句:not exists (子查询),如果子查询的结果没有数据,则为True,查询所有的book记录;否则不查询book表
4.带any关键字的子查询:表示只要满足子查询中的任何一个条件
#查book表;只要book表的价格price大于任何一个pricelevel中的价格,即符合条件 select price from pricelevel; select * from book where price >= any (select price from pricelevel);
第一条语句:子查询的结果集
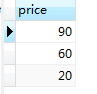
第二条语句:price 大于等于,必须是一个具体的数值;而上面的子查询结果是一个集合,使用any,即可满足和大于等于的比较;同时只要any子查询的结果中的任何一个条件满足,即满足
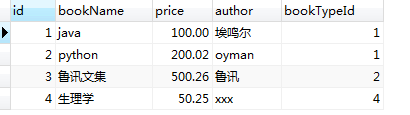
5.带all关键字的子查询:all关键字,表示要满足所有条件
select * from book where price >= all (select price from pricelevel);
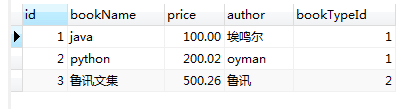
四、合并查询
1.union:使用union关键字,数据库系统会将所有的查询结果合并到一起,然后去除掉相同的记录
2. union all:不会去重;
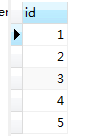
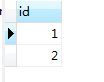
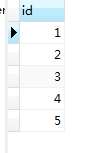
select id from book; select id from booktype; select id from book union select id from booktype; select id from book union all select id from booktype;
第一条语句的查询结果:
第二条语句查询的结果:
第三条语句的结果:
第四条语句:

posted on 2018-09-15 19:57 myworldworld 阅读(577) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号