复学day05
关于Scanner
Scanner是一个工具类,用来获取用户的输入。
基本语法:
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
通过Scanner类的next()与nextLine()方法获取输入的字符串,另外可以通过hasNext()与hasNextLine()方法来判断是否有输入的数据。
PS:Scanner类属于IO流,在使用后需要进行关闭释放资源。
相关代码:
psvm{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("使用next方式接收:");
if(scanner.hasNext()){ //此时关于hasNext()方法存疑,这个返回值存在false吗?
String str = scanner,next(); //运行时,程序会停留至此,开始输入
System.out.println("输出的内容为:"+str);
}
scanner.close();
}
hasNext()的方法解释:Returns true if this scanner has another token in its input.
百度后,暂时了解到,hasNext()方法并不会返回false,取而代之的是将方法阻塞,等待输入内容后继续扫描。该方法相关知识,下链接有详细的扩展补充。
关于sc.next()以及sc.nextLine():

关于if、Switch、While、DoWhile、For语句
if语法:
if(布尔表达式1){
//表达式1为true时,执行的相关代码
}else if(布尔表达式2){
//表达式2为true时,执行的相关代码
}else if(布尔表达式3){
//表达式3为true时,执行的相关代码
}else {
//上述表达式均不为true时执行代码
}
ps:if语句至多有一个else语句,且else语句置于所有else if语句之后;一旦其中一条布尔表达式检测为true,则后续语句跳过执行。
Switch语句:
switch(expression){
case value1:
//当expression的值等于value1时执行代码
break;//可选,跳转语句,若未写该语句可能会发生case穿透现象
case value2:
//当expression的值等于value2时执行代码
break;
...
default:
//当上述情况均不满足时,执行代码
}
switch语句中的变量类型可以是:
byte、short、int或者char(javase7之后 支持String类型);case标签必须为字符串常量或字面量。
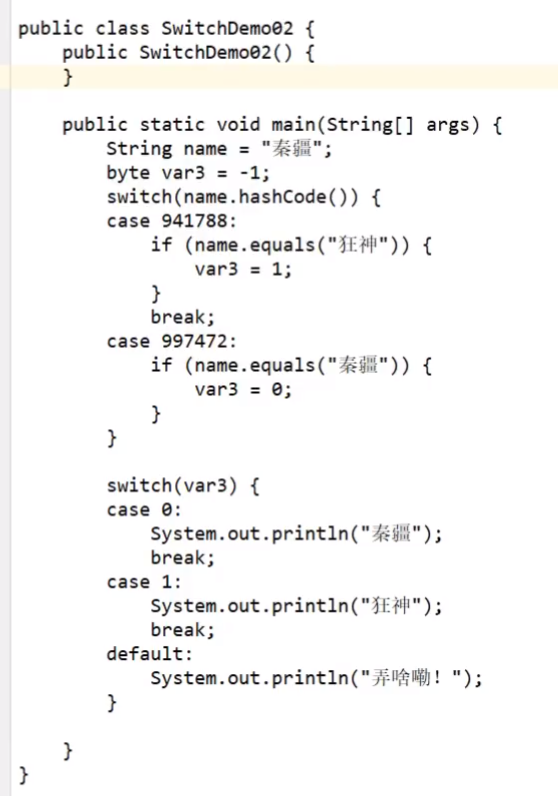
下述图片为switch的反编译代码(知识扩展)
while语句
while(布尔表达式){
//循环语句
}
while是最基本的循环,只要布尔表达式为true,循环就会一直执行下去
int i = 0;
int sum = 0;
while(i <= 100){
sum = sum + i;
i++;
}//常见100求和代码
do...while循环
do{
//循环语句
}while(布尔表达式);
该语句至少将循环语句执行一次
int i = 0;
int sum = 0;
do{
sum = sum + i;
i++;
}while(i <= 100);
For循环
相对于上述循环语句,for语句是最有效、最灵活的循环结构
for(初始化;布尔表达式;更新){
//代码语句
}
int m;
for(int i = 1;i <= 9;i++){
m = 1;
while(m <= i){
System.out.print(i + "*" + m + "=" + (i*m)+"\t");
m++;
}
System.out.println("");
}//打印九九乘法表,该实现方式不唯一
增强for循环:
for( element : 数组 ){
System.out.println(element);
}
增强for循环用于遍历数组、集合,暂时先了解


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号