Tensorflow2.0进阶学习-RNN生成音频 (十二)
引包
import collections
import datetime
import fluidsynth
import glob
import numpy as np
import pathlib
import pandas as pd
import pretty_midi
import seaborn as sns
import tensorflow as tf
from IPython import display
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Sequence, Tuple
啰哩啰嗦一大堆,要注意fluidsynth和pretty_midi的安装,可参照网上资料。
数据熟悉
一些预先准备
seed = 42
tf.random.set_seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
# 设定音频的采样率,这里设定为16000
_SAMPLING_RATE = 16000
下载数据
data_dir = pathlib.Path('data/maestro-v2.0.0')
if not data_dir.exists():
tf.keras.utils.get_file(
'maestro-v2.0.0-midi.zip',
origin='https://storage.googleapis.com/magentadata/datasets/maestro/v2.0.0/maestro-v2.0.0-midi.zip',
extract=True,
cache_dir='.', cache_subdir='data',
)
看看下载数据有多大
filenames = glob.glob(str(data_dir/'**/*.mid*'))
print('Number of files:', len(filenames))
# 一共1282个文件
# Number of files: 1282
对MIDI文件进行处理
再看看下载数据格式,是midi格式的文件,这个需要PrettyMIDI库来处理
sample_file = filenames[1]
print(sample_file)
# data/maestro-v2.0.0/2013/ORIG-MIDI_03_7_6_13_Group__MID--AUDIO_09_R1_2013_wav--2.midi
将其定义为pretty_midi实例,方便以后操作
pm = pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI(sample_file)
再定一个方法对数据进行播放,播放时长可以自定义
def display_audio(pm: pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI, seconds=30):
waveform = pm.fluidsynth(fs=_SAMPLING_RATE)
# Take a sample of the generated waveform to mitigate kernel resets
waveform_short = waveform[:seconds*_SAMPLING_RATE]
return display.Audio(waveform_short, rate=_SAMPLING_RATE)
在jupyter执行下面代码,会出现播放控件,可以播放
display_audio(pm)
pm里除了音乐还有一些音乐介绍
print('Number of instruments:', len(pm.instruments))
instrument = pm.instruments[0]
instrument_name = pretty_midi.program_to_instrument_name(instrument.program)
print('Instrument name:', instrument_name)
# Number of instruments: 1
# Instrument name: Acoustic Grand Piano
数据打印
打印出来的pm可以看成乐谱,有一些音符信息,有音高,有持续时间,还有步长
for i, note in enumerate(instrument.notes[:10]):
note_name = pretty_midi.note_number_to_name(note.pitch)
duration = note.end - note.start
print(f'{i}: pitch={note.pitch}, note_name={note_name},'
f' duration={duration:.4f}')
0: pitch=75, note_name=D#5, duration=0.0677
1: pitch=63, note_name=D#4, duration=0.0781
2: pitch=75, note_name=D#5, duration=0.0443
3: pitch=63, note_name=D#4, duration=0.0469
4: pitch=75, note_name=D#5, duration=0.0417
5: pitch=63, note_name=D#4, duration=0.0469
6: pitch=87, note_name=D#6, duration=0.0443
7: pitch=99, note_name=D#7, duration=0.0690
8: pitch=87, note_name=D#6, duration=0.0378
9: pitch=99, note_name=D#7, duration=0.0742
将pm信息处理成模型可输入的格式
def midi_to_notes(midi_file: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
pm = pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI(midi_file)
instrument = pm.instruments[0]
notes = collections.defaultdict(list)
# Sort the notes by start time
sorted_notes = sorted(instrument.notes, key=lambda note: note.start)
prev_start = sorted_notes[0].start
for note in sorted_notes:
start = note.start
end = note.end
notes['pitch'].append(note.pitch)
notes['start'].append(start)
notes['end'].append(end)
notes['step'].append(start - prev_start)
notes['duration'].append(end - start)
prev_start = start
return pd.DataFrame({name: np.array(value) for name, value in notes.items()})
raw_notes = midi_to_notes(sample_file)
raw_notes.head()
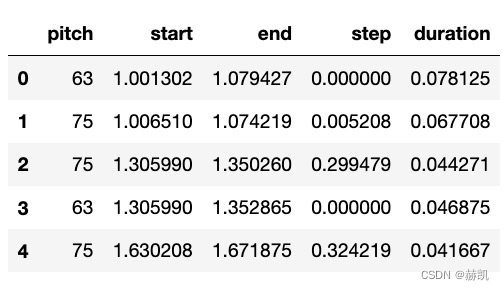
也可以看一些音符信息
get_note_names = np.vectorize(pretty_midi.note_number_to_name)
sample_note_names = get_note_names(raw_notes['pitch'])
sample_note_names[:10]
# array(['D#4', 'D#5', 'D#5', 'D#4', 'D#5', 'D#4', 'D#7', 'D#6', 'D#7', 'D#6'], dtype='<U3')
可以用图的形式来表达乐谱
def plot_piano_roll(notes: pd.DataFrame, count: Optional[int] = None):
if count:
title = f'First {count} notes'
else:
title = f'Whole track'
count = len(notes['pitch'])
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
plot_pitch = np.stack([notes['pitch'], notes['pitch']], axis=0)
plot_start_stop = np.stack([notes['start'], notes['end']], axis=0)
plt.plot(
plot_start_stop[:, :count], plot_pitch[:, :count], color="b", marker=".")
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Pitch')
_ = plt.title(title)
plot_piano_roll(raw_notes, count=100)
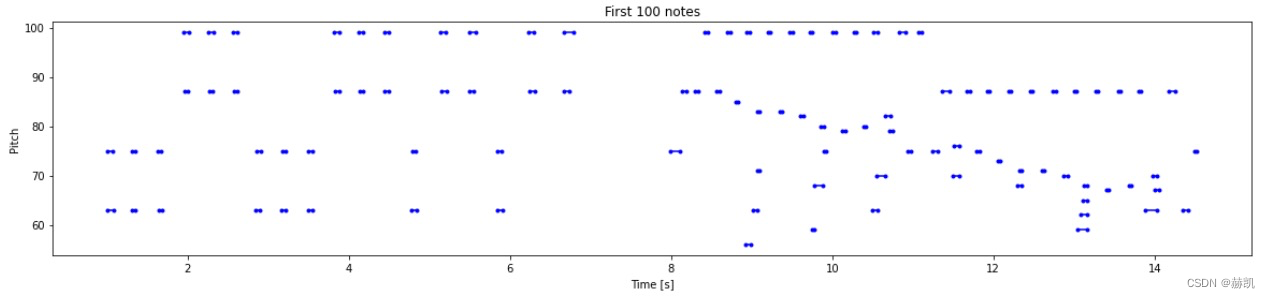
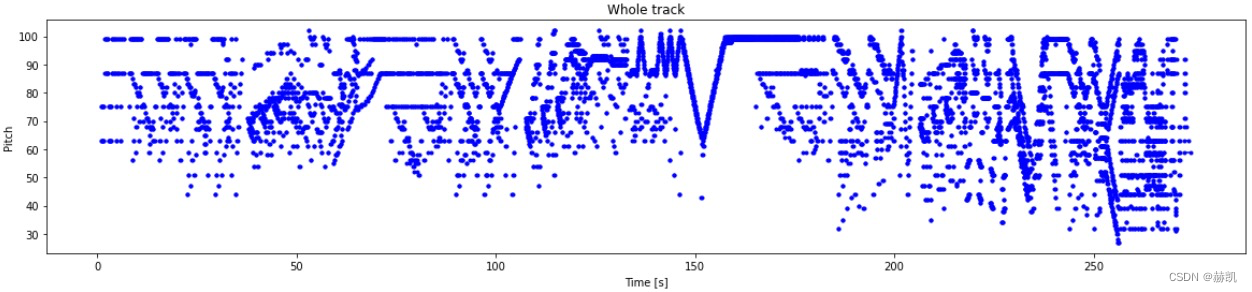
来看下全部的样子
plot_piano_roll(raw_notes)
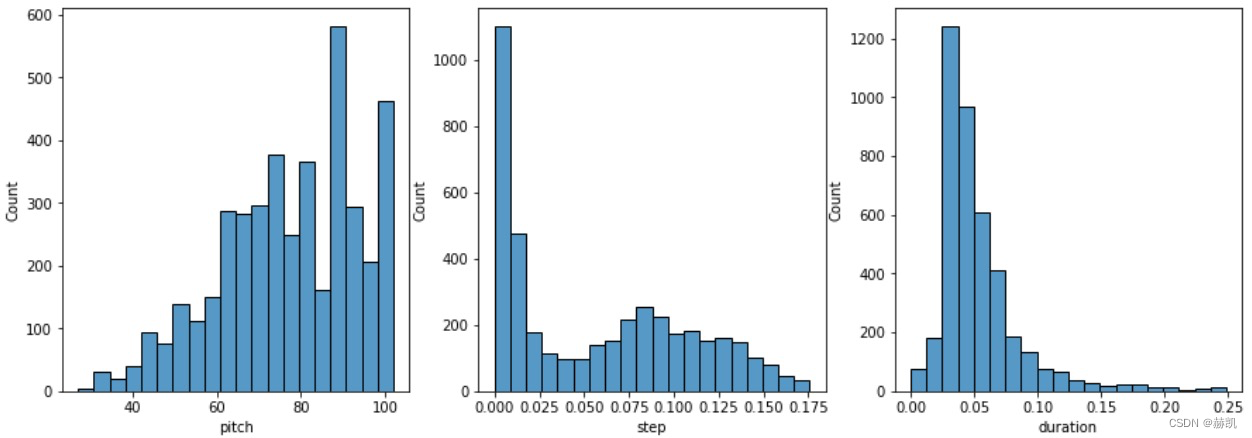
看看他们的直方图
def plot_distributions(notes: pd.DataFrame, drop_percentile=2.5):
plt.figure(figsize=[15, 5])
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
sns.histplot(notes, x="pitch", bins=20)
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
max_step = np.percentile(notes['step'], 100 - drop_percentile)
sns.histplot(notes, x="step", bins=np.linspace(0, max_step, 21))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
max_duration = np.percentile(notes['duration'], 100 - drop_percentile)
sns.histplot(notes, x="duration", bins=np.linspace(0, max_duration, 21))
plot_distributions(raw_notes)
创造MIDI文件
这个是方法
def notes_to_midi(
notes: pd.DataFrame,
out_file: str,
instrument_name: str,
velocity: int = 100, # note loudness
) -> pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI:
pm = pretty_midi.PrettyMIDI()
instrument = pretty_midi.Instrument(
program=pretty_midi.instrument_name_to_program(
instrument_name))
prev_start = 0
for i, note in notes.iterrows():
start = float(prev_start + note['step'])
end = float(start + note['duration'])
note = pretty_midi.Note(
velocity=velocity,
pitch=int(note['pitch']),
start=start,
end=end,
)
instrument.notes.append(note)
prev_start = start
pm.instruments.append(instrument)
pm.write(out_file)
return pm
# 用上面的note信息试一下
example_file = 'example.midi'
example_pm = notes_to_midi(
raw_notes, out_file=example_file, instrument_name=instrument_name)
display_audio(example_pm)
两个方法notes_to_midi和midi_to_notes可以将音频转换为模型输入数据,也可将输入数据转换为音频,这里打通了就好说了。
数据准备
先用小数据训练
num_files = 5
all_notes = []
for f in filenames[:num_files]:
notes = midi_to_notes(f)
all_notes.append(notes)
all_notes = pd.concat(all_notes)
n_notes = len(all_notes)
print('Number of notes parsed:', n_notes)
# Number of notes parsed: 15435
终于转变为我们喜闻乐见的tf.data.Dataset了
key_order = ['pitch', 'step', 'duration']
train_notes = np.stack([all_notes[key] for key in key_order], axis=1)
notes_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(train_notes)
notes_ds.element_spec
# TensorSpec(shape=(3,), dtype=tf.float64, name=None)
既然是RNN,就是用一段连续的数据,预测这段数据接下来的数据,需要维护一个窗口去生成input和label
def create_sequences(
dataset: tf.data.Dataset,
seq_length: int,
vocab_size = 128,
) -> tf.data.Dataset:
"""Returns TF Dataset of sequence and label examples."""
seq_length = seq_length+1
# Take 1 extra for the labels
windows = dataset.window(seq_length, shift=1, stride=1,
drop_remainder=True)
# `flat_map` flattens the" dataset of datasets" into a dataset of tensors
flatten = lambda x: x.batch(seq_length, drop_remainder=True)
sequences = windows.flat_map(flatten)
# Normalize note pitch
def scale_pitch(x):
x = x/[vocab_size,1.0,1.0]
return x
# Split the labels
def split_labels(sequences):
inputs = sequences[:-1]
labels_dense = sequences[-1]
labels = {key:labels_dense[i] for i,key in enumerate(key_order)}
return scale_pitch(inputs), labels
return sequences.map(split_labels, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
seq_length = 25
vocab_size = 128
seq_ds = create_sequences(notes_ds, seq_length, vocab_size)
seq_ds.element_spec
# (TensorSpec(shape=(25, 3), dtype=tf.float64, name=None),
# {'pitch': TensorSpec(shape=(), dtype=tf.float64, name=None),
# 'step': TensorSpec(shape=(), dtype=tf.float64, name=None),
# 'duration': TensorSpec(shape=(), dtype=tf.float64, name=None)})
看一个训练数据和标签
for seq, target in seq_ds.take(1):
print('sequence shape:', seq.shape)
print('sequence elements (first 10):', seq[0: 10])
print()
print('target:', target)
sequence shape: (25, 3)
sequence elements (first 10): tf.Tensor(
[[0.6015625 0. 0.09244792]
[0.3828125 0.00390625 0.40234375]
[0.5703125 0.109375 0.06510417]
[0.53125 0.09895833 0.06119792]
[0.5703125 0.10807292 0.05989583]
[0.4765625 0.06640625 0.05338542]
[0.6015625 0.01302083 0.0703125 ]
[0.5703125 0.11979167 0.07682292]
[0.3984375 0.109375 0.43619792]
[0.609375 0.00130208 0.09505208]], shape=(10, 3), dtype=float64)
target: {'pitch': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=54.0>, 'step': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=0.005208333333333037>, 'duration': <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=0.46875>}
用25个数据去预测最后一个数据,每个数据包含音高、步长和持续时间。
真正的训练数据
batch_size = 64
buffer_size = n_notes - seq_length # the number of items in the dataset
train_ds = (seq_ds
.shuffle(buffer_size)
.batch(batch_size, drop_remainder=True)
.cache()
.prefetch(tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE))
train_ds.element_spec
# (TensorSpec(shape=(64, 25, 3), dtype=tf.float64, name=None),
# {'pitch': TensorSpec(shape=(64,), dtype=tf.float64, name=None),
# 'step': TensorSpec(shape=(64,), dtype=tf.float64, name=None),
# 'duration': TensorSpec(shape=(64,), dtype=tf.float64, name=None)})
模型准备
自定义一个损失函数
def mse_with_positive_pressure(y_true: tf.Tensor, y_pred: tf.Tensor):
mse = (y_true - y_pred) ** 2
positive_pressure = 10 * tf.maximum(-y_pred, 0.0)
return tf.reduce_mean(mse + positive_pressure)
定义输入尺寸、学习率、网络模型。
input_shape = (seq_length, 3)
learning_rate = 0.005
inputs = tf.keras.Input(input_shape)
x = tf.keras.layers.LSTM(128)(inputs)
outputs = {
'pitch': tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, name='pitch')(x),
'step': tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, name='step')(x),
'duration': tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, name='duration')(x),
}
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
loss = {
'pitch': tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(
from_logits=True),
'step': mse_with_positive_pressure,
'duration': mse_with_positive_pressure,
}
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate)
model.compile(loss=loss, optimizer=optimizer)
model.summary()
# 输出
Model: "model"
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 25, 3)] 0 []
lstm (LSTM) (None, 128) 67584 ['input_1[0][0]']
duration (Dense) (None, 1) 129 ['lstm[0][0]']
pitch (Dense) (None, 128) 16512 ['lstm[0][0]']
step (Dense) (None, 1) 129 ['lstm[0][0]']
==================================================================================================
Total params: 84,354
Trainable params: 84,354
Non-trainable params: 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
可以看到损失函数也是三个数字的形式
losses = model.evaluate(train_ds, return_dict=True)
losses
{'loss': 5.4322004318237305,
'duration_loss': 0.5619576573371887,
'pitch_loss': 4.848946571350098,
'step_loss': 0.021296977996826172}
对模型损失进行一些权重设置,出来的结果就小多了
model.compile(
loss=loss,
loss_weights={
'pitch': 0.05,
'step': 1.0,
'duration':1.0,
},
optimizer=optimizer,
)
model.evaluate(train_ds, return_dict=True)
{'loss': 0.8257018327713013,
'duration_loss': 0.5619576573371887,
'pitch_loss': 4.848946571350098,
'step_loss': 0.021296977996826172}
跑起来
callbacks = [
tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
filepath='./training_checkpoints/ckpt_{epoch}',
save_weights_only=True),
tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor='loss',
patience=5,
verbose=1,
restore_best_weights=True),
]
epochs = 50
history = model.fit(
train_ds,
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=callbacks,
)
Epoch 33/50
240/240 [==============================] - 9s 37ms/step - loss: 0.2175 - duration_loss: 0.0320 - pitch_loss: 3.4723 - step_loss: 0.0118
Epoch 34/50
240/240 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2179 - duration_loss: 0.0344 - pitch_loss: 3.4621 - step_loss: 0.0104Restoring model weights from the end of the best epoch: 29.
240/240 [==============================] - 9s 36ms/step - loss: 0.2179 - duration_loss: 0.0344 - pitch_loss: 3.4621 - step_loss: 0.0104
Epoch 34: early stopping
看下损失函数的曲线
plt.plot(history.epoch, history.history['loss'], label='total loss')
plt.show()
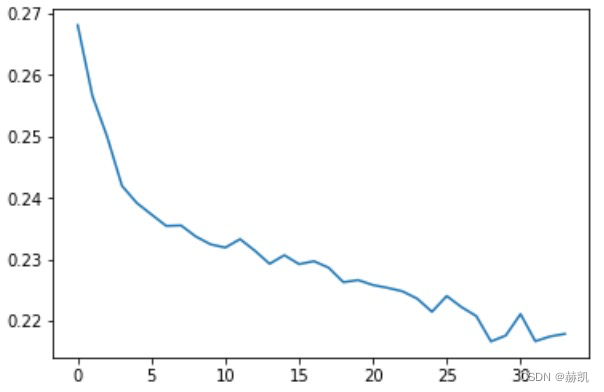
生成notes
预测方法
def predict_next_note(
notes: np.ndarray,
keras_model: tf.keras.Model,
temperature: float = 1.0) -> int:
"""Generates a note IDs using a trained sequence model."""
assert temperature > 0
# Add batch dimension
inputs = tf.expand_dims(notes, 0)
predictions = model.predict(inputs)
pitch_logits = predictions['pitch']
step = predictions['step']
duration = predictions['duration']
pitch_logits /= temperature
pitch = tf.random.categorical(pitch_logits, num_samples=1)
pitch = tf.squeeze(pitch, axis=-1)
duration = tf.squeeze(duration, axis=-1)
step = tf.squeeze(step, axis=-1)
# `step` and `duration` values should be non-negative
step = tf.maximum(0, step)
duration = tf.maximum(0, duration)
return int(pitch), float(step), float(duration)
预测一波
temperature = 2.0
num_predictions = 120
sample_notes = np.stack([raw_notes[key] for key in key_order], axis=1)
# The initial sequence of notes; pitch is normalized similar to training
# sequences
input_notes = (
sample_notes[:seq_length] / np.array([vocab_size, 1, 1]))
generated_notes = []
prev_start = 0
for _ in range(num_predictions):
pitch, step, duration = predict_next_note(input_notes, model, temperature)
start = prev_start + step
end = start + duration
input_note = (pitch, step, duration)
generated_notes.append((*input_note, start, end))
input_notes = np.delete(input_notes, 0, axis=0)
input_notes = np.append(input_notes, np.expand_dims(input_note, 0), axis=0)
prev_start = start
generated_notes = pd.DataFrame(
generated_notes, columns=(*key_order, 'start', 'end'))
查看预测的数据
generated_notes.head(10)
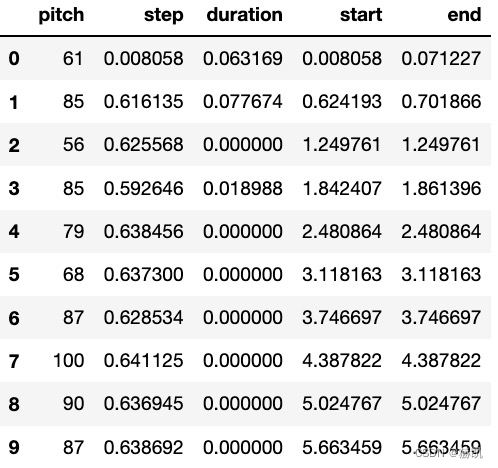
听一下
out_file = 'output.mid'
out_pm = notes_to_midi(
generated_notes, out_file=out_file, instrument_name=instrument_name)
display_audio(out_pm)
看一下图
plot_piano_roll(generated_notes)
plot_distributions(generated_notes)
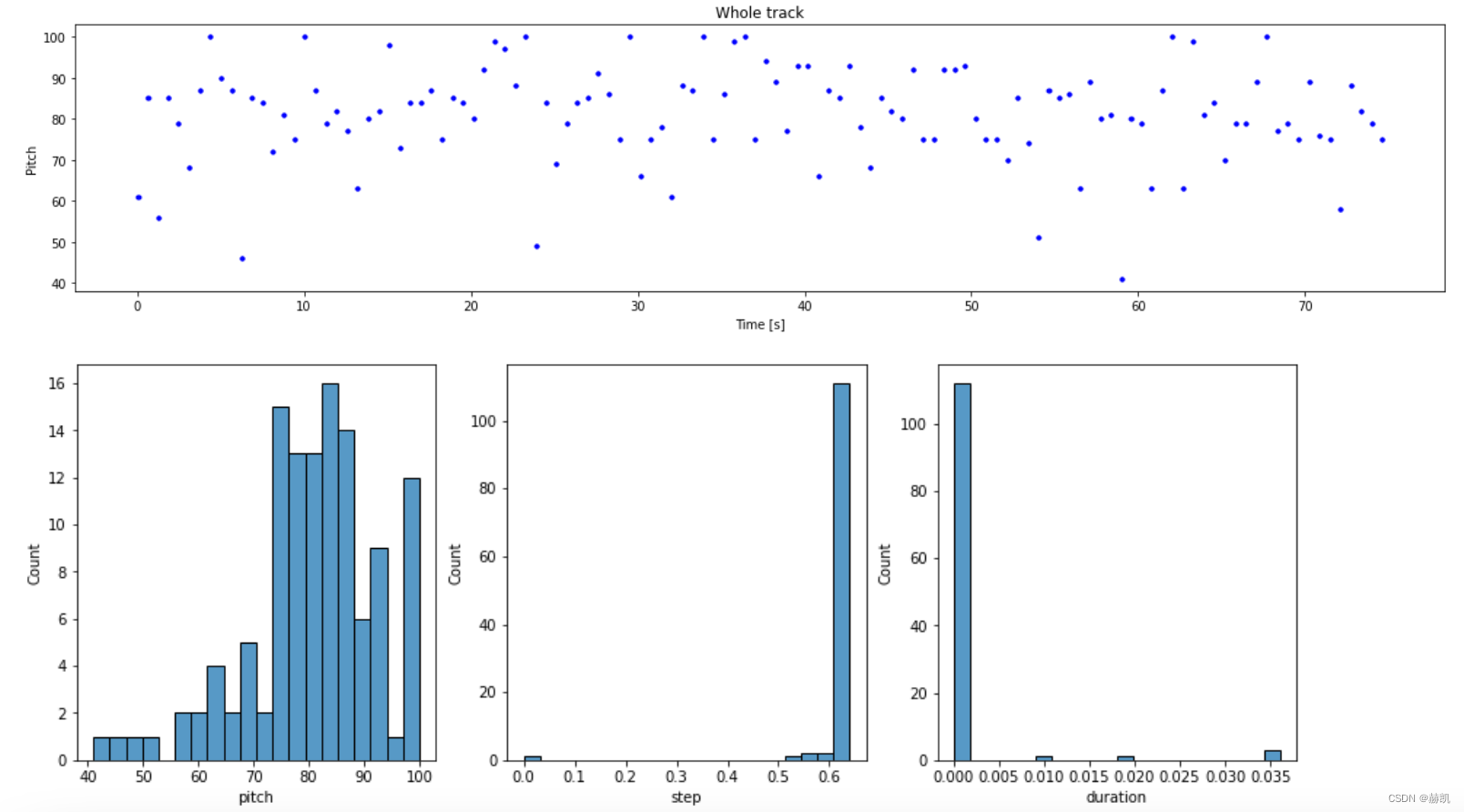
还是蛮有意思的
总结
损失函数的自定义,还有RNN输入数据输出数据的生成
本文来自博客园,作者:赫凯,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/heKaiii/p/17137404.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号