day42 vue基础指令和生命周期
作业思考:
为什么vue直接改变数组不响应:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/31043198
vue中的计算属性-computered
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div id="app">
<div>{{cfn}}</div>
<div>{{cfn}}</div>
<div>{{fn()}}</div>
<div>{{fn()}}</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
num:10
},
methods:{
fn(){
console.log('methods')
return this.num
}
},
computed:{
cfn(){
console.log('computed')
return this.num
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
vue的watch侦听器:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div id="app">
<p>
<input type="text" v-model='firstname' placeholder="姓">
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" v-model='lastname' placeholder="名">
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" v-model='fullname' placeholder="全名">
</p>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
firstname:'',
lastname:'',
fullname:''
},
watch:{
firstname:function(val){
this.fullname = val + ' ' + this.lastname
},
lastname:function(val) {
this.fullname = this.firstname + ' ' +val
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
watch用法 深度监听第二种 监听属性和立即监听
new Vue({ el:'#root6', watch:{ 'deepMessage.a.b':'handleMessage' }, data(){ return { message:'hello vue', message1:'', deepMessage:{ a:{ b:'deep message22222' } }, } }, methods:{ handleMessage(value) { this.message1 = value } } })
vue 自定义指令
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-red>
我是第一个
</div>
<div v-color ='"orange"'>
我是第二个 v-color里面的东西
</div>
<input type="text" v-model='phone' v-mobile>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script >
// 全局指令
Vue.directive('red',{
inserted:function(el){
el.style.color = 'red'
}
})
Vue.directive('color',{
inserted:function(el,binding){
el.style.color = binding.value
}
})
var vue = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
fruits:['apple','pear','banana','orange'],
phone:''
},
directives:{
mobile:{
update:function(el) {
console.log(el.value)
if(!(/^1[3-9]\d{9}$/).test(el.value)) {
el.style.color = 'red'
} else {
el.style.color ='black'
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
04 VUE生命周期的理解
首先,我们可以进行一下分类:
创建期间生命周期函数:beforeCreate,created,beforeMount,mounted
运行期间生命周期函数:beforeUpdate,updated
销毁期间生命周期函数:beforeDestroy,destroyed
然后,简单介绍一下:
创建阶段:
第一个生命周期函数:beforeCreat,当执行beforeCreate生命周期函数时,vue实例还没有被完全创建出来,此时data,methods等内部没有初始化,我们这个时候在函数内调用数据的话,后台会显示undefined。
第二个生命周期函数:created,执行这个函数的时候,vue实例已经初始化了,可以在这里调用数据,不过还没渲染到页面上。 在当前函数中我们可以访问到data中的属性, 更可以进行 axios 前后端分离 请求
第三个生命周期函数:beforeMount,这时,vue已经将模板字符串编译成内存DOM,模板已经编译完成,还没有渲染到页面上。
第四个:mounted,创建阶段完成,页面渲染完毕,进入运行阶段。
运行阶段
当数据发生变化,比如触发了点击事件改动数据
beforeUpdate:内存中的数据已经改变,页面上的还没更新
updated:页面上数据和内存中的一致
销毁阶段
beforeDestroy:出发这个函数时,还没开始销毁,此时刚刚脱离运行阶段。data,methods,指令之类的都在正常运行。在这个生命周期函数中我们可以将绑定的事件进行移除
destroyed:组件销毁完毕,data,methods,指令之类的不可用。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 id="h1">
{{msg}}
</h1>
<h1>{{num}}</h1>
<button @click='num1'>我要更新数据</button>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
fruits: ['apple', 'pear', 'banana', 'orange'],
msg: 'aaa',
num: 0,
num2: 1111111
},
methods: {
num1(){
console.log(this.num++)
}
},
beforeCreate() { },
created() {
var h = document.getElementById('h1')
console.log(h)
},
beforeMount() {
var h = document.getElementById('h1')
console.log(h)
},
mounted() {
var h = document.getElementById('h1')
console.log(h)
},
beforeUpdate() { console.log('beforeupdate')},
updated() {console.log('updated') },
beforeDestroy() {console.log('bdes') },
destroyed() {console.log('des') }
})
</script>
</html>
05 mixin 混入 其实就是逻辑复用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>
mixin学习
</h1>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var mymixin = {
created:function(){
this.hello()
},
methods:{
hello:function(){
console.log('我进入mixin的hello里面了')
}
}
}
var app = new Vue({
mixins:[mymixin],
el: '#app',
data: {
fruits: ['apple', 'pear', 'banana', 'orange']
},
})
</script>
</html>
axios的优势和特点
axios 是一个基于Promise 用于浏览器和 nodejs 的 HTTP 客户端,它本身具有以下特征:
- 从浏览器中创建 XMLHttpRequest
- 从 node.js 发出 http 请求
- 支持 Promise API
- 拦截请求和响应
- 转换请求和响应数据
- 取消请求
- 自动转换JSON数据
- 客户端支持防止CSRF/XSRF
- axios既提供了并发的封装,也没有fetch的各种问题,而且体积也较小,当之无愧现在最应该选用的请求的方式。
三选一绝必是axios了。其流程图如下:
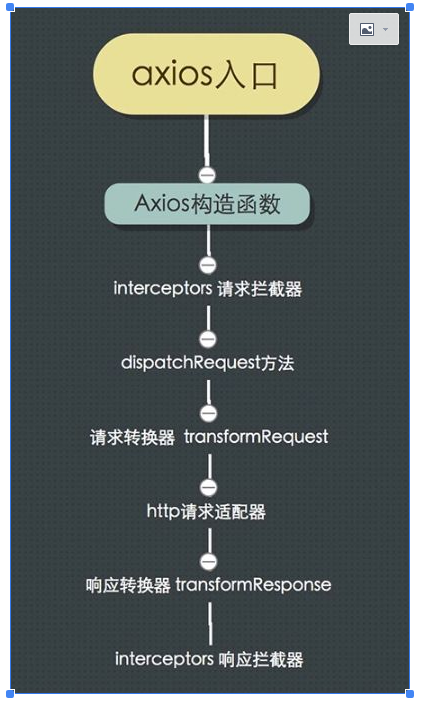
- 简单易用,api接近于jquery,比原生的fetch之类的简单
- 浏览器兼容性好,都能兼容IE7,使用fetch就得自己处理兼容
- 通用性好,能在node和浏览器中使用,api一致
- 稳定大牌,vue官网文档有推荐
- 尤雨溪 官方多次 重点推荐axios



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号