vue项目分析
前言
我们在开发vue项目的时候,一般是使用vue init webpack my_project命令来创建项目的。
创建好的项目可以说比较复杂,文件比较多,让人难以把控。
今天下定决心,把vue init webpack生成的项目中各种文件给搞懂了,接下来就可以更进一步了。
目录结构
vue init webpack创建的项目目录结构如下:
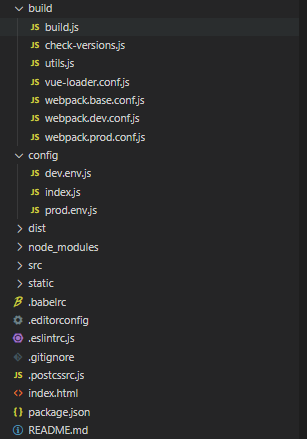
我们主要关注build目录和config目录。
build目录下存放着与编译有关的文件,config目录下的文件其实也和编译有关,而webpack.base.conf.js等这些文件也是配置文件,所以我觉得这样设计目录结构挺别扭的。
但别扭归别扭,毕竟这是官方的目录结构,我们还是得去适应它,明白了各文件的用处其实也没必要去纠结目录结构了。
模块依赖图

可以看出,build目录和config目录下的模块的依赖关系还是挺复杂的, 下面我一个模块一个模块地分析。
build/build.js
该文件不复杂,主要就是读取build/webpack.prod.conf.js,并用webpack执行编译。
'use strict'
require('./check-versions')()
process.env.NODE_ENV = 'production'
const ora = require('ora') // ora模块实现node.js命令环境的loading效果,和显示各种状态的图标等
const rm = require('rimraf') // 删除文件夹的模块
const path = require('path') // 用例文件的模块
const chalk = require('chalk') // 用于修改控制台中字符串的样式(字体样式、字体颜色、背景颜色)的模块
const webpack = require('webpack')
const config = require('../config')
const webpackConfig = require('./webpack.prod.conf') // 因为是编译,所以直接导入生产环境的配置
// 开始loading
const spinner = ora('building for production...')
spinner.start()
// 删除编译输出目录
rm(path.join(config.build.assetsRoot, config.build.assetsSubDirectory), err => {
if (err) throw err
// 开始打包
webpack(webpackConfig, (err, stats) => {
// 停止loading
spinner.stop()
if (err) throw err
// 输出打包信息
process.stdout.write(stats.toString({
colors: true,
modules: false,
children: false, // If you are using ts-loader, setting this to true will make TypeScript errors show up during build.
chunks: false,
chunkModules: false
}) + '\n\n')
if (stats.hasErrors()) {
console.log(chalk.red(' Build failed with errors.\n'))
process.exit(1)
}
console.log(chalk.cyan(' Build complete.\n'))
console.log(chalk.yellow(
' Tip: built files are meant to be served over an HTTP server.\n' +
' Opening index.html over file:// won\'t work.\n'
))
})
})
build/webpack.prod.conf.js
该文件就是production环境下的配置文件,在build/webpack.base.conf.js基础上,添加了styleLoader以及多种用于优化的插件。
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const config = require('../config')
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
const OptimizeCSSPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin')
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin')
const env = require('../config/prod.env')
const webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
rules: utils.styleLoaders({
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
extract: true,
usePostCSS: true
})
},
devtool: config.build.productionSourceMap ? config.build.devtool : false,
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: utils.assetsPath('js/[name].[chunkhash].js'),
chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath('js/[id].[chunkhash].js')
},
plugins: [
// 该插件用于在编译时将指定的变量替换为指定的常量。
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': env
}),
// 该插件用来压缩优化js文件。
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
compress: {
warnings: false
}
},
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
parallel: true
}),
// 该插件用于提取css到单独的文件。
new ExtractTextPlugin({
filename: utils.assetsPath('css/[name].[contenthash].css'),
allChunks: true,
}),
// 该插件用于压缩提取出来的css文件。
new OptimizeCSSPlugin({
cssProcessorOptions: config.build.productionSourceMap
? { safe: true, map: { inline: false } }
: { safe: true }
}),
// 该插件用于创建html入口文件,并未引入的外部资源如script、link动态添加每次编译后的hash,防止引用缓存的外部文件。
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.index,
template: 'index.html',
inject: true,
minify: {
removeComments: true,
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true
},
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
// keep module.id stable when vendor modules does not change
new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin(),
// 该插件用于启用作用域提升,从而让代码文件更小、运行得更快。
new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(),
// CommonsChunkPlugin插件用来提取第三方库和公共模块,避免首屏加载的bundle文件或者按需加载的bundle文件体积过大,从而导致加载时间过长。
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ // 抽取第三方js到单独的文件。
name: 'vendor',
minChunks(module) {
return (
module.resource &&
/\.js$/.test(module.resource) &&
module.resource.indexOf(
path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules')
) === 0
)
}
}),
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ // 抽取webpack运行时和模块清单到单独的文件,以防第三方文件的hash在app bundle文件被更新时更新。
name: 'manifest',
minChunks: Infinity
}),
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ // 抽取共享的chunk,并放到一个单独的chunk中,类似于vender chunk。
name: 'app',
async: 'vendor-async',
children: true,
minChunks: 3
}),
// 该插件将单个文件或目录复制到构建目录,这里就是转移static目录。
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
{
from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'),
to: config.build.assetsSubDirectory,
ignore: ['.*']
}
])
]
})
// 如果需要压缩,则加上压缩插件
if (config.build.productionGzip) {
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
webpackConfig.plugins.push(
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
asset: '[path].gz[query]',
algorithm: 'gzip',
test: new RegExp(
'\\.(' +
config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join('|') +
')$'
),
threshold: 10240,
minRatio: 0.8
})
)
}
// 如果需要生成分析报告,则加上分析插件
if (config.build.bundleAnalyzerReport) {
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin
webpackConfig.plugins.push(new BundleAnalyzerPlugin())
}
module.exports = webpackConfig
build/webpack.dev.conf.js
'use strict'
const utils = require('./utils')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const config = require('../config')
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const path = require('path')
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const FriendlyErrorsPlugin = require('friendly-errors-webpack-plugin')
const portfinder = require('portfinder')
const HOST = process.env.HOST
const PORT = process.env.PORT && Number(process.env.PORT)
const devWebpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
rules: utils.styleLoaders({
sourceMap: config.dev.cssSourceMap,
usePostCSS: true
// 和webpack.prod.conf.js中的styleLoaders相比,少了一个extract属性。
})
},
devtool: config.dev.devtool,
/**
* 开发服务器配置
*/
devServer: {
clientLogLevel: 'warning',
historyApiFallback: {
rewrites: [
{ from: /.*/, to: path.posix.join(config.dev.assetsPublicPath, 'index.html') },
],
},
hot: true,
contentBase: false, // since we use CopyWebpackPlugin.
compress: true,
host: HOST || config.dev.host,
port: PORT || config.dev.port,
open: config.dev.autoOpenBrowser,
overlay: config.dev.errorOverlay
? { warnings: false, errors: true }
: false,
publicPath: config.dev.assetsPublicPath,
proxy: config.dev.proxyTable,
quiet: true, // necessary for FriendlyErrorsPlugin
watchOptions: {
poll: config.dev.poll,
}
},
/**
* 插件
*
* 相较于webpack.prod.conf.js中少了:
* * UglifyJsPlugin:用于压缩js代码,开发环境不需要。
* * ExtractTextPlugin:抽取css代码到单独文件,开发环境不需要。
* * OptimizeCSSPlugin:压缩css代码,开发环境不需要。
* * HashedModuleIdsPlugin:给资源名加上hash标记,开发环境不需要。
* * ModuleConcatenationPlugin:开启作用域提升,让代码文件更小、运行得更快,开发环境不需要。
* 多了:
* * HotModuleReplacementPlugin:热部署。
* * NamedMouldePlugin:开启HMR(热部署)时用于显示模块的相对路径。
* * NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin:在编译出现错误的时候,跳过输出阶段。在网上没有通俗的解释,不知道该插件的意义何在。
*/
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': require('../config/dev.env')
}),
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(),
new webpack.NamedModulesPlugin(),
new webpack.NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin(),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'index.html',
template: 'index.html',
inject: true
}),
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
{
from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'),
to: config.dev.assetsSubDirectory,
ignore: ['.*']
}
])
]
})
module.exports = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
portfinder.basePort = process.env.PORT || config.dev.port
portfinder.getPort((err, port) => {
if (err) {
reject(err)
} else {
// 发布新的端口,在e2e tests下是必要的。
process.env.PORT = port
// 添加端口号到devServer配置
devWebpackConfig.devServer.port = port
// 顾名思义,添加了一个用于友好显示错误的插件
devWebpackConfig.plugins.push(new FriendlyErrorsPlugin({
compilationSuccessInfo: {
messages: [`Your application is running here: http://${devWebpackConfig.devServer.host}:${port}`],
},
onErrors: config.dev.notifyOnErrors
? utils.createNotifierCallback()
: undefined
}))
// 返回配置
resolve(devWebpackConfig)
}
})
})
build/webpack.base.conf.js
该文件是development环境和production环境的公共配置文件,除了指定出入口之外,还加上了对vue文件、js文件、图片文件、音频文件、字体文件的各种loader。
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
const config = require('../config')
const vueLoaderConfig = require('./vue-loader.conf')
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir)
}
module.exports = {
context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'),
// 编译入口
entry: {
app: './src/main.js'
},
// 编译出口
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot, // 输出路径,即static目录和index.html所在的目录的路径
filename: '[name].js',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' // 编译后嵌入在资源url中的前缀
? config.build.assetsPublicPath
: config.dev.assetsPublicPath
},
// 自定义模块寻找方式
resolve: {
extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'],
alias: {
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
'@': resolve('src'),
}
},
// loader,用于转换各种文件
module: {
rules: [
// vue文件
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: vueLoaderConfig
},
// js文件
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test'), resolve('node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client')]
},
// 图片文件
{
test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
// 音频文件
{
test: /\.(mp4|webm|ogg|mp3|wav|flac|aac)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('media/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
// 字体文件
{
test: /\.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
}
]
},
// 该配置说明打包后是要部署在node上的
node: {
// prevent webpack from injecting useless setImmediate polyfill because Vue
// source contains it (although only uses it if it's native).
setImmediate: false,
// prevent webpack from injecting mocks to Node native modules
// that does not make sense for the client
dgram: 'empty',
fs: 'empty',
net: 'empty',
tls: 'empty',
child_process: 'empty'
}
}
build/utils.js
提供了四个方法:
- assetsPath(__path):获取__path指定的资源名的路径;
- cssLoaders(options):获取各种样式文件的loader列表(loader即rule中use属性的值);
- styleLoaders(options):获取各种样式文件的rule列表(rule即module中rules数组中的元素);
- createNotifierCallback():获取脚手架错误的函数;
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
const config = require('../config')
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
const packageConfig = require('../package.json')
/**
* 返回一个资源的干净的相对根路径
* @param {*} _path
* @returns
*/
exports.assetsPath = function (_path) {
const assetsSubDirectory = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? config.build.assetsSubDirectory
: config.dev.assetsSubDirectory
return path.posix.join(assetsSubDirectory, _path) // path.posix.join返回完整路径的相对路径,而path.json返回完整路径
}
/**
* 获取各种后缀样式文件的loader列表
* @param {*} options
* @returns
*
* @callby build/vue-loader.conf.js
* @callby 当前文件的exports.styleLoaders
*/
exports.cssLoaders = function (options) {
options = options || {}
// 预定义css-loader、postcss-loader两种loader,在接下来的generateLoaders()中会用到
const cssLoader = {
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap // 是否开启css map
}
}
const postcssLoader = {
loader: 'postcss-loader',
options: {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
}
}
/**
* 获取指定样式的loader列表(注意,这里的loader是指webpack配置文件中loader的use键对应的值
* @param {*} loader 样式类型,比如less、sass、stylus
* @param {*} loaderOptions 额外的配置
* @returns
*/
function generateLoaders(loader, loaderOptions) {
// 默认每种样式都使用css-loader,如果options.usePostCSS为true,则再添加postcss-loader
const loaders = options.usePostCSS ? [cssLoader, postcssLoader] : [cssLoader]
// 如果loader参数有值,则生成对应的loader配置对象
if (loader) {
loaders.push({
loader: loader + '-loader',
options: Object.assign({}, loaderOptions, {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
})
})
}
// 当option.extract为true时,提取css文件
// (只有下production下有效)
if (options.extract) {
return ExtractTextPlugin.extract({
use: loaders,
fallback: 'vue-style-loader'
})
} else {
return ['vue-style-loader'].concat(loaders)
}
}
// 返回最终的结果
return {
css: generateLoaders(),
postcss: generateLoaders(),
less: generateLoaders('less'),
sass: generateLoaders('sass', { indentedSyntax: true }),
scss: generateLoaders('sass'),
stylus: generateLoaders('stylus'),
styl: generateLoaders('stylus')
}
}
/**
* 生成各种样式文件的rule列表
* @param {*} options
* @returns
*/
exports.styleLoaders = function (options) {
const output = []
const loaders = exports.cssLoaders(options)
for (const extension in loaders) {
const loader = loaders[extension]
output.push({
test: new RegExp('\\.' + extension + '$'),
use: loader
})
}
return output
}
/**
* 返回脚手架错误的函数
* @returns
*/
exports.createNotifierCallback = () => {
const notifier = require('node-notifier')
return (severity, errors) => {
if (severity !== 'error') return
const error = errors[0]
const filename = error.file && error.file.split('!').pop()
notifier.notify({
title: packageConfig.name,
message: severity + ': ' + error.name,
subtitle: filename || '',
icon: path.join(__dirname, 'logo.png')
})
}
}
build/check-version.js
'use strict'
const chalk = require('chalk')
const semver = require('semver') // 用来对特定的版本号作判断的模块
const packageConfig = require('../package.json')
const shell = require('shelljs') // 用来执行unix脚本的模块
function exec(cmd) {
return require('child_process').execSync(cmd).toString().trim()
}
// 版本要求清单
const versionRequirements = [
{
name: 'node',
currentVersion: semver.clean(process.version), // 获取当前计算机上的node版本。semver.clean()把版本信息转化为规定格式,比如把=v1.2.3转化为1.2.3。
versionRequirement: packageConfig.engines.node // 从package.json中获取node版本信息(及要求当前计算机上的node要符合package.json中的node版本要求)
}
]
// 如果当前计算机上安装了npm,则添加npm的版本要求
if (shell.which('npm')) {
versionRequirements.push({
name: 'npm',
currentVersion: exec('npm --version'), // 获取当前计算机上的npm版本。
versionRequirement: packageConfig.engines.npm // 从package.json中获取npm版本信息。
})
}
module.exports = function () {
const warnings = []
// 检查每一项要求,如果不符合,则将警告信息放到warnings中
for (let i = 0; i < versionRequirements.length; i++) {
const mod = versionRequirements[i]
if (!semver.satisfies(mod.currentVersion, mod.versionRequirement)) {
warnings.push(mod.name + ': ' +
chalk.red(mod.currentVersion) + ' should be ' +
chalk.green(mod.versionRequirement)
)
}
}
// 如果warnings不为空,则输出警告信息
if (warnings.length) {
console.log('')
console.log(chalk.yellow('To use this template, you must update following to modules:'))
console.log()
for (let i = 0; i < warnings.length; i++) {
const warning = warnings[i]
console.log(' ' + warning)
}
console.log()
process.exit(1)
}
}
build/vue-loader.conf.js
'use strict'
const utils = require('./utils')
const config = require('../config')
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
// 根据环境获取是否需要生成css source map文件
const sourceMapEnabled = isProduction
? config.build.productionSourceMap
: config.dev.cssSourceMap
module.exports = {
loaders: utils.cssLoaders({
sourceMap: sourceMapEnabled, // 是否需要生成source map
extract: isProduction // 是否需要单独抽离css
}),
cssSourceMap: sourceMapEnabled,
cacheBusting: config.dev.cacheBusting,
// 在编译模块的过程中,将比如src转为require调用
transformToRequire: {
video: ['src', 'poster'],
source: 'src',
img: 'src',
image: 'xlink:href'
}
}
config/index.js
'use strict'
// Template version: 1.3.1
const path = require('path')
module.exports = {
dev: {
/**
* 路径
*/
assetsSubDirectory: 'static', // 见build
assetsPublicPath: '/', // 见build
/**
* 代理(用来跨域)
*/
proxyTable: {
'/api': {
target: 'http://localhost:8080',
changeOrigin: true,
ws: true,
pathRewrite: {
'^/api': '/english_reading' //通过pathRewrite重写地址,将前缀/api转为/appName
}
}
},
/**
* 服务器
*/
host: 'localhost', // can be overwritten by process.env.HOST
port: 8080, // can be overwritten by process.env.PORT, if port is in use, a free one will be determined
autoOpenBrowser: false,
errorOverlay: true,
notifyOnErrors: true,
poll: false,
/**
* Source Maps
*/
devtool: 'cheap-module-eval-source-map',
cacheBusting: true, // 如果你在用devtools对vue文件debug时出现了问题,将这个设为false可能会有用
cssSourceMap: true
},
build: {
/**
* 路径
*/
index: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../english_reading/src/main/webapp/static/html/index.html'), // index.html输出路径,必须是绝对路径。
assetsRoot: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../english_reading/src/main/webapp'), // 指向包含应用程序所有静态资产的根目录,必须是绝对路径。
assetsSubDirectory: 'static', // 被编译处理过的资源文件都会在这个目录下,实际路径是assetsRoot/assetsSubDirectory。
assetsPublicPath: '/english_reading', // 在webpack.base.conf.js中会将其设为output的publicPath,而publicPath是用来在编译后嵌入url的。
// publicPath: '/english_reading',
/**
* Source Maps
*/
productionSourceMap: true, // 在构建production版本是是否开启source map。
devtool: '#source-map',
/**
* Gzip
*
* Gzip off by default as many popular static hosts such as
* Surge or Netlify already gzip all static assets for you.
* Before setting to `true`, make sure to:
* npm install --save-dev compression-webpack-plugin
*/
productionGzip: false, // 是否开启gzip
productionGzipExtensions: ['js', 'css'], // 需要使用gzip压缩的文件扩展名
// 执行npm run build时加上--report参数可以查看打包分析报告。
bundleAnalyzerReport: process.env.npm_config_report // 是否开启
}
}
config/prod.env.js
这份文件内容很少,就是导出一个对象,对象中有一个NODE_ENV属性,其值为'"production"'。
该文件被build/webpack.prod.conf.js引用,给process.env赋值。
'use strict'
module.exports = {
NODE_ENV: '"production"'
}
config/dev.env.js
和config/prod.env.js相比,除了有一个NODE_ENV属性外,还与config/prod.env.js进行了合并。
'use strict'
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const prodEnv = require('./prod.env')
module.exports = merge(prodEnv, {
NODE_ENV: '"development"'
})




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号