神经网络与深度学习(邱锡鹏)编程练习 3 Logistic回归 - Jupyter导出版 TensorFlow2.9
修改了两个地方:
- 生成数据的时候,把数值类型float64改为改为float32
- 去掉了两个@tf.function
Logistic Regression Example
生成数据集, 看明白即可,无需填写代码
'+' 从高斯分布采样 (X, Y) ~ N(3, 6, 1, 1, 0)
'o' 从高斯分布采样 (X, Y) ~ N(6, 3, 1, 1, 0)
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import animation, rc
from IPython.display import HTML
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
dot_num = 100
x_p = np.random.normal(3., 1, dot_num)
print(x_p[0].dtype) # 检查数据类型
x_p = np.float32(x_p) # 转换为 float32 Edit by David 2022.6.1
print(x_p[0].dtype) # 检查数据类型
y_p = np.random.normal(6., 1, dot_num)
y_p = np.float32(y_p) # 转换为 float32
y = np.ones(dot_num)
# print(y[0].dtype) # 检查数据类型
y = np.float32(y) # 转换为 float32
C1 = np.array([x_p, y_p, y]).T
x_n = np.random.normal(6., 1, dot_num)
x_n = np.float32(x_n) # 转换为 float32
y_n = np.random.normal(3., 1, dot_num)
y_n = np.float32(y_n) # 转换为 float32
y = np.zeros(dot_num)
y = np.float32(y) # 转换为 float32
C2 = np.array([x_n, y_n, y]).T
plt.scatter(C1[:, 0], C1[:, 1], c='b', marker='+')
plt.scatter(C2[:, 0], C2[:, 1], c='g', marker='o')
data_set = np.concatenate((C1, C2), axis=0)
np.random.shuffle(data_set)
float64
float32
建立模型
建立模型类,定义loss函数,定义一步梯度下降过程函数
填空一:实现sigmoid的交叉熵损失函数(不使用tf内置的loss 函数)
epsilon = 1e-12
class LogisticRegression():
def __init__(self):
self.W = tf.Variable(shape=[2, 1], dtype=tf.float32,
initial_value=tf.random.uniform(shape=[2, 1], minval=-0.1, maxval=0.1))
self.b = tf.Variable(shape=[1], dtype=tf.float32, initial_value=tf.zeros(shape=[1]))
self.trainable_variables = [self.W, self.b]
@tf.function
def __call__(self, inp):
logits = tf.matmul(inp, self.W) + self.b # shape(N, 1)
pred = tf.nn.sigmoid(logits)
return pred
# @tf.function Edit by David 2022.6.1
def compute_loss(pred, label):
# print(label)
if not isinstance(label, tf.Tensor): # isinstance()是Python中的一个内建函数。是用来判断一个对象的变量类型。
label = tf.constant(label, dtype=tf.float32) # 创建常量
pred = tf.squeeze(pred, axis=1)
'''============================='''
#输入label shape(N,), pred shape(N,)
#输出 losses shape(N,) 每一个样本一个loss
#todo 填空一,实现sigmoid的交叉熵损失函数(不使用tf内置的loss 函数)
losses = -label*tf.math.log(pred+epsilon) - (1.-label)* tf.math.log(1.-pred+epsilon)
'''============================='''
loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses)
pred = tf.where(pred>0.5, tf.ones_like(pred), tf.zeros_like(pred))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(label, pred), dtype=tf.float32))
return loss, accuracy
# @tf.function Edit by David 2022.6.1
def train_one_step(model, optimizer, x, y):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
pred = model(x)
loss, accuracy = compute_loss(pred, y)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))
return loss, accuracy, model.W, model.b
实例化一个模型,进行训练
# 调试1 TypeError: Input 'b' of 'MatMul' Op has type float32 that does not match type float64 of argument 'a'.
# 解决方案:在数据源增加数据类型转换。 David 2022.6.1
# x1, x2, y = list(zip(*data_set))
# x = list(zip(x1, x2))
# x[0][0].dtype
# 调试2 TypeError: Expected float32, but got Tensor("label:0", shape=(), dtype=float32) of type 'Tensor'.
# 解决方案: # @tf.function 自动把 float 转为 tensor, 所以需要去掉。
# 不知道是不tf版本升级后的问题。看例程和参考博客,都带着 @tf.function
# David 2022.6.1
如果实验中x的内的数值dtype('float64'),会产生错误。需要将输入数据调整为float32。
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = LogisticRegression()
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
x1, x2, y = list(zip(*data_set))
x = list(zip(x1, x2))
animation_fram = []
for i in range(200):
loss, accuracy, W_opt, b_opt = train_one_step(model, opt, x, y)
animation_fram.append((W_opt.numpy()[0, 0], W_opt.numpy()[1, 0], b_opt.numpy(), loss.numpy()))
if i%20 == 0:
print(f'loss: {loss.numpy():.4}\t accuracy: {accuracy.numpy():.4}')
loss: 0.6835 accuracy: 0.5
loss: 0.5124 accuracy: 0.985
loss: 0.4103 accuracy: 0.985
loss: 0.3446 accuracy: 0.985
loss: 0.2993 accuracy: 0.985
loss: 0.2663 accuracy: 0.985
loss: 0.2412 accuracy: 0.985
loss: 0.2215 accuracy: 0.985
loss: 0.2055 accuracy: 0.985
loss: 0.1924 accuracy: 0.985
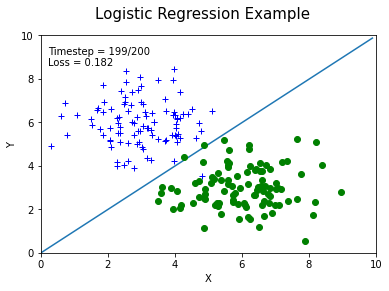
结果展示,无需填写代码
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,4)) #f是图像对象,ax是坐标轴对象
f.suptitle('Logistic Regression Example', fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.xlabel('X')
ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax.set_ylim(0, 10)
line_d, = ax.plot([], [], label='fit_line')
C1_dots, = ax.plot([], [], '+', c='b', label='actual_dots')
C2_dots, = ax.plot([], [], 'o', c='g' ,label='actual_dots')
frame_text = ax.text(0.02, 0.95,'',horizontalalignment='left',verticalalignment='top', transform=ax.transAxes)
def init():
line_d.set_data([],[])
C1_dots.set_data([],[])
C2_dots.set_data([],[])
return (line_d,) + (C1_dots,) + (C2_dots,)
def animate(i):
xx = np.arange(10, step=0.1)
a = animation_fram[i][0]
b = animation_fram[i][1]
c = animation_fram[i][2]
yy = a/-b * xx +c/-b
line_d.set_data(xx, yy)
C1_dots.set_data(C1[:, 0], C1[:, 1])
C2_dots.set_data(C2[:, 0], C2[:, 1])
frame_text.set_text('Timestep = %.1d/%.1d\nLoss = %.3f' % (i, len(animation_fram), animation_fram[i][3]))
return (line_d,) + (C1_dots,) + (C2_dots,)
#FuncAnimation函数绘制动图,f是画布,animate是自定义动画函数,init_func自定义开始帧,即传入init初始化函数,
#frames动画长度,一次循环包含的帧数,在函数运行时,其值会传递给函数animate(i)的形参“i”,interval更新频率,以ms计,blit选择更新所有点,还是仅更新产生变化的点。
anim = animation.FuncAnimation(f, animate, init_func=init, frames=len(animation_fram), interval=30, blit=True)
HTML(anim.to_html5_video())


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号