二叉树
一 . 一维数组二叉
所用知识点:1 . 左子树 = 二倍根 ; 2 . 右子树 = 二倍根子树 + 1 ;
2 . 一棵树有 2 的 k 次方 减一个节点 ;
3 . 一棵树最后一行有 2 的 k-1 次方个节点;
解题链接:P4715 【深基16.例1】淘汰赛 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int n; struct human{ int id,eng; }a[100000]; int main(){ cin>>n; int f=pow(2,n);//1<<n for(int i=1;i<=f;i++){ cin>>a[f+i-1].eng; a[f+i-1].id=i; // cout<<a[f+i-1].id <<" "<<a[f+i-1].eng <<endl; } for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){ int o=1; for(int i=f+o-1;i<=f+f-1;i+=2){ if(a[i].eng >a[i+1].eng ){//将获胜方存入位置 a[i/2].eng =a[i].eng ; a[i/2].id =a[i].id ; }else{ a[i/2].eng =a[i+1].eng ; a[i/2].id =a[i+1].id ; } //a[i/2].eng=max(a[i].eng ,a[i+1].eng ); o+=2; } f/=2; } int p=0; if(a[2].eng >a[3].eng )cout<<a[3].id; else cout<<a[2].id; return 0; }
二 . 二叉树的遍历
知识点:1 . 中序遍历:按照左子树,根,右子树的顺序访问节点;
2 . 前序遍历:按照根,左子树,右子树的顺序访问节点;
3 . 后序遍历:按照左子树,右子树,根的顺序访问节点。
如此这般,我们可知前序与中序求后序,或根据中序与后序求前序;
【模板】遍历三项
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int n; 4 struct tree{ 5 int left,right; 6 }a[10000]; 7 void front(int m){ 8 if(m==0)return ; 9 cout<<m<<" ";//根 10 front(a[m].left);//左 11 front(a[m].right);//右 12 } 13 void mid(int m){ 14 if(m==0)return ; 15 mid(a[m].left);//左 16 cout<<m<<" ";//根 17 mid(a[m].right);//右 18 } 19 void last(int m){ 20 if(m==0)return ; 21 last(a[m].left);//左 22 last(a[m].right);//右 23 cout<<m<<" ";//根 24 } 25 int main(){ 26 cin>>n; 27 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 28 cin>>a[i].left>>a[i].right; 29 } 30 front(1); 31 cout<<endl; 32 mid(1); 33 cout<<endl; 34 last(1); 35 return 0; 36 }
综上,可得例题:P1827 [USACO3.4] 美国血统 American Heritage - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 string zx,qx,hx,op,i,o; 4 void bl(string q,string z){ 5 if(q.empty()) return ; 6 char t=q[0]; 7 int k=z.find(t);//找出地址 8 q.erase(q.begin());//用完即丢!方便后续操作 。。。 9 bl(q.substr(0,k),z.substr(0,k)); 10 bl(q.substr(k),z.substr(k+1));//分别便利左儿子和右儿子 11 cout<<t; 12 } 13 14 int main(){ 15 cin>>zx>>qx; 16 bl(qx,zx); 17 return 0; 18 }
【变式】求线序数列:P1030 [NOIP2001 普及组] 求先序排列 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 string q,z,h; 4 void dfs_q(string zx,string hx){ 5 if(zx.empty())return ; 6 char s=hx[hx.size()-1]; 7 cout<<s; 8 int pos=zx.find(s,0); 9 string zx_left=zx.substr(0,pos),hx_left=hx.substr(0,pos);//在函数substr内,pos是指下标下一位; 10 string zx_right=zx.substr(pos+1,zx.size()-1),hx_right=hx.substr(hx_left.size(),zx_right.size()); 11 // cout<<zx_left<<" "<<zx_right<<endl; 12 // cout<<hx_left<<" "<<hx_right<<endl; 13 // cout<<endl; 14 dfs_q(zx_left,hx_left); 15 dfs_q(zx_right,hx_right); 16 } 17 int main(){ 18 cin>>z>>h; 19 dfs_q(z,h); 20 return 0; 21 }
一道很不错的暴力二叉树(广搜+二叉树):P1364 医院设置 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int n,vis[105],total=1e9,ans; 4 struct node{int peo,l,r,f;}a[105]; 5 struct hspt{int id,dis;}; 6 queue<hspt>q; 7 int main(){ 8 cin>>n; 9 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 10 cin>>a[i].peo>>a[i].l>>a[i].r; 11 a[a[i].l].f=i;a[a[i].r].f=i; 12 } 13 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 14 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); 15 vis[i]=1; 16 ans=0; 17 q.push({i,0}); 18 while(!q.empty()){ 19 hspt tmp=q.front();q.pop(); 20 //父节点 21 if(a[tmp.id].f&&!vis[a[tmp.id].f]){ 22 ans+=a[a[tmp.id].f].peo*(tmp.dis+1); 23 vis[a[tmp.id].f]=1; 24 q.push({a[tmp.id].f,tmp.dis+1}); 25 } 26 //左儿子 27 if(a[tmp.id].l&&!vis[a[tmp.id].l]){ 28 ans+=a[a[tmp.id].l].peo*(tmp.dis+1); 29 vis[a[tmp.id].l]=1; 30 q.push({a[tmp.id].l,tmp.dis+1}); 31 } 32 //右儿子 33 if(a[tmp.id].r&&!vis[a[tmp.id].r]){ 34 ans+=a[a[tmp.id].r].peo*(tmp.dis+1); 35 vis[a[tmp.id].r]=1; 36 q.push({a[tmp.id].r,tmp.dis+1}); 37 } 38 39 } 40 total=min(ans,total); 41 } 42 cout<<total; 43 return 0; 44 }
三.二叉搜索树(BST)
1.BST性质
(1)左子树小于根,右子树大于根
(2)二叉搜索树的每一棵子树都是一颗二叉搜索树
2.二叉树的查询
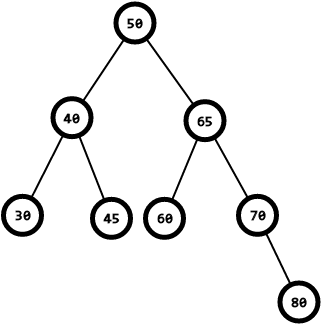
根据二叉树的性质,如果根节点的数刚好是查找的数,则返回根节点的值;不然有两种情况,一是此数比根节点小,则查询此根左子树,二是此数比根节点大,则查询此根右子树。
例如上图,
我们要查询60
从根节点50开始,60 > 50 往右子树里找,到65,65 > 60 往右子树里找,找到60
3.二叉树的插入
与查询一样,依次判断寻找子树,直到叶子节点后加入此数。
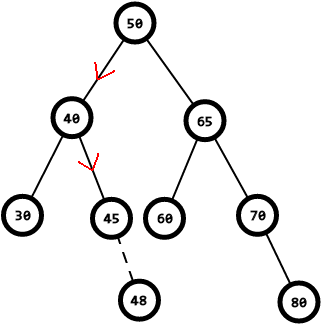
如图我们要插入48
48 < 50,去左子树,到40
48 > 40,去右子树,到45
48 > 45,45没有子节点了,48成为45的右儿子
4.二叉树的最值
最小值 >> 一直在左子树找
最大值 >> 一直在右子树找
5.二叉树的删除
在二叉树中,最好删除的是叶子结点,如此我们可以看此节点是否为叶子结点,如果不是,就在不破坏二叉树性质的前提下,将其与左/右节点交换位置,直到它成为叶子结点。
6.例题讲解
1.首先读题可知,题目中需要我们的操作是
(1)查询排名为x的数
(2)查询数x的排名
(3)求x的前驱与后继
(4)插入数x
ok,这样让我们一个个来讲解查看
首先,也是最重要的一点,我们先构建一棵二叉查找树
(1)造树
普及一个小知识,结构体内连接初始值操作方法如下
1 struct Node{//此结构体有两个构造函数 2 int left,right,size,value,num; 3 Node(int l,int r,int s,int v):left(l),right(r),size(s),value(v),num(1){ }//构造初始值 4 Node(){ }//无参默认构造函数 5 }t[MAXN];
使用inline’关键字可以提高函数调用的效率,但它通常用于短小的函数,因为将函数内容嵌入到每个调用点可能会增加代码大小。在这里,它被用于、update’函数,因为这个函数的目的是在每个节点的更新中执行一些小的计算,内联它可以提高执行效率。
1 //左子树坐标下左子树大小 + 右子树坐标下右子树的大小 + 根节点的大小 2 inline void update(int root){ 3 t[root].size =t[t[root].left ].size +t[t[root].right ].size +t[root].num;//不断将每一个点的大小加入根节点并汇总 4 //更新节点信息 5 }
汇总:所有的预备工作
1 struct Node{//此结构体有两个构造函数 2 int left,right,size,value,num; 3 Node(int l,int r,int s,int v):left(l),right(r),size(s),value(v),num(1){ }//构造初始值 4 Node(){ }//无参默认构造函数 5 }t[MAXN]; 6 inline void update(int root){ 7 t[root].size =t[t[root].left ].size +t[t[root].right ].size +t[root].num;//不断将每一个点的大小加入根节点并汇总 8 //更新节点信息 9 }
其次,我们先看最常用的查询操作
(2)查询
1.查询数x的排名
因为我们知道二叉树的性质,左子树中数都小于根,右子树中数都大于根,所以我们可以在查询中判断x是否大于根,又或是小于根,那么就在右/左子树中递归查找(注意如果在右子树中查找时记得将左子树大小加入答案),直到根就是左子树,输出答案即可。
1 int rank(int x,int root){//查找数x的排名 2 if(root){//根中有叶子而不为0 3 if(x<t[root].value)//如果此点小于根,则进入左子树查找 4 return rank(x,t[root].left); 5 if(x>t[root].value)//如果此点大于根,则进入右子树查找 6 return rank(x,t[root].right+t[t[root].left ].size +t[root].num); 7 return t[root].num +t[t[root].left ].size ;//如果刚好查到其本身,则返回左子树与根的大小总和 8 } 9 return 1;//如果该树未有叶子,则直接返回值一 10 }
2.查询排名为x的数
此查找与上一段最显著的差别就是,这个是以排名查找树的值,而上一个是以树的值查找排名;
则此时则也有三种情况:
(1)x 这个排名比根节点排名小,则进入左子树
(2)x 这个排名比根节点排名大,则进入右子树,同时把 x 减去左子树的排名
(3)x 这个排名就是根节点排名,返回根节点的值
1 int kth(int x,int root){//查询排名为 x 的数 2 if(x<=t[t[root].left ].size )return kth(x,t[root].left );//排名为x的数在左子树,故进入左子树 3 if(x<=t[t[root].left ].size +t[root].num )return t[root].value;//当前根节点为要找的数,直接返回 4 return kth(x-t[t[root].left ].size -t[root].num ,t[root].right ); 5 //排名为x的数在右子树,进入右子树并把x减去左子树 size+t[root].num(根节点). 6 }
(3)插入
插入的规则很容易理解,首先判断插到哪棵子树,在递归寻找没有左或右子节点的树,新建后插入
记得每次插入后跟新节点总值
1 //插入的规则很容易理解,首先判断插到哪棵子树,在递归寻找没有左或右子节点的树,新建后插入 2 void insert(int x,int &root){ 3 if(x<t[root].value ){//是否在左子树中 4 if(!t[root].left)//是否有左子树 5 t[t[root].left=cnt++]=Node(0,0,1,x);//新建所需节点 6 else 7 insert(x,t[root].left );//递归查询 8 }else if(x>t[root].value ){//是否在右子树中 9 if(!t[root].right ){//是否有右子树 10 t[t[root].right =cnt++]=Node(0,0,1,x);//新建节点 11 }else{ 12 insert(x,t[root].right );//递归查询 13 } 14 }else{//如果根节点就是这个数 15 t[root].num ++;//根节点个数 16 } 17 update(root); //更新此时节点信息 18 }
至此之上,便是这道题目主要考察的算法点了
本文来自博客园,作者:{追屿},转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/happy-yu/p/17708190.html
 二叉树与BST
二叉树与BST

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号