Vue响应式原理
本文只分析了data中数据变为响应式对象,及修改触发dom更新的过程,computed和watch暂不讨论
一、Vue如何实现数据响应式
1、new Vue() 实例时,调用原型上_init() 方法
function Vue (options) { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !(this instanceof Vue) ) { warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword') } this._init(options) }
2、_init方法中主要代码如下,其中调用initState方法
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) { const vm: Component = this // a uid vm._uid = uid++ // a flag to avoid this being observed vm._isVue = true // merge options if (options && options._isComponent) { // optimize internal component instantiation // since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the // internal component options needs special treatment. initInternalComponent(vm, options) } else { vm.$options = mergeOptions( resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor), options || {}, vm ) } /* istanbul ignore else */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { initProxy(vm) } else { vm._renderProxy = vm } // expose real self vm._self = vm initLifecycle(vm) initEvents(vm) initRender(vm) callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate') initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props initState(vm) initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props callHook(vm, 'created') if (vm.$options.el) { vm.$mount(vm.$options.el) } }
3、initState方法主要初始化了props、data、methods、computed、watch等
export function initState (vm: Component) { vm._watchers = [] const opts = vm.$options if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props) if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods) if (opts.data) { initData(vm) } else { observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */) } if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed) if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) { initWatch(vm, opts.watch) } }
4、首先分析initData方法,方法最后调用 observe 方法
function initData (vm: Component) { let data = vm.$options.data data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function' ? getData(data, vm) : data || {} /** 省略代码 * 1、提示data方法应该返回一个对象 * 2、对比data和props、methods中的属性,如果重复则抛出警告 * 3、代理 使通过this.x 访问data中的x属性值时,实际访问的是this._data.x */ // observe data observe(data, true /* asRootData */) }
observe 方法实现
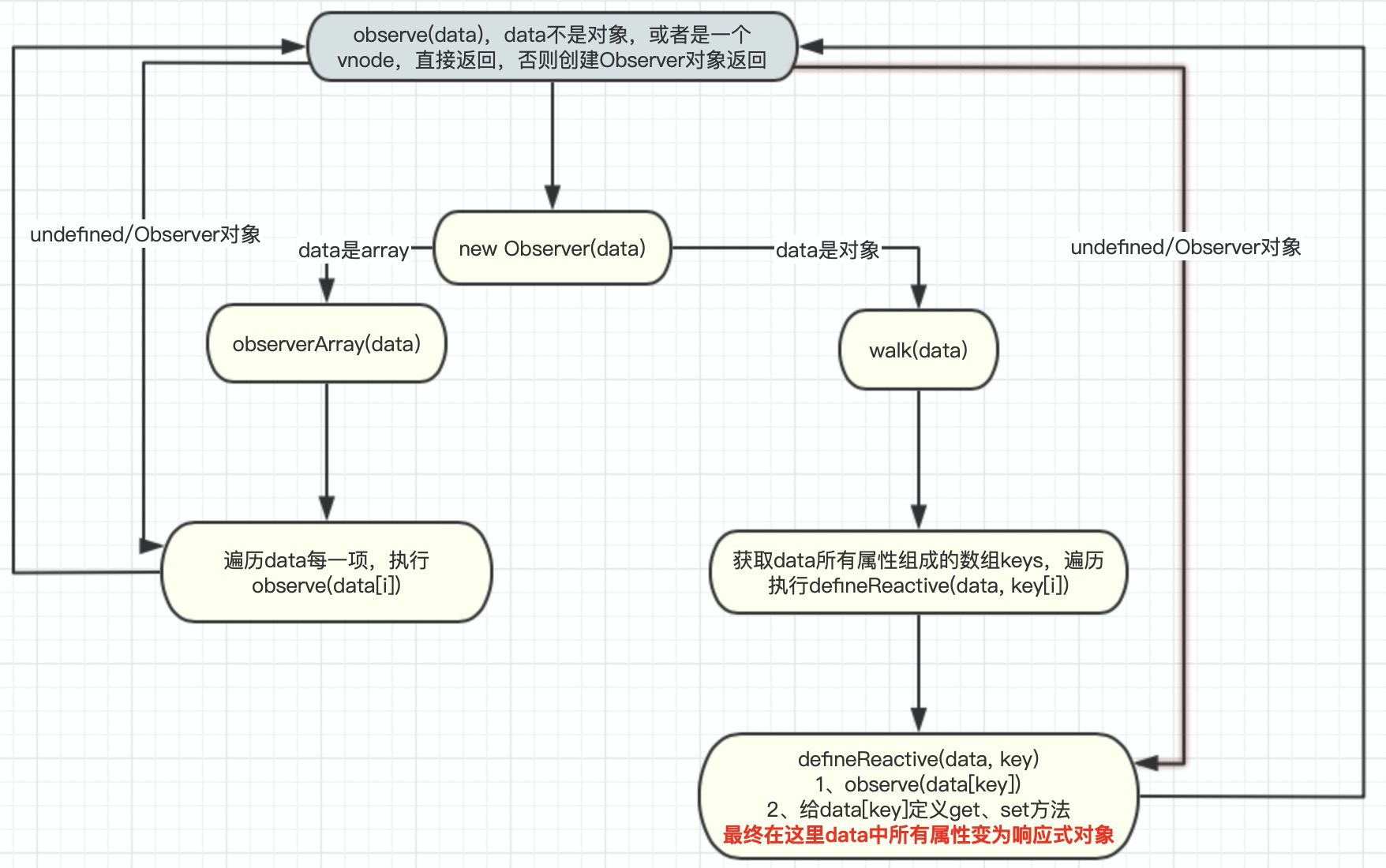
function observe (value, asRootData) { // 如果观测的数据不是一个对象或者是一个VNode,则直接返回 if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) { return } var ob; // 如果观测的对象已经包含了__ob__,说明该对象已经处于观测中,__ob__实际上是一个Observer实例,后面会介绍如何定义 if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) { ob = value.__ob__; } else if ( shouldObserve && !isServerRendering() && (Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) && Object.isExtensible(value) && !value._isVue ) { // 否则满足上述条件下,new Observer ob = new Observer(value); } if (asRootData && ob) { ob.vmCount++; } return ob }
5、Observer对象源码如下
export class Observer { value: any; dep: Dep; vmCount: number; // number of vms that have this object as root $data constructor (value: any) { this.value = value this.dep = new Dep() this.vmCount = 0
// 给被观测的数据定义__ob__ 属性,属性值为当前Observer实例对象
// def方法是对Object.defineProperty方法的封装,第四个参数如果不传递或者传入false,则表示不可枚举
def(value, '__ob__', this)
// 被观测对象是数组 if (Array.isArray(value)) {
// 绑定一些数组方法,包括push、pop、shift、unshift、splice、reverse、sort方法,可以触发视图更新操作等 if (hasProto) { protoAugment(value, arrayMethods) } else { copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys) }
// 调用observeArray 方法,该方法主要遍历数组每项,并对每项执行observe方法,进行观测 this.observeArray(value) } else {
// 被观测数据是对象,调用walk方法,该方法主要遍历对象所有属性,并将对应属性值全部变成响应式对象 this.walk(value) } } walk (obj: Object) { const keys = Object.keys(obj) for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
// 将对象变成响应式对象的方法调用 defineReactive(obj, keys[i]) } } observeArray (items: Array<any>) { for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) { observe(items[i]) } } }
6、defineReactive方法源码如下
export function defineReactive ( obj: Object, key: string, val: any, customSetter?: ?Function, shallow?: boolean ) { const dep = new Dep()
// 省略。。。,最终结果可以认为val = obj[key] val = obj[key]
// 对对象属性递归执行observe方法,将每个对象属性值设置get、set方法,变成响应式对象
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val) Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { enumerable: true, configurable: true, get: function reactiveGetter () {
// 这个方法在render方法执行时,会访问数据,则调用get方法,在这个方法中会进行依赖收集 const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val if (Dep.target) { dep.depend() if (childOb) { childOb.dep.depend() if (Array.isArray(value)) { dependArray(value) } } } return value }, set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) { const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val /* eslint-disable no-self-compare */ if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) { return } /* eslint-enable no-self-compare */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) { customSetter() } // #7981: for accessor properties without setter if (getter && !setter) return if (setter) { setter.call(obj, newVal) } else { val = newVal } childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal) dep.notify() } }) }
通过上述流程,则将data中的数据全部变成响应式对象,用一张图表示
二、依赖收集
上面提到,当访问某项数据时,会触发该数据的访问器get属性,那么什么时候会访问数据呢,其实是在render方法执行,生成vdom的过程中会进行数据的访问
从上面_init方法中看到,最后执行了vm.$mount ()方法
$mount()方法的前半部分主要是生成render函数,最后调用runtime-only和runtime-compiler版本共同的mount方法,可以参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/happy-dog/p/13697646.html
Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( el?: string | Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating) }
mountComponent 方法实现
export function mountComponent ( vm: Component, el: ?Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { vm.$el = el /** 省略代码,提示使用了runtime-only版本下使用了template方式,应该换成render方式或者切换到runtime-compiler版本 */ callHook(vm, 'beforeMount') // 调用生命周期函数 let updateComponent /** 省略updateComponent的一些判断赋值,主要是增加了性能统计的一些代码 */ updateComponent = () => { vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating) // 1、render方法在updateComponent方法执行时执行,那么updateComponent方法什么时候执行呢 } new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, { // 2、updateComponent方法作为实例化Watcher对象的参数, 这个Watcher对象是一个渲染watcher before () { if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) { callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate') } } }, true /* isRenderWatcher */) hydrating = false if (vm.$vnode == null) { vm._isMounted = true callHook(vm, 'mounted') } return vm }
watcher 构造函数和get方法实现
constructor ( vm: Component, expOrFn: string | Function, cb: Function, options?: ?Object, isRenderWatcher?: boolean ) { this.vm = vm if (isRenderWatcher) { vm._watcher = this } vm._watchers.push(this) /** 省略一些实例属性的赋值,目前不那么重要 */ this.cb = cb this.id = ++uid // uid for batching this.deps = [] this.newDeps = [] this.depIds = new Set() this.newDepIds = new Set() this.expression = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' ? expOrFn.toString() : '' this.getter = expOrFn this.value = this.get() // 1、实例化Watcher时,最后调用了get方法 } get () { pushTarget(this) // 2、首先执行pushTarget方法,该方法位于在源码dep.js文件中,给Dep订阅器设置唯一的watcher,并把当前watcher推入targetStack中 let value const vm = this.vm try { // 实际调用updateComponent方法 value = this.getter.call(vm, vm) // 3、执行getter方法,实际上就是执行updateComponent方法,即会执行vm_render()方法,该方法返回vnode,会访问数据,从而触发访问器属性get } catch (e) { /** updateComponent函数调用错误处理, */ } finally { if (this.deep) { traverse(value) } popTarget() // 4、此时依赖收集完成,从targetStack中弹出更新完的watcher,并把Dep.target置为targetStack中上一个watcher this.cleanupDeps() // 5、做一个newDepIds —— depIds,newDeps —— deps;并把newDepIds 和 newDeps清空 } return value }
回到Vue把数据变成响应式对象时,定义的get属性
get: function reactiveGetter () { const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val if (Dep.target) { dep.depend() // Dep对象的depend方法判断Dep.target存在,执行Dep.target.addDep(dep),即调用Watcher对象的addDep方法 if (childOb) { childOb.dep.depend() if (Array.isArray(value)) { dependArray(value) } } } return value },
addDep (dep: Dep) { const id = dep.id if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) { this.newDepIds.add(id) this.newDeps.push(dep) if (!this.depIds.has(id)) { // 判断 dep.addSub(this) } } }
// 把订阅器dep放在当前watcher的newDeps和newDepIds中,并且如果把当前watcher放在dep的subs中,即watcher中保存了dep,dep中也保存了watcher
通过上述过程,即完成了依赖收集
三、派发更新
从前面的分析中,知道vdom生成过程中,进行了数据的访问,完成了收集依赖,接下来分析修改数据,更新dom的过程
修改数据时,触发访问器属性,set方法中,最后调用了dep.notify()
notify () { // stabilize the subscriber list first const subs = this.subs.slice() /** 省略判断非异步更新的情况 */ // 遍历subs中的watcher,触发update方法 for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) { subs[i].update() } }
update () { if (this.lazy) { this.dirty = true } else if (this.sync) { this.run() // 如果是同步更新,不用放在下一个tick,直接执行run方法 } else { queueWatcher(this) // 一般都会走到这里,调用queueWatcher方法 } }
queueWatcher 主要代码实现
export function queueWatcher (watcher: Watcher) { const id = watcher.id if (has[id] == null) { has[id] = true queue.push(watcher) // 用队列收集需要更新的watcher nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue) // 执行nextTick方法 } }
// nextTick 主要代码实现
const callbacks = []
export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) { let _resolve callbacks.push(() => { cb.call(ctx) }) // 回调函数统一收集传入的cb函数,即flushSchedulerQueue if (!pending) { pending = true timerFunc() // 执行timerFunc() } }
let timerFunc if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) { const p = Promise.resolve() timerFunc = () => { p.then(flushCallbacks) if (isIOS) setTimeout(noop) } isUsingMicroTask = true } else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && ( isNative(MutationObserver) || MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]' )) { let counter = 1 const observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks) const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter)) observer.observe(textNode, { characterData: true }) timerFunc = () => { counter = (counter + 1) % 2 textNode.data = String(counter) } isUsingMicroTask = true } else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) { timerFunc = () => { setImmediate(flushCallbacks) } } else { timerFunc = () => { setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0) } }
主要是上面把callbacks中存放的flushSchedulerQueue方法放在异步中调用,如果浏览器支持原生Promise或者MutationObserver,则表示使用的微任务,否则表示回调放在宏任务中执行,
这样只有当执行栈中所有同步代码执行完成,才会执行nextTick方法中传入的flushSchedulerQueue
flushSchedulerQueue 主要代码实现
function flushSchedulerQueue () { currentFlushTimestamp = getNow() flushing = true let watcher, id /** 排序原因 * 对watcher进行排序,因为组件更新是从父组件到子组件的,一个组件的自定义watcher在渲染watcher之前, * 自定义组件先于渲染watcher被创建(initState方法创建了自定义watcher,new Watcher创建渲染watcher), * 如果执行父组件的watcher时,子组件被销毁,则子组件的watcher可以被跳过,不执行 */ queue.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id) // 遍历queue队列中watcher,进行更新 for (index = 0; index < queue.length; index++) { watcher = queue[index] if (watcher.before) { watcher.before() // 执行beforeUpdate钩子函数 } id = watcher.id has[id] = null watcher.run() // 执行watcher.run, 触发vdom的重新生成渲染 /** 省略非生产环境下,判断是否触发了死循环,watcher一个对象变化,在里面又触发了这个对象变化,导致的死循环 */ } const activatedQueue = activatedChildren.slice() // keep-alive组件相关,暂时不管 const updatedQueue = queue.slice() // 暂存watcher队列,因为下面一行代码会做一些变量重置,queue会被重置为空数组 resetSchedulerState() // 重置queue,has,wait,flush callActivatedHooks(activatedQueue) // keep-alive组件相关,暂时不管 callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue) // 所有watcher执行完成之后触发updated钩子函数 }
watcher run主要代码实现
run () { if (this.active) {
// 触发get方法实现,前面分析过get方法主要操作
// 1、pushTarget
// 2、调用this.getter() ,即updateComponent方法,该方法主要是先生成vdom,然后执行vm._update来更新dom
// 3、popTarget
// 4、cleanupDeps,清空newDeps
const value = this.get()
// 省略了不影响主逻辑的代码,涉及到自定义watcher的一些实现 } }
cleanupDeps 主要代码实现
cleanupDeps () {
// 不是第一次收集依赖时,deps不为空 let i = this.deps.length while (i--) { const dep = this.deps[i]
// 遍历deps,移除旧的订阅,防止某些组件被删除了,但是订阅却依然存在,导致不必要的浪费
// 依赖收集是每次更新数据时都会做的事情,所以虽然旧的订阅被移除了,但是如果下次访问对应数据,还是会进行依赖的收集 if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) { dep.removeSub(this) } }
// 将newDeps和newDepIds分别赋值给deps和depIds,并移除newDeps和newDepIds let tmp = this.depIds this.depIds = this.newDepIds this.newDepIds = tmp this.newDepIds.clear() tmp = this.deps this.deps = this.newDeps this.newDeps = tmp this.newDeps.length = 0 }
整个派发更新的过程到此就结束了,中间其实跳过了很多自己不理解的代码,但是对主要流程不影响
整个过程是看完 黄佚老师的视频之后(https://coding.imooc.com/learn/list/228.html),自己又梳理了一遍,后面如果有更深刻的认识,会在补充
beforeMount执行时机:new Watcher之前,创建vdom之前
beforeUpdate执行时机:调用watcher.run之前,即重新生成vdom之前
updated执行时机:页面更新完成之后



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号