Codeforces 976C Nested Segments
题面:
C. Nested Segments
Input file: standard input
Output file: standard output
Time limit: 2 second
Memory limit: 256 megabytes
You are given a sequence a1, a2, ..., an of one-dimensional segments numbered 1 through n. Your task is to find two distinct indices i and j such that segment ai lies within segment aj.
Segment [l1, r1] lies within segment [l2, r2] if l1 ≥ l2 and r1 ≤ r2.
Print indices i and j. If there are multiple answers, print any of them. If no answer exists, print -1 -1.
Input
The first line contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3·10^5) — the number of segments.
Each of the next n lines contains two integers li and ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 10^9) — the i-th segment.
Output
Print two distinct indices i and j such that segment ai lies within segment aj. If there are multiple answers, print any of them. If no answer exists, print -1 -1.
Example
Input
5
1 10
2 9
3 9
2 3
2 9
Output
2 1
Input
3
1 5
2 6
6 20
Output
-1 -1
Note
In the first example the following pairs are considered correct:
- (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1), (5, 1) — not even touching borders;
- (3, 2), (4, 2), (3, 5), (4, 5) — touch one border;
- (5, 2), (2, 5) — match exactly.
题目描述:
题目给出N个区间,分别编号为1-N,要找出哪一个区间会包含另一个区间,输出区间的编号。
题目分析:
这道题其实我们可以这样想:一个区间包含另一个区间的特点是什么?题目告诉我们:被包含的区间左端点要大于等于包含区间的左端点,被包含的区间的右端点要小于等于包含区间的右端点:

(区间[1,8]和[4,6])
那么我们直接选两个判断吗?题目数据有3*10^5个区间,任选两个区间作比较肯定是会超时的。这时我们就要找突破口,找到比O(n^2)复杂度更小的想法。刚刚特点告诉我们:是被包含区间的必要条件就是左端点要大于等于包含区间的左端点。那么,我们可不可以先把这N个区间按左端点进行从小到大排序,然后比较右端点就行了?排序的时间复杂度用c++ algorithm里面的sort最坏仅是O(nlogn),对于题目的数据量来说是不会超时的。之后,我们怎么进行比较?只要我们从第1-N个区间遍历一次,区间比较右端点的大小:如果发现当前的右端点比之前遍历过的区间的最大右端点要小或相等,就可以输出答案了。因为这时从1-N的方向遍历保证了被包含区间的左端点肯定是大于等于主动包含区间的左端点,这时发现被包含区间的右端点小于等于包含区间的右端点,所以可以直接输出答案:

(对区间按照左端点从小到大排完序后,就是先遍历[1,8]区间,再遍历[4,6]区间)
如果发现当前的右端点比之前遍历过的区间要大,那么更新右端点最远能到哪里,并记录这个区间的编号,为什么要这样做?
这里当遍历到[4,9]这个区间时,因为9比7大,所以[4,9]这个区间不可能包含[3,7],但是[4,9]有可能包含后面的区间,而且后面如果有能被[3,7]包含的区间,[4,9]也一定能包含:

([5,6]区间既被[3,7]包含,又被[4,9]包含)
但是可能是这样:
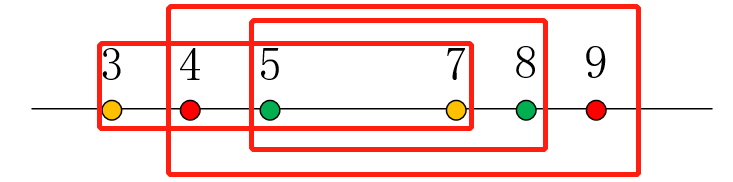
这时[4,9]能包含的区间([5,8]),[3,7]却不能包含。因为像[5,8]这样的区间有个特点:它们的左端点绝对是大于等于之前的区间(已经排好序了,而且我们是按顺序遍历的),那么,我们在选择右端点的时候,就要贪心地选择右端点较大的,还有记录这个右端点来自哪个区间,才能找到我们想要的答案。如果遍历一遍都还没有找到答案的话,就不存在答案:
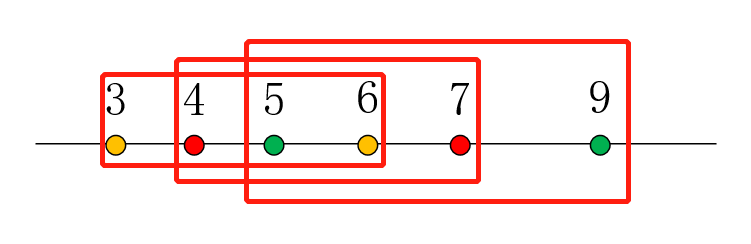
这里有一点要注意的是:如果有一个区间的右端点要大于之前的之前区间的最大右端点,但是这个区间的左端点和上一个区间的左端点一样的话:
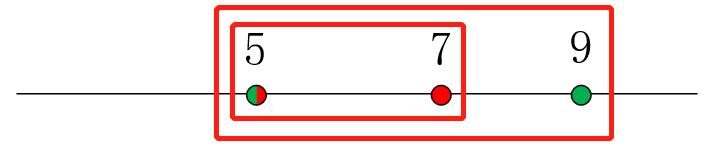
这时候输出答案就好啦,不用继续遍历下去。还要注意题目输出的是“被包含区间编号 包含区间编号”,不要弄反了。
AC代码:
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cmath> 5 #include <set> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <algorithm> 8 #include <utility> 9 using namespace std; 10 const int maxn = 3e5+5; 11 struct node{ 12 int l, r; //左右端点 13 int num; //编号 14 }; 15 node seg[maxn]; //存放区间 16 17 bool cmp(node a, node b){ 18 return a.l < b.l; //使区间按左端点从小到大排序 19 } 20 21 int main(){ 22 int n; 23 scanf("%d", &n); 24 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ 25 scanf("%d%d", &seg[i].l, &seg[i].r); 26 seg[i].num = i; 27 } 28 29 sort(seg+1, seg+n+1, cmp); 30 31 int max_right = seg[0].r; //最大的右端点 32 int max_i = 0; //最大右端对应区间 33 34 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ 35 if(seg[i].r > max_right){ 36 if(seg[i].l == seg[i-1].l){ 37 cout << seg[i-1].num << " "; 38 cout << seg[i].num << endl; 39 return 0; 40 } 41 else{ 42 max_right = seg[i].r; //更新最大右端点 43 max_i = i; //记录位置 44 } 45 } 46 else { 47 cout << seg[i].num << " "; 48 cout << seg[max_i].num << endl; 49 return 0; 50 } 51 } 52 cout << "-1 -1\n"; 53 return 0; 54 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号