【IO编程】3.字节流和字符流
1. FileInputStream介绍
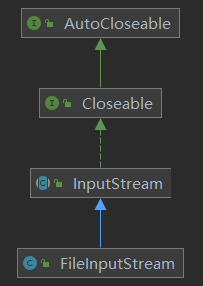
- 构造方法
- FileInputStream(String name)
- name: 文件名
- FileInputStream(File file)
- file: 文件
- FileInputStream(String name)
- 成员方法
- int read(byte[] buf)
- 批量读取字节到数组中,返回读取到的字节数,如果到文件末尾返回-1
- int read()
- 读取一个字节
- void close()
- 关闭流,需要捕获IO异常
- int read(byte[] buf)
使用FileInputStream读取文件,注意流关闭时也需要捕获IOException
@Test
public void readFile1() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
int readData = -1;
try {
// FileNotFoundException 如果找不到该文件就抛出异常
fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\test.txt");
// read() 方法会抛出IO异常
while ((readData = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)readData);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
// 流关闭时需要捕获IOException
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
以上方式没有加缓存,读取效率低。可以增加一个byte数组作为缓存来提高效率,并且需要一个值去记录读取数据的长度。代码如下:
@Test
public void readFile2() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
// 字节数组,当作缓存来提高读取效率
byte[] buffer = new byte[4];
// 读取数据的长度
int readLength = 0;
try {
// FileNotFoundException 如果找不到该文件就抛出异常
fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\test.txt");
// read() 方法会抛出IO异常
while ((readLength = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, readLength));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. FileOutputStream介绍
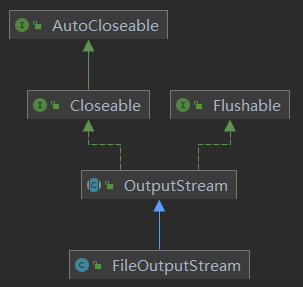
-
构造方法
- FileOutputStream(String name)
- name为文件名,调用此方法创建的对象将以覆盖的方式写文件
- FileOutputStream(File file)
- FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)
- name为文件名,append为是否为追加方式
- append为false是以覆盖的方式写文件,为true是以追加的方式写文件
- FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)
- FileOutputStream(String name)
-
成员方法
- write(int b)
- 写入一个字节b
- write(byte[] b)
- 写入一个字节数组b
- write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
- 写入一个字节数组b,且从索引off开始,长度为len
- void close()
- 关闭流,需要捕获IO异常
- write(int b)
将字符串内容写入到文件中,代码如下:
@Test
public void writeFile1() {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("e:\\test.txt");
String str = "hello, world";
fos.write(str.getBytes());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3. 使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream实现文件拷贝
实现思路为每次用FileInputStream读取数据后立即使用FileOutputStream将这部分数据写入到一个新文件中。代码如下:
public boolean copyFile(String sourceFilePath, String destFilePath) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int readLength = 0;
boolean success = false;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(sourceFilePath);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath);
while ((readLength = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0, readLength);
}
success = true;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
if (fos != null) {
fos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return success;
}
4. FileReader介绍
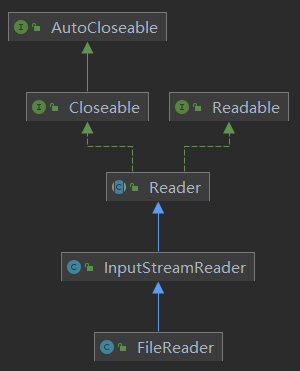
- 构造方法
- FileReader(String filename)
- FileReader(File file)
- 成员方法
- int read()
- 读取单个字符,如果到文件末尾返回-1
- int read(char[] cbuf)
- 批量读取字符到数组中,返回读取到的字符数,如果到文件末尾返回-1
- void close()
- 关闭流,需要捕获IO异常
- int read()
使用FileReader读取文件
@Test
public void readFile() {
FileReader fr = null;
char[] buffer = new char[4];
int readLength = 0;
try {
fr = new FileReader("e:\\test.txt");
while ((readLength = fr.read(buffer)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, readLength));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fr != null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5. FileWriter介绍
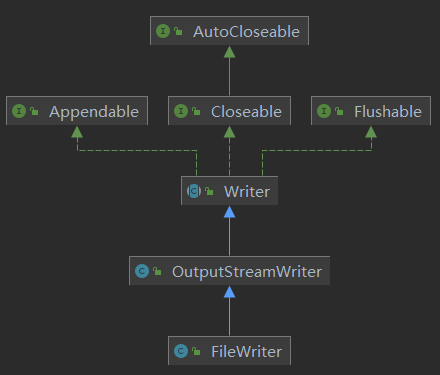
- 构造方法
- FileWriter(String filename)
- FileWriter(File file)
- FileWriter(String file, boolean append)
- FileWriter(File file, boolean append)
- 使用FileWriter(String filename)或FileWriter(File file)创建的对象是以覆盖的方式写文件。对于FileWriter(String file, boolean append)和FileWriter(File file, boolean append)而言,当append为true是为追加的方式写文件,为false是以覆盖的方式写文件。
- 成员方法
- write(int c)
- 写入单个字符
- write(char[] cbuf)
- 写入指定数组
- write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
- 写入指定数组的指定部分,以索引off开始,长度为len
- write(String str)
- 写入指定字符串
- write(String str, int off, int len)
- 写入指定字符串的指定部分,以索引off开始,长度为len
- void close()
- 关闭流,需要捕获IO异常
- write(int c)
- 注意:使用FileWriter后,必须调用close()方法或者flush()方法,否则无法写入内容。
使用FileWriter写入文件,代码如下:
@Test
public void writeFile() {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("e:\\test.txt");
fw.write("hello, world!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号