Mybatis原理
在Mybatis框架中,当我们需要对数据库进行操作时,主要分为四步,同时也涉及到了四大对象(executor 执行器对象、StatementHandler 预编译处理对象、ParameterHandler 参数处理对象、ResultSetHandler 结果集处理对象),下面我们具体说明一下这四步以及各部分涉及的东西。
第一步,需要通过读取Mybartis配置文件中的信息,通过加载流的形式,来获取SqlSessionFactory这个工厂对象
//创建sqlSessionFactory
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
static {
String config = "mybatis.xml";
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream (config);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ().build (inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace ();
}
}
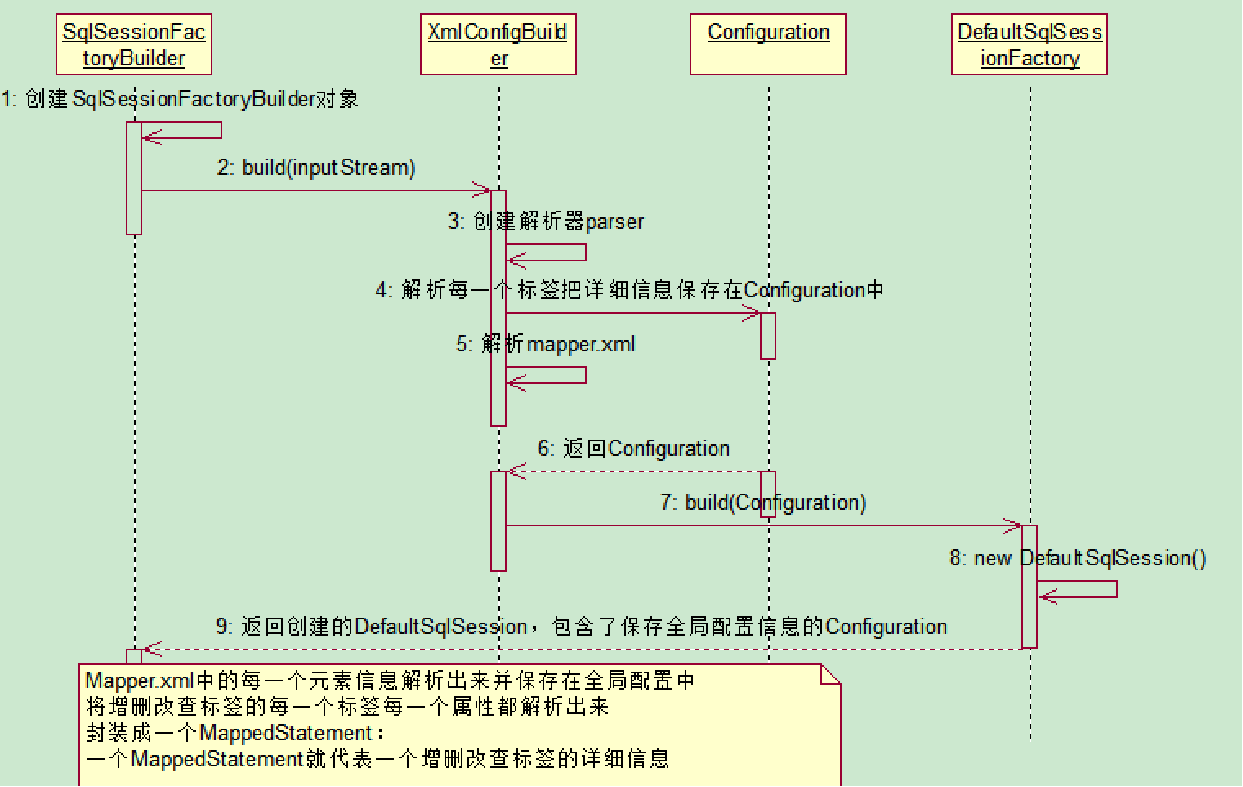
总结:把配置文件的信息解析并保存在Configuration对象中,返回包含了Configuration并且实现了SqlSessionFactory的DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象。
第二步,获取完工厂对象后,我们应该要从SqlSessionFactory这个工厂中获取我们需要的对象即SqlSession
//获取sqlSession对象
public static SqlSession getSqlSession()
{
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
if(sqlSessionFactory != null)
{
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession ();
return sqlSession;
}
return null;
}
其中SqlSessionFactory中定义了通过openSession()方法,而SqlSessionFactory的实现类为DefaultSqlSessionFactory,
他里面定义了一个Configuration对象属性这个属性在创建 SqlSessionFactory时就将数据库的全局配置信息都包含在内。
在调用DefaultFactory中的openSession()方法时,又调用了openSessionFromDataSource方法来获得数据源并进行一些事务操作的处理,同时也生成了executor这个执行器对象
openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
我们再进入newExecutor方法
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
可以发现 默认的执行器类型是ExecutorType.SIMPLE,并且在创建执行器的方法中还会判断是否存在二级缓存的配置,
如果存在则通过new CachingExecutor创建二级缓存 ,然后会通过拦截器将executor包装并返回
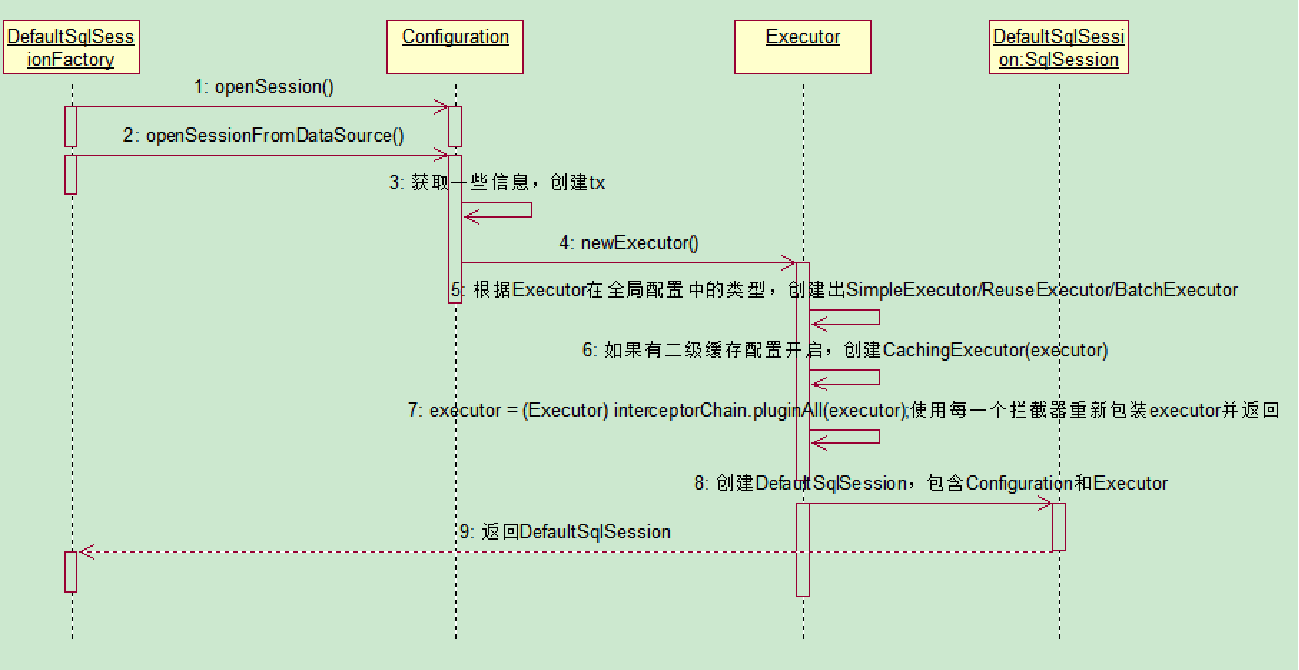
总结:返回SqlSession的实现类DefaultSqlSession对象,他里面包含了Executor和Configuration,Executor会在这一步被创建
第三步,获取到SqlSession对象后,通过映射获得Dao的代理对象
StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession.getMapper (StudentDao.class);
其中调用了getMapper方法
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
我们通过查看,仍然发现他是通过配置对象中的getMapper方法返回了一个泛型类对象
mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
又调用了mapperRegistory的方法
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
此方法中使用了 MapperProxyFactory获取工厂的对象,并且通过工厂传入sqlSession获取到了一个实例 而这个实例就是代理对象,getMapper返回接口的代理对象包含了SqlSession对象
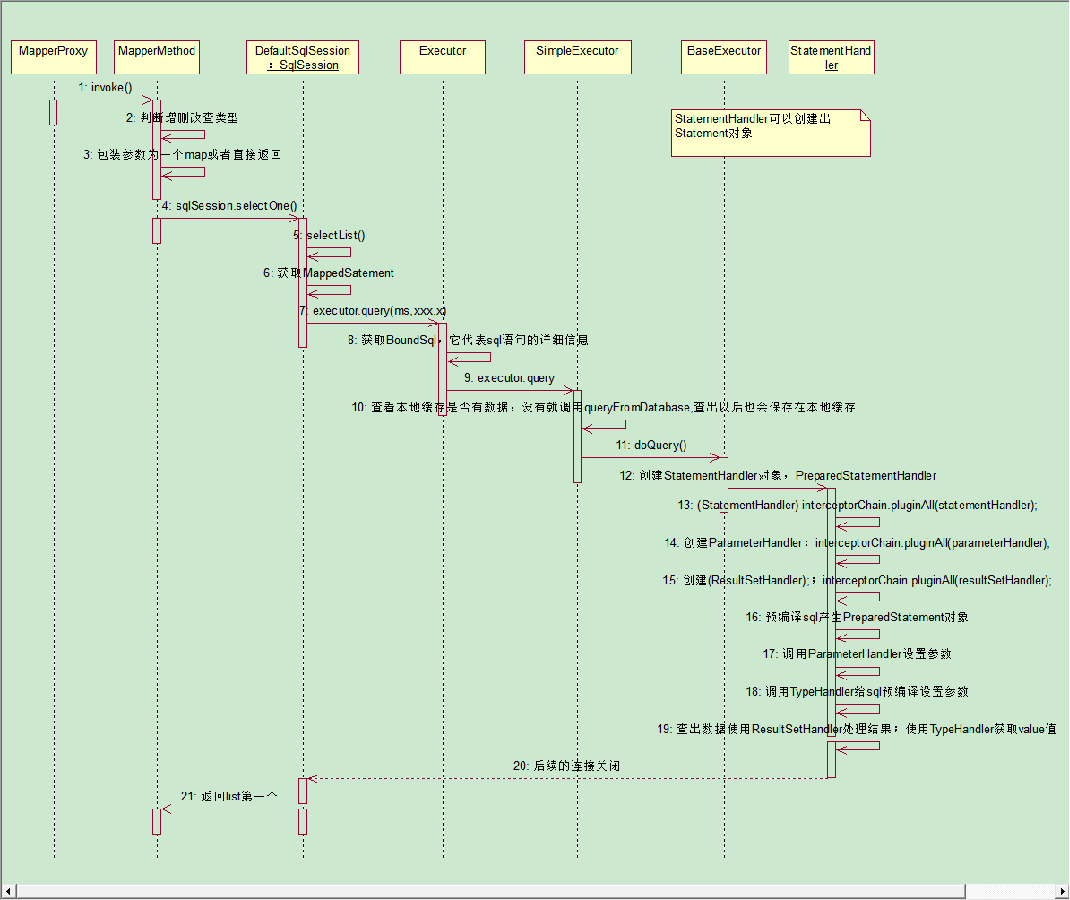
第四步,查询流程
在上一步创建代理对象的途中,底层也通过反射调用了代理对象的方法,具体流程如下


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号