java中带继承类的加载顺序详解及实战
一、背景:
在面试中,在java基础方面,类的加载顺序经常被问及,很多时候我们是搞不清楚到底类的加载顺序是怎么样的,那么今天我们就来看看带有继承的类的加载顺序到底是怎么一回事?在此记下也方便以后复习巩固!
二、测试步骤:
1.父类代码
1 package com.hafiz.zhang; 2 3 public class Fu 4 { 5 private int i = print("this is father common variable"); 6 private static int j = print("this is father static variable"); 7 static{ 8 System.out.println("this is father static code block"); 9 } 10 { 11 System.out.println("this is father common code block"); 12 } 13 public Fu(){ 14 System.out.println("this is father constructor"); 15 } 16 17 static int print(String str){ 18 System.out.println(str); 19 return 2; 20 } 21 }
2.子类代码
1 package com.hafiz.zhang; 2 3 public class Zi extends Fu 4 { 5 private int l = print("this is son common variable"); 6 private static int m = print("this is son stati variable"); 7 static{ 8 System.out.println("this is son static code block"); 9 } 10 { 11 System.out.println("this is son common code block"); 12 } 13 public Zi(){ 14 System.out.println("this is son constructor"); 15 } 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 new Zi(); 18 } 19 }
最后运行结果为:
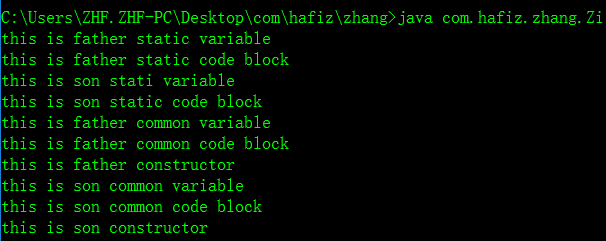
下面让我们修改一下两个类中静态代码块和静态成员变量的位置并重新运行
3.修改后的父类代码
1 package com.hafiz.zhang; 2 3 public class Fu 4 { 5 static{ 6 System.out.println("this is father static code block"); 7 } 8 { 9 System.out.println("this is father common code block"); 10 } 11 public Fu(){ 12 System.out.println("this is father constructor"); 13 } 14 15 static int print(String str){ 16 System.out.println(str); 17 return 2; 18 } 19 private int i = print("this is father common variable"); 20 private static int j = print("this is father static variable"); 21 }
4.修改后的子类代码
1 package com.hafiz.zhang; 2 3 public class Zi extends Fu 4 { 5 static{ 6 System.out.println("this is son static code block"); 7 } 8 { 9 System.out.println("this is son common code block"); 10 } 11 public Zi(){ 12 System.out.println("this is son constructor"); 13 } 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 new Zi(); 16 } 17 private int l = print("this is son common variable"); 18 private static int m = print("this is son stati variable"); 19 }
修改后的运行结果:
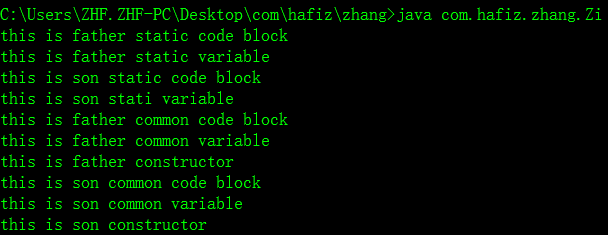
三、测试结果
由测试结果可知:程序首先加载类,然后再对类进行初始化。
加载类的顺序为:先加载基类,基类加载完毕后再加载子类。
初始化的顺序为:先初始化基类,基类初始化完毕后再初始化子类。
最后得出类加载顺序为:先按照声明顺序初始化基类静态变量和静态代码块,接着按照声明顺序初始化子类静态变量和静态代码块,而后按照声明顺序初始化基类普通变量和普通代码块,然后执行基类构造函数,接着按照声明顺序初始化子类普通变量和普通代码块,最后执行子类构造函数。
对于本测试中的执行顺序为:先初始化static的变量,在执行main()方法之前就需要进行加载。再执行main方法,如果new一个对象,则先对这个对象类的基本成员变量进行初始化(非方法),包括构造代码块,这两种是按照编写顺序按序执行的,再调用构造函数。 关于继承的初始化机制,首先执行含有main方法的类,观察到Zi类含有基类Fu,即先加载Fu类的static变量,再加载Zi类的static变量。加载完static变量之后,调用main()方法,new Zi()则先初始化基类的基本变量和构造代码块,再调用基类的构造方法。然后再初始化子类Zi的基本变量和构造代码块,再执行子类的构造函数。
感谢您花时间阅读此篇文章,如果您觉得这篇文章你学到了东西也是为了犒劳下博主的码字不易不妨打赏一下吧,让博主能喝上一杯咖啡,在此谢过了!
如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下左下角“推荐”按钮,您的将是我最大的写作动力!另外您也可以选择【关注我】,可以很方便找到我!
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,来源网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hafiz 欢迎各位转载,但是未经作者本人同意,转载文章之后必须在文章页面明显位置给出作者和原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利!





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号