Python pyQt4/PyQt5 学习笔记3(绝对对位,盒布局,网格布局)
本节研究布局管理的内容。
(一)绝对对位
import sys from PyQt4 import QtGui class Example(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self): super(Example, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): lbl1 = QtGui.QLabel('ZetCode', self) lbl1.move(15, 10) lbl2 = QtGui.QLabel('tutorials', self) lbl2.move(35, 40) lbl3 = QtGui.QLabel('for programmers', self) lbl3.move(55, 70) self.setGeometry(300, 300, 250, 150) self.setWindowTitle('Absolute') self.show() def main(): app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv) ex = Example() sys.exit(app.exec_()) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
运行效果:
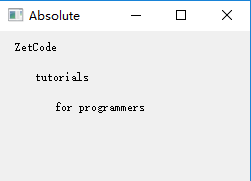
在这种方式中,编程者指定各种部件的位置和大小。但是当你使用绝对定位时,需要知道有以下的限制:
- 如果我们改变窗口的大小,部件的大小和位置并不会改变。
- 你的应用在不同平台下可能长得不太一样。
- 改变应用中使用的字体可能会扰乱布局。
- 如果我们想改变现有的布局的话,我们必须完全重写布局,这很乏味而且浪费时间。
PyQt5相同功能的例子:(macOS版本)
1 import sys 2 from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget,QApplication,QLabel 3 4 class Example(QWidget): 5 def __init__(self): 6 super(Example,self).__init__() 7 self.initui() 8 9 def initui(self): 10 lab1=QLabel('blue',self) 11 lab1.move(15,10) 12 13 lab2=QLabel('red',self) 14 lab2.move(35,40) 15 16 lab3=QLabel('green',self) 17 lab3.move(55,70) 18 19 self.setGeometry(300,300,250,150) 20 self.setWindowTitle('testSample') 21 self.show() 22 23 24 def main(): 25 app=QApplication(sys.argv) 26 ex=Example() 27 sys.exit(app.exec_()) 28 29 if __name__=='__main__': 30 main()
(二)盒布局(Box layout)
import sys from PyQt4 import QtGui class Example(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self): super(Example, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): okButton = QtGui.QPushButton("OK") cancelButton = QtGui.QPushButton("Cancel") hbox = QtGui.QHBoxLayout() hbox.addStretch(1) hbox.addWidget(okButton) hbox.addWidget(cancelButton) vbox = QtGui.QVBoxLayout() vbox.addStretch(1) vbox.addLayout(hbox) self.setLayout(vbox) self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 150) self.setWindowTitle('Buttons') self.show() def main(): app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv) ex = Example() sys.exit(app.exec_()) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
效果如下:
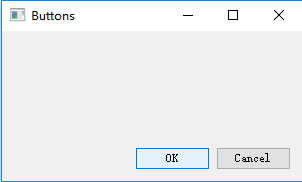
这个例子中我们将两个按钮放在了窗口的右下角。即使我们改变窗口的大小,它们也会在那个地方
相同功能的PyQt5的例子:(macOS例子)
1 import sys 2 from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QWidget,QPushButton,QHBoxLayout,QVBoxLayout 3 4 class Exaple(QWidget): 5 def __init__(self): 6 super().__init__() 7 self.initui() 8 9 def initui(self): 10 btn1=QPushButton("OK") 11 btn2=QPushButton("Cancel") 12 13 #QHBoxLayout和QVBoxLayout两个布局类。 14 #这里我们创建了一个水平箱布局,并且增加了一个拉伸因子和两个按钮。 15 # 拉伸因子在两个按钮之前增加了一个可伸缩空间。这会将按钮推到窗口的右边。 16 hbox=QHBoxLayout() 17 hbox.addStretch(1) 18 hbox.addWidget(btn1) 19 hbox.addWidget(btn2) 20 21 #我们把水平布局放置在垂直布局内。 22 # 拉伸因子将把包含两个按钮的水平箱布局推到窗口的底边。 23 vbox=QVBoxLayout() 24 vbox.addStretch(1) 25 vbox.addLayout(hbox) 26 self.setLayout(vbox) 27 28 self.setGeometry(300,300,300,150) 29 self.show() 30 31 if __name__=='__main__': 32 33 app=QApplication(sys.argv) 34 ex=Exaple() 35 sys.exit(app.exec_())
(三)网格布局
1 #网格布局演示,PyQt5,macOS的例子 2 import sys 3 from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QWidget,QGridLayout,QPushButton 4 5 class Example(QWidget): 6 def __init__(self): 7 super().__init__() 8 self.initui() 9 10 def initui(self): 11 #创建了一个全是按钮的网格布局。并且把这个类设为应用窗口的布局 12 grid=QGridLayout() 13 self.setLayout(grid) 14 15 names=['Cls', 'Bck', '', 'Close', 16 '7', '8', '9', '/', 17 '4', '5', '6', '*', 18 '1', '2', '3', '-', 19 '0', '.', '=', '+'] 20 pos=[(i,j) for i in range(5) for j in range(4)] 21 for p,name in zip(pos,names): 22 if name=='': 23 continue 24 #创建出按钮组件,并使用addWidget()方法向布局中添加按钮。 25 button=QPushButton(name) 26 grid.addWidget(button,*p) 27 28 self.move(300,150) 29 self.setWindowTitle('calc') 30 self.show() 31 32 if __name__=='__main__': 33 app=QApplication(sys.argv) 34 ex=Example() 35 sys.exit(app.exec_())
(三)一个网格布局的例子
1 import sys 2 from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget,QLabel,QLineEdit,QTextEdit,QGridLayout,QApplication) 3 4 class Exaple(QWidget): 5 def __init__(self): 6 super().__init__() 7 self.initui() 8 9 def initui(self): 10 #包含三个标签,两个单行编辑框和一个文本编辑框组件的窗口。 11 # 布局使用了QGridLayout布局 12 title=QLabel('Title') 13 author=QLabel('Author') 14 review=QLabel('Review') 15 titleEdit=QLineEdit() 16 authorEdit=QLineEdit() 17 reviewEdit=QTextEdit() 18 19 #创建了一个网格布局并且设置了组件之间的间距 20 grid=QGridLayout() 21 grid.setSpacing(10) 22 23 grid.addWidget(title,1,0) 24 grid.addWidget(titleEdit,1,1) 25 26 grid.addWidget(author,2,0) 27 grid.addWidget(authorEdit,2,1) 28 29 grid.addWidget(review,3,0) 30 #如果我们向网格布局中增加一个组件,我们可以提供组件的跨行和跨列参数。 31 # 在这个例子中,我们让reviewEdit组件跨了5行。 32 grid.addWidget(reviewEdit,3,1,5,1) 33 34 self.setLayout(grid) 35 36 self.setGeometry(300,300,300,300) 37 self.setWindowTitle('Review') 38 self.show() 39 40 if __name__=='__main__': 41 app=QApplication(sys.argv) 42 ex=Exaple() 43 sys.exit(app.exec_())



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号