MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(MQ)是一种应用程序对应用程序的通信方法。应用程序通过读写出入队列的消息(针对应用程序的数据)来通信,而无需专用连接来链接它们。消息传递指的是程序之间通过在消息中发送数据进行通信,而不是通过直接调用彼此来通信,直接调用通常是用于诸如远程过程调用的技术。排队指的是应用程序通过 队列来通信。队列的使用除去了接收和发送应用程序同时执行的要求
Linux下安装RabbitMQ
环境:Linux(CentOS 7.2)
1、安装Erlang环境,Erlang版本是21.1。参考【Erlang】源码安装
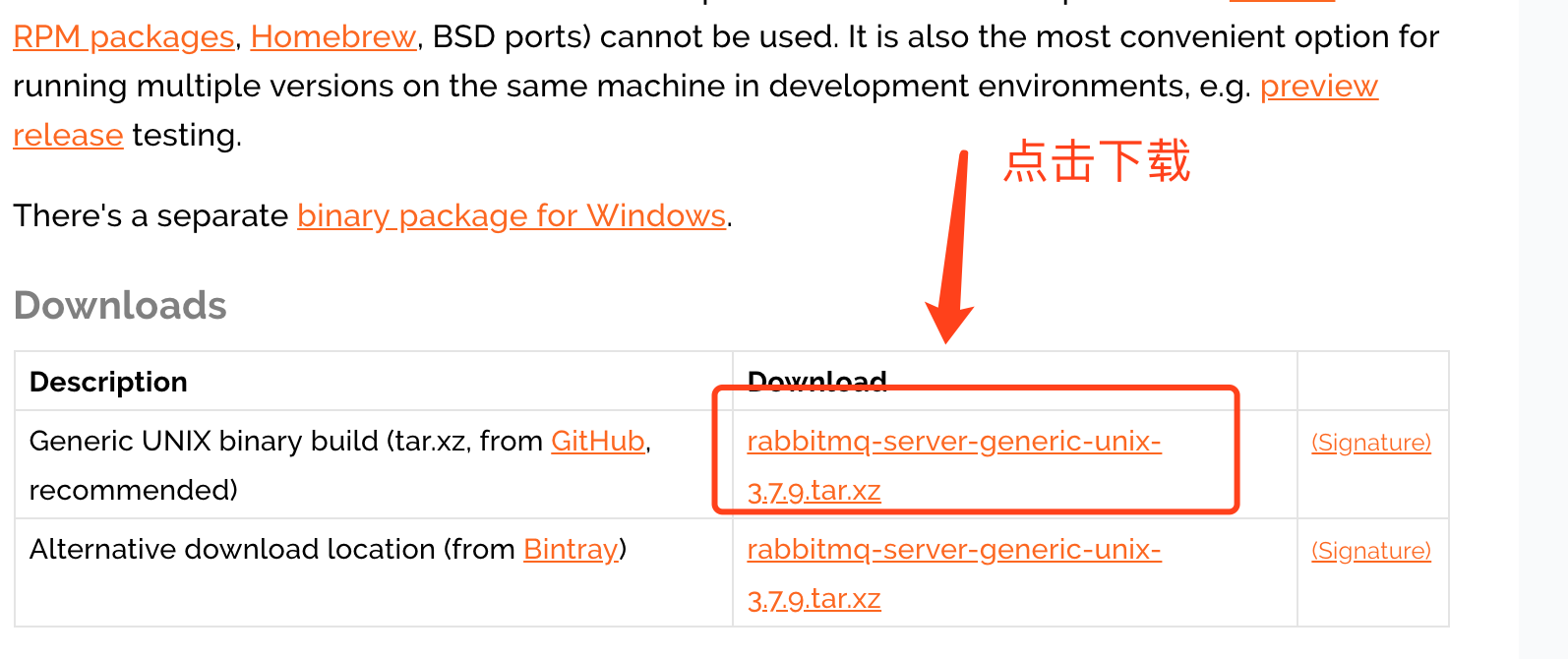
2、下载源码包(rabbitmq-server-generic-unix-3.7.9.tar.xz),版本:3.7.9
下载地址:https://www.rabbitmq.com/download.html
3、解压,命令:tar -xvf rabbitmq-server-generic-unix-3.7.9.tar.xz,解压后文件目录如下:

其中sbin目录下文件说明:
rabbitmq-env // 环境配置脚本
rabbitmq-defaults // 默认参数设置脚本
rabbitmqctl // 管理工具脚本
rabbitmq-plugins // 插件管理工具脚本
rabbitmq-server // rabbitmq服务脚本
4、可以自由拷贝解压后的文件到的制定目录,然后配置环境变量
a、编辑文件/etc/profile,命令:vim /etc/profile;增加如下内容:
1 export RABBIT_HOME=/data/soft/rabbitmq_server-3.7.9 2 export PATH=$RABBIT_HOME/sbin:$PATH
b、使环境变量生效,命令:source /etc/profile。
5、操作服务,启动默认监听端口:5672
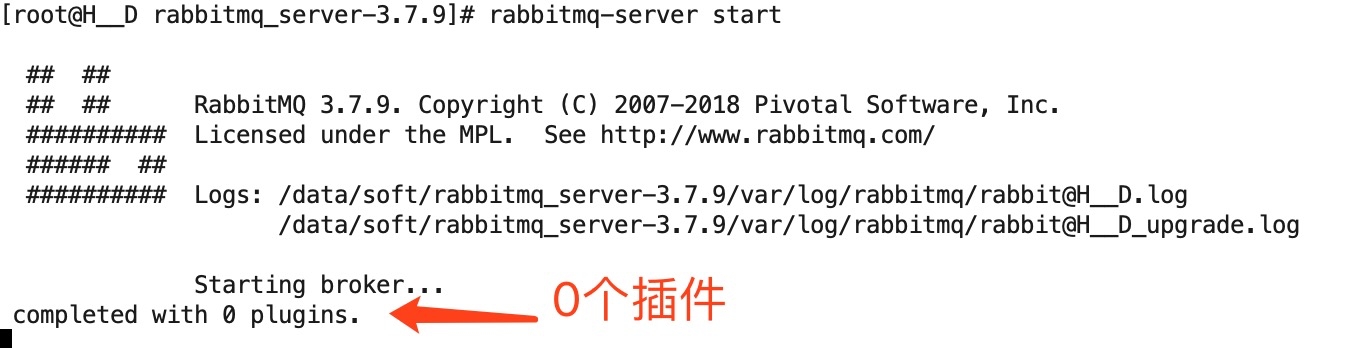
启动服务(前台启动):rabbitmq-server start
启动服务(后台启动):rabbitmq-server start -detached
重启服务:rabbitmq-server restart
关闭服务:rabbitmqctl stop
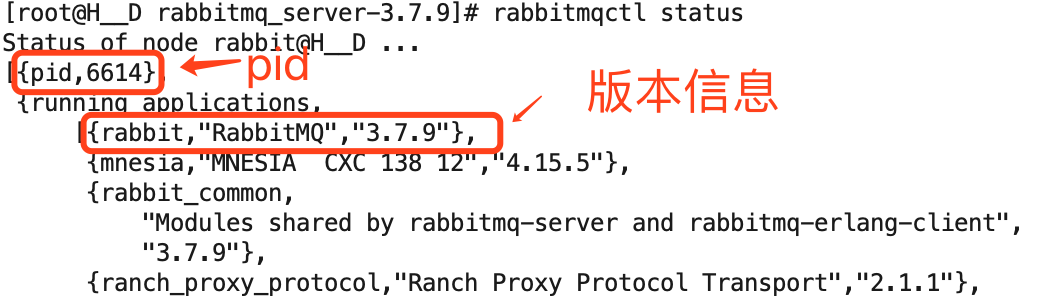
查看服务状态:rabbitmqctl status
查看mq用户:rabbitmqctl list_users
查看用户权限:rabbitmqctl list_user_permissions guest
新增用户: rabbitmqctl add_user admin 123456
赋予管理员权限:rabbitmqctl set_user_tags admin administrator
分配权限:rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / admin '.*' '.*' '.*'
效果图如下:
a、启动命令
b、查看状态
c、查看日志配置文件为空
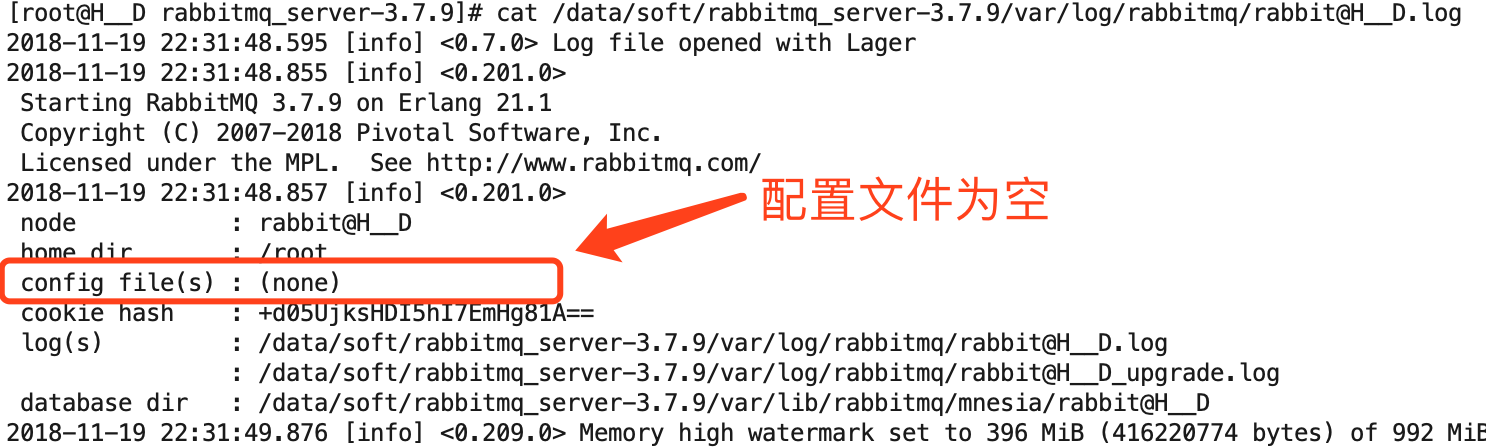
注意:a、启动报错:Error description: noproc。
解决方案:Erlang版本和RabbitMQ不支持的原因,应该安装对应版本。参考地址:https://www.rabbitmq.com/which-erlang.html
6、启用插件,RabbitMQ的web控制台,命令:rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management,然后重启RabbitMQ服务
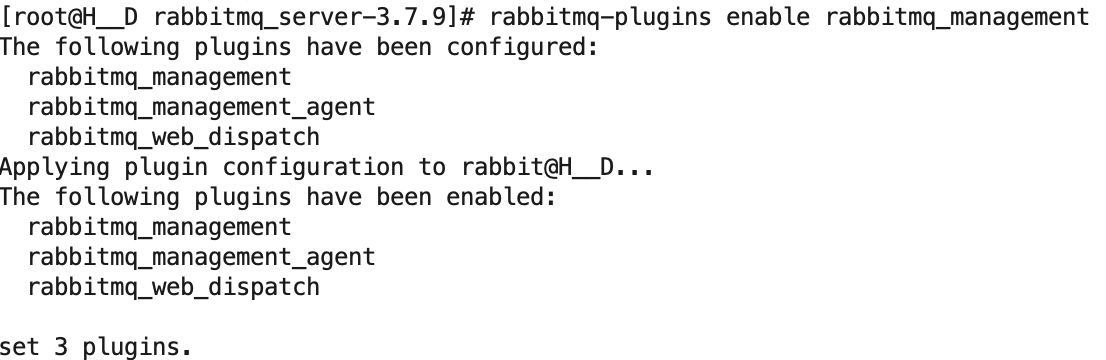
7、浏览器输入http://ip:15672,端口是15672,访问RabbitMQ的web控制台,默认用户名/密码:guest/guest。
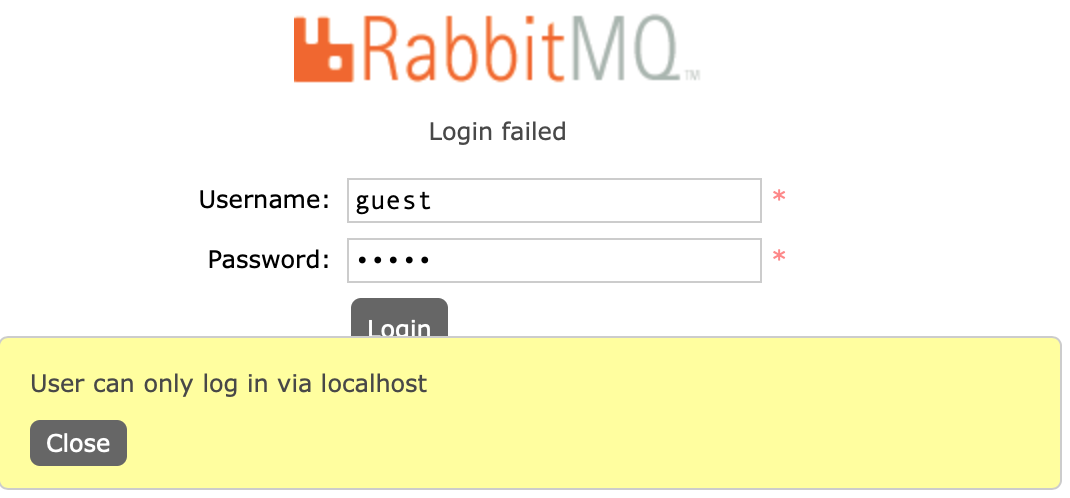
默认情况下,RabbitMQ的默认的guest用户只允许本机访问
由于不是在本机上访问报错,如下:
8、通过 find / -name rabbitmq-defaults 查找rabbitmq-defaults文件(/data/soft/rabbitmq_server-3.7.9/sbin/rabbitmq-defaults),查看config文件的存储路径
a、下载模版,配置文件模版下载:https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/blob/master/docs/rabbitmq.conf.example

1 # ====================================== 2 # RabbitMQ broker section 3 # ====================================== 4 5 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/configure.html. See 6 ## http://rabbitmq.com/documentation.html for documentation ToC. 7 8 ## Networking 9 ## ==================== 10 ## 11 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/networking.html. 12 ## 13 ## By default, RabbitMQ will listen on all interfaces, using 14 ## the standard (reserved) AMQP 0-9-1 and 1.0 port. 15 ## 16 # listeners.tcp.default = 5672 17 18 19 ## To listen on a specific interface, provide an IP address with port. 20 ## For example, to listen only on localhost for both IPv4 and IPv6: 21 ## 22 # IPv4 23 # listeners.tcp.local = 127.0.0.1:5672 24 # IPv6 25 # listeners.tcp.local_v6 = ::1:5672 26 27 ## You can define multiple listeners using listener names 28 # listeners.tcp.other_port = 5673 29 # listeners.tcp.other_ip = 10.10.10.10:5672 30 31 32 ## TLS listeners are configured in the same fashion as TCP listeners, 33 ## including the option to control the choice of interface. 34 ## 35 # listeners.ssl.default = 5671 36 37 ## Number of Erlang processes that will accept connections for the TCP 38 ## and TLS listeners. 39 ## 40 # num_acceptors.tcp = 10 41 # num_acceptors.ssl = 1 42 43 44 ## Maximum time for AMQP 0-8/0-9/0-9-1 handshake (after socket connection 45 ## and TLS handshake), in milliseconds. 46 ## 47 # handshake_timeout = 10000 48 49 ## Set to 'true' to perform reverse DNS lookups when accepting a 50 ## connection. Hostnames will then be shown instead of IP addresses 51 ## in rabbitmqctl and the management plugin. 52 ## 53 # reverse_dns_lookups = true 54 55 ## 56 ## Security, Access Control 57 ## ============== 58 ## 59 60 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html. 61 62 ## The default "guest" user is only permitted to access the server 63 ## via a loopback interface (e.g. localhost). 64 ## {loopback_users, [<<"guest">>]}, 65 ## 66 # loopback_users.guest = true 67 68 ## Uncomment the following line if you want to allow access to the 69 ## guest user from anywhere on the network. 70 # loopback_users.guest = false 71 72 ## TLS configuration. 73 ## 74 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/ssl.html. 75 ## 76 # ssl_options.verify = verify_peer 77 # ssl_options.fail_if_no_peer_cert = false 78 # ssl_options.cacertfile = /path/to/cacert.pem 79 # ssl_options.certfile = /path/to/cert.pem 80 # ssl_options.keyfile = /path/to/key.pem 81 # 82 # ssl_options.honor_cipher_order = true 83 # ssl_options.honor_ecc_order = true 84 85 # ssl_options.ciphers.1 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 86 # ssl_options.ciphers.2 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 87 # ssl_options.ciphers.3 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384 88 # ssl_options.ciphers.4 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384 89 # ssl_options.ciphers.5 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 90 # ssl_options.ciphers.6 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 91 # ssl_options.ciphers.7 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384 92 # ssl_options.ciphers.8 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-SHA384 93 # ssl_options.ciphers.9 = DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 94 # ssl_options.ciphers.10 = DHE-DSS-AES256-GCM-SHA384 95 # ssl_options.ciphers.11 = DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256 96 # ssl_options.ciphers.12 = DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA256 97 # ssl_options.ciphers.13 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 98 # ssl_options.ciphers.14 = ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 99 # ssl_options.ciphers.15 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256 100 # ssl_options.ciphers.16 = ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256 101 # ssl_options.ciphers.17 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 102 # ssl_options.ciphers.18 = ECDH-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 103 # ssl_options.ciphers.19 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256 104 # ssl_options.ciphers.20 = ECDH-RSA-AES128-SHA256 105 # ssl_options.ciphers.21 = DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256 106 # ssl_options.ciphers.22 = DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256 107 # ssl_options.ciphers.23 = DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256 108 # ssl_options.ciphers.24 = DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256 109 # ssl_options.ciphers.25 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA 110 # ssl_options.ciphers.26 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA 111 # ssl_options.ciphers.27 = DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA 112 # ssl_options.ciphers.28 = DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA 113 # ssl_options.ciphers.29 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-SHA 114 # ssl_options.ciphers.30 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-SHA 115 # ssl_options.ciphers.31 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA 116 # ssl_options.ciphers.32 = ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA 117 # ssl_options.ciphers.33 = DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA 118 # ssl_options.ciphers.34 = DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA 119 # ssl_options.ciphers.35 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES128-SHA 120 # ssl_options.ciphers.36 = ECDH-RSA-AES128-SHA 121 122 ## Select an authentication/authorisation backend to use. 123 ## 124 ## Alternative backends are provided by plugins, such as rabbitmq-auth-backend-ldap. 125 ## 126 ## NB: These settings require certain plugins to be enabled. 127 ## 128 ## Related doc guides: 129 ## 130 ## * http://rabbitmq.com/plugins.html 131 ## * http://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html 132 ## 133 134 # auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_internal 135 136 ## uses separate backends for authentication and authorisation, 137 ## see below. 138 # auth_backends.1.authn = rabbit_auth_backend_ldap 139 # auth_backends.1.authz = rabbit_auth_backend_internal 140 141 ## The rabbitmq_auth_backend_ldap plugin allows the broker to 142 ## perform authentication and authorisation by deferring to an 143 ## external LDAP server. 144 ## 145 ## Relevant doc guides: 146 ## 147 ## * http://rabbitmq.com/ldap.html 148 ## * http://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html 149 ## 150 ## uses LDAP for both authentication and authorisation 151 # auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_ldap 152 153 ## uses HTTP service for both authentication and 154 ## authorisation 155 # auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_http 156 157 ## uses two backends in a chain: HTTP first, then internal 158 # auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_http 159 # auth_backends.2 = rabbit_auth_backend_internal 160 161 ## Authentication 162 ## The built-in mechanisms are 'PLAIN', 163 ## 'AMQPLAIN', and 'EXTERNAL' Additional mechanisms can be added via 164 ## plugins. 165 ## 166 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/authentication.html. 167 ## 168 # auth_mechanisms.1 = PLAIN 169 # auth_mechanisms.2 = AMQPLAIN 170 171 ## The rabbitmq-auth-mechanism-ssl plugin makes it possible to 172 ## authenticate a user based on the client's x509 (TLS) certificate. 173 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/authentication.html. 174 ## 175 ## To use auth-mechanism-ssl, the EXTERNAL mechanism should 176 ## be enabled: 177 ## 178 # auth_mechanisms.1 = PLAIN 179 # auth_mechanisms.2 = AMQPLAIN 180 # auth_mechanisms.3 = EXTERNAL 181 182 ## To force x509 certificate-based authentication on all clients, 183 ## exclude all other mechanisms (note: this will disable password-based 184 ## authentication even for the management UI!): 185 ## 186 # auth_mechanisms.1 = EXTERNAL 187 188 ## This pertains to both the rabbitmq-auth-mechanism-ssl plugin and 189 ## STOMP ssl_cert_login configurations. See the RabbitMQ STOMP plugin 190 ## configuration section later in this file and the README in 191 ## https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-auth-mechanism-ssl for further 192 ## details. 193 ## 194 ## To use the TLS cert's CN instead of its DN as the username 195 ## 196 # ssl_cert_login_from = common_name 197 198 ## TLS handshake timeout, in milliseconds. 199 ## 200 # ssl_handshake_timeout = 5000 201 202 203 ## Password hashing implementation. Will only affect newly 204 ## created users. To recalculate hash for an existing user 205 ## it's necessary to update her password. 206 ## 207 ## To use SHA-512, set to rabbit_password_hashing_sha512. 208 ## 209 # password_hashing_module = rabbit_password_hashing_sha256 210 211 ## When importing definitions exported from versions earlier 212 ## than 3.6.0, it is possible to go back to MD5 (only do this 213 ## as a temporary measure!) by setting this to rabbit_password_hashing_md5. 214 ## 215 # password_hashing_module = rabbit_password_hashing_md5 216 217 ## 218 ## Default User / VHost 219 ## ==================== 220 ## 221 222 ## On first start RabbitMQ will create a vhost and a user. These 223 ## config items control what gets created. 224 ## Relevant doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html 225 ## 226 # default_vhost = / 227 # default_user = guest 228 # default_pass = guest 229 230 # default_permissions.configure = .* 231 # default_permissions.read = .* 232 # default_permissions.write = .* 233 234 ## Tags for default user 235 ## 236 ## For more details about tags, see the documentation for the 237 ## Management Plugin at http://rabbitmq.com/management.html. 238 ## 239 # default_user_tags.administrator = true 240 241 ## Define other tags like this: 242 # default_user_tags.management = true 243 # default_user_tags.custom_tag = true 244 245 ## 246 ## Additional network and protocol related configuration 247 ## ===================================================== 248 ## 249 250 ## Set the default AMQP 0-9-1 heartbeat interval (in seconds). 251 ## Related doc guides: 252 ## 253 ## * http://rabbitmq.com/heartbeats.html 254 ## * http://rabbitmq.com/networking.html 255 ## 256 # heartbeat = 60 257 258 ## Set the max permissible size of an AMQP frame (in bytes). 259 ## 260 # frame_max = 131072 261 262 ## Set the max frame size the server will accept before connection 263 ## tuning occurs 264 ## 265 # initial_frame_max = 4096 266 267 ## Set the max permissible number of channels per connection. 268 ## 0 means "no limit". 269 ## 270 # channel_max = 128 271 272 ## Customising TCP Listener (Socket) Configuration. 273 ## 274 ## Related doc guides: 275 ## 276 ## * http://rabbitmq.com/networking.html 277 ## * http://www.erlang.org/doc/man/inet.html#setopts-2 278 ## 279 280 # tcp_listen_options.backlog = 128 281 # tcp_listen_options.nodelay = true 282 # tcp_listen_options.exit_on_close = false 283 # 284 # tcp_listen_options.keepalive = true 285 # tcp_listen_options.send_timeout = 15000 286 # 287 # tcp_listen_options.buffer = 196608 288 # tcp_listen_options.sndbuf = 196608 289 # tcp_listen_options.recbuf = 196608 290 291 ## 292 ## Resource Limits & Flow Control 293 ## ============================== 294 ## 295 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/memory.html. 296 297 ## Memory-based Flow Control threshold. 298 ## 299 # vm_memory_high_watermark.relative = 0.4 300 301 ## Alternatively, we can set a limit (in bytes) of RAM used by the node. 302 ## 303 # vm_memory_high_watermark.absolute = 1073741824 304 305 ## Or you can set absolute value using memory units (with RabbitMQ 3.6.0+). 306 ## Absolute watermark will be ignored if relative is defined! 307 ## 308 # vm_memory_high_watermark.absolute = 2GB 309 ## 310 ## Supported units suffixes: 311 ## 312 ## kb, KB: kibibytes (2^10 bytes) 313 ## mb, MB: mebibytes (2^20) 314 ## gb, GB: gibibytes (2^30) 315 316 317 318 ## Fraction of the high watermark limit at which queues start to 319 ## page message out to disc in order to free up memory. 320 ## For example, when vm_memory_high_watermark is set to 0.4 and this value is set to 0.5, 321 ## paging can begin as early as when 20% of total available RAM is used by the node. 322 ## 323 ## Values greater than 1.0 can be dangerous and should be used carefully. 324 ## 325 ## One alternative to this is to use durable queues and publish messages 326 ## as persistent (delivery mode = 2). With this combination queues will 327 ## move messages to disk much more rapidly. 328 ## 329 ## Another alternative is to configure queues to page all messages (both 330 ## persistent and transient) to disk as quickly 331 ## as possible, see http://rabbitmq.com/lazy-queues.html. 332 ## 333 # vm_memory_high_watermark_paging_ratio = 0.5 334 335 ## Selects Erlang VM memory consumption calculation strategy. Can be `allocated`, `rss` or `legacy` (aliased as `erlang`), 336 ## Introduced in 3.6.11. `rss` is the default as of 3.6.12. 337 ## See https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/issues/1223 and rabbitmq/rabbitmq-common#224 for background. 338 # vm_memory_calculation_strategy = rss 339 340 ## Interval (in milliseconds) at which we perform the check of the memory 341 ## levels against the watermarks. 342 ## 343 # memory_monitor_interval = 2500 344 345 ## The total memory available can be calculated from the OS resources 346 ## - default option - or provided as a configuration parameter. 347 # total_memory_available_override_value = 2GB 348 349 ## Set disk free limit (in bytes). Once free disk space reaches this 350 ## lower bound, a disk alarm will be set - see the documentation 351 ## listed above for more details. 352 ## 353 ## Absolute watermark will be ignored if relative is defined! 354 # disk_free_limit.absolute = 50000 355 356 ## Or you can set it using memory units (same as in vm_memory_high_watermark) 357 ## with RabbitMQ 3.6.0+. 358 # disk_free_limit.absolute = 500KB 359 # disk_free_limit.absolute = 50mb 360 # disk_free_limit.absolute = 5GB 361 362 ## Alternatively, we can set a limit relative to total available RAM. 363 ## 364 ## Values lower than 1.0 can be dangerous and should be used carefully. 365 # disk_free_limit.relative = 2.0 366 367 ## 368 ## Clustering 369 ## ===================== 370 ## 371 # cluster_partition_handling = ignore 372 373 ## pause_if_all_down strategy require additional configuration 374 # cluster_partition_handling = pause_if_all_down 375 376 ## Recover strategy. Can be either 'autoheal' or 'ignore' 377 # cluster_partition_handling.pause_if_all_down.recover = ignore 378 379 ## Node names to check 380 # cluster_partition_handling.pause_if_all_down.nodes.1 = rabbit@localhost 381 # cluster_partition_handling.pause_if_all_down.nodes.2 = hare@localhost 382 383 ## Mirror sync batch size, in messages. Increasing this will speed 384 ## up syncing but total batch size in bytes must not exceed 2 GiB. 385 ## Available in RabbitMQ 3.6.0 or later. 386 ## 387 # mirroring_sync_batch_size = 4096 388 389 ## Make clustering happen *automatically* at startup. Only applied 390 ## to nodes that have just been reset or started for the first time. 391 ## 392 ## Relevant doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com//cluster-formation.html 393 ## 394 395 # cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_classic_config 396 # 397 # cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.1 = rabbit1@hostname 398 # cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.2 = rabbit2@hostname 399 # cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.3 = rabbit3@hostname 400 # cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.4 = rabbit4@hostname 401 402 ## DNS-based peer discovery. This backend will list A records 403 ## of the configured hostname and perform reverse lookups for 404 ## the addresses returned. 405 406 # cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_dns 407 # cluster_formation.dns.hostname = discovery.eng.example.local 408 409 ## This node's type can be configured. If you are not sure 410 ## what node type to use, always use 'disc'. 411 # cluster_formation.node_type = disc 412 413 ## Interval (in milliseconds) at which we send keepalive messages 414 ## to other cluster members. Note that this is not the same thing 415 ## as net_ticktime; missed keepalive messages will not cause nodes 416 ## to be considered down. 417 ## 418 # cluster_keepalive_interval = 10000 419 420 ## 421 ## Statistics Collection 422 ## ===================== 423 ## 424 425 ## Set (internal) statistics collection granularity. 426 ## 427 ## Can be none, coarse or fine 428 # collect_statistics = none 429 430 # collect_statistics = coarse 431 432 ## Statistics collection interval (in milliseconds). Increasing 433 ## this will reduce the load on management database. 434 ## 435 # collect_statistics_interval = 5000 436 437 ## 438 ## Misc/Advanced Options 439 ## ===================== 440 ## 441 ## NB: Change these only if you understand what you are doing! 442 ## 443 444 ## Explicitly enable/disable hipe compilation. 445 ## 446 # hipe_compile = false 447 448 ## Timeout used when waiting for Mnesia tables in a cluster to 449 ## become available. 450 ## 451 # mnesia_table_loading_retry_timeout = 30000 452 453 ## Retries when waiting for Mnesia tables in the cluster startup. Note that 454 ## this setting is not applied to Mnesia upgrades or node deletions. 455 ## 456 # mnesia_table_loading_retry_limit = 10 457 458 ## Size in bytes below which to embed messages in the queue index. 459 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/persistence-conf.html 460 ## 461 # queue_index_embed_msgs_below = 4096 462 463 ## You can also set this size in memory units 464 ## 465 # queue_index_embed_msgs_below = 4kb 466 467 ## Whether or not to enable background periodic forced GC runs for all 468 ## Erlang processes on the node in "waiting" state. 469 ## 470 ## Disabling background GC may reduce latency for client operations, 471 ## keeping it enabled may reduce median RAM usage by the binary heap 472 ## (see https://www.erlang-solutions.com/blog/erlang-garbage-collector.html). 473 ## 474 ## Before trying this option, please take a look at the memory 475 ## breakdown (http://www.rabbitmq.com/memory-use.html). 476 ## 477 # background_gc_enabled = false 478 479 ## Target (desired) interval (in milliseconds) at which we run background GC. 480 ## The actual interval will vary depending on how long it takes to execute 481 ## the operation (can be higher than this interval). Values less than 482 ## 30000 milliseconds are not recommended. 483 ## 484 # background_gc_target_interval = 60000 485 486 ## Whether or not to enable proxy protocol support. 487 ## Once enabled, clients cannot directly connect to the broker 488 ## anymore. They must connect through a load balancer that sends the 489 ## proxy protocol header to the broker at connection time. 490 ## This setting applies only to AMQP clients, other protocols 491 ## like MQTT or STOMP have their own setting to enable proxy protocol. 492 ## See the plugins documentation for more information. 493 ## 494 # proxy_protocol = false 495 496 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 497 ## Advanced Erlang Networking/Clustering Options. 498 ## 499 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/clustering.html 500 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 501 502 # ====================================== 503 # Kernel section 504 # ====================================== 505 506 # net_ticktime = 60 507 508 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 509 ## RabbitMQ Management Plugin 510 ## 511 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/management.html. 512 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 513 514 # ======================================= 515 # Management section 516 # ======================================= 517 518 ## Preload schema definitions from the following JSON file. 519 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/management.html#load-definitions. 520 ## 521 # management.load_definitions = /path/to/exported/definitions.json 522 523 ## Log all requests to the management HTTP API to a file. 524 ## 525 # management.http_log_dir = /path/to/access.log 526 527 ## Change the port on which the HTTP listener listens, 528 ## specifying an interface for the web server to bind to. 529 ## Also set the listener to use TLS and provide TLS options. 530 ## 531 532 # management.listener.port = 15672 533 # management.listener.ip = 127.0.0.1 534 # management.listener.ssl = true 535 536 # management.listener.ssl_opts.cacertfile = /path/to/cacert.pem 537 # management.listener.ssl_opts.certfile = /path/to/cert.pem 538 # management.listener.ssl_opts.keyfile = /path/to/key.pem 539 540 ## One of 'basic', 'detailed' or 'none'. See 541 ## http://rabbitmq.com/management.html#fine-stats for more details. 542 # management.rates_mode = basic 543 544 ## Configure how long aggregated data (such as message rates and queue 545 ## lengths) is retained. Please read the plugin's documentation in 546 ## http://rabbitmq.com/management.html#configuration for more 547 ## details. 548 ## Your can use 'minute', 'hour' and 'day' keys or integer key (in seconds) 549 # management.sample_retention_policies.global.minute = 5 550 # management.sample_retention_policies.global.hour = 60 551 # management.sample_retention_policies.global.day = 1200 552 553 # management.sample_retention_policies.basic.minute = 5 554 # management.sample_retention_policies.basic.hour = 60 555 556 # management.sample_retention_policies.detailed.10 = 5 557 558 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 559 ## RabbitMQ Shovel Plugin 560 ## 561 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/shovel.html 562 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 563 564 ## See advanced.config.example for a Shovel plugin example 565 566 567 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 568 ## RabbitMQ STOMP Plugin 569 ## 570 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/stomp.html 571 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 572 573 # ======================================= 574 # STOMP section 575 # ======================================= 576 577 ## Network Configuration. The format is generally the same as for the core broker. 578 ## 579 # stomp.listeners.tcp.default = 61613 580 581 ## Same for ssl listeners 582 ## 583 # stomp.listeners.ssl.default = 61614 584 585 ## Number of Erlang processes that will accept connections for the TCP 586 ## and TLS listeners. 587 ## 588 # stomp.num_acceptors.tcp = 10 589 # stomp.num_acceptors.ssl = 1 590 591 ## Additional TLS options 592 593 ## Extract a name from the client's certificate when using TLS. 594 ## 595 # stomp.ssl_cert_login = true 596 597 ## Set a default user name and password. This is used as the default login 598 ## whenever a CONNECT frame omits the login and passcode headers. 599 ## 600 ## Please note that setting this will allow clients to connect without 601 ## authenticating! 602 ## 603 # stomp.default_user = guest 604 # stomp.default_pass = guest 605 606 ## If a default user is configured, or you have configured use TLS client 607 ## certificate based authentication, you can choose to allow clients to 608 ## omit the CONNECT frame entirely. If set to true, the client is 609 ## automatically connected as the default user or user supplied in the 610 ## TLS certificate whenever the first frame sent on a session is not a 611 ## CONNECT frame. 612 ## 613 # stomp.implicit_connect = true 614 615 ## Whether or not to enable proxy protocol support. 616 ## Once enabled, clients cannot directly connect to the broker 617 ## anymore. They must connect through a load balancer that sends the 618 ## proxy protocol header to the broker at connection time. 619 ## This setting applies only to STOMP clients, other protocols 620 ## like MQTT or AMQP have their own setting to enable proxy protocol. 621 ## See the plugins or broker documentation for more information. 622 ## 623 # stomp.proxy_protocol = false 624 625 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 626 ## RabbitMQ MQTT Adapter 627 ## 628 ## See https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-mqtt/blob/stable/README.md 629 ## for details 630 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 631 632 # ======================================= 633 # MQTT section 634 # ======================================= 635 636 ## Set the default user name and password used for anonymous connections (when client 637 ## provides no credentials). Anonymous connections are highly discouraged! 638 ## 639 # mqtt.default_user = guest 640 # mqtt.default_pass = guest 641 642 ## Enable anonymous connections. If this is set to false, clients MUST provide 643 ## credentials in order to connect. See also the mqtt.default_user/mqtt.default_pass 644 ## keys. Anonymous connections are highly discouraged! 645 ## 646 # mqtt.allow_anonymous = true 647 648 ## If you have multiple vhosts, specify the one to which the 649 ## adapter connects. 650 ## 651 # mqtt.vhost = / 652 653 ## Specify the exchange to which messages from MQTT clients are published. 654 ## 655 # mqtt.exchange = amq.topic 656 657 ## Specify TTL (time to live) to control the lifetime of non-clean sessions. 658 ## 659 # mqtt.subscription_ttl = 1800000 660 661 ## Set the prefetch count (governing the maximum number of unacknowledged 662 ## messages that will be delivered). 663 ## 664 # mqtt.prefetch = 10 665 666 ## TCP/SSL Configuration (as per the broker configuration). 667 ## 668 # mqtt.listeners.tcp.default = 1883 669 670 ## Same for ssl listener 671 ## 672 # mqtt.listeners.ssl.default = 1884 673 674 ## Number of Erlang processes that will accept connections for the TCP 675 ## and TLS listeners. 676 ## 677 # mqtt.num_acceptors.tcp = 10 678 # mqtt.num_acceptors.ssl = 10 679 680 ## TCP listener options (as per the broker configuration). 681 ## 682 # mqtt.tcp_listen_options.backlog = 128 683 # mqtt.tcp_listen_options.nodelay = true 684 685 ## Whether or not to enable proxy protocol support. 686 ## Once enabled, clients cannot directly connect to the broker 687 ## anymore. They must connect through a load balancer that sends the 688 ## proxy protocol header to the broker at connection time. 689 ## This setting applies only to STOMP clients, other protocols 690 ## like STOMP or AMQP have their own setting to enable proxy protocol. 691 ## See the plugins or broker documentation for more information. 692 ## 693 # mqtt.proxy_protocol = false 694 695 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 696 ## RabbitMQ AMQP 1.0 Support 697 ## 698 ## See https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-amqp1.0/blob/stable/README.md. 699 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 700 701 # ======================================= 702 # AMQP 1.0 section 703 # ======================================= 704 705 706 ## Connections that are not authenticated with SASL will connect as this 707 ## account. See the README for more information. 708 ## 709 ## Please note that setting this will allow clients to connect without 710 ## authenticating! 711 ## 712 # amqp1_0.default_user = guest 713 714 ## Enable protocol strict mode. See the README for more information. 715 ## 716 # amqp1_0.protocol_strict_mode = false 717 718 ## Logging settings. 719 ## 720 ## See http://rabbitmq.com/logging.html and https://github.com/erlang-lager/lager for details. 721 ## 722 723 ## Log direcrory, taken from the RABBITMQ_LOG_BASE env variable by default. 724 ## 725 # log.dir = /var/log/rabbitmq 726 727 ## Logging to file. Can be false or a filename. 728 ## Default: 729 # log.file = rabbit.log 730 731 ## To disable logging to a file 732 # log.file = false 733 734 ## Log level for file logging 735 ## 736 # log.file.level = info 737 738 ## File rotation config. No rotation by default. 739 ## DO NOT SET rotation date to ''. Leave the value unset if "" is the desired value 740 # log.file.rotation.date = $D0 741 # log.file.rotation.size = 0 742 743 ## Logging to console (can be true or false) 744 ## 745 # log.console = false 746 747 ## Log level for console logging 748 ## 749 # log.console.level = info 750 751 ## Logging to the amq.rabbitmq.log exchange (can be true or false) 752 ## 753 # log.exchange = false 754 755 ## Log level to use when logging to the amq.rabbitmq.log exchange 756 ## 757 # log.exchange.level = info 758 759 760 761 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 762 ## RabbitMQ LDAP Plugin 763 ## 764 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/ldap.html. 765 ## 766 ## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 767 768 # ======================================= 769 # LDAP section 770 # ======================================= 771 772 ## 773 ## Connecting to the LDAP server(s) 774 ## ================================ 775 ## 776 777 ## Specify servers to bind to. You *must* set this in order for the plugin 778 ## to work properly. 779 ## 780 # auth_ldap.servers.1 = your-server-name-goes-here 781 782 ## You can define multiple servers 783 # auth_ldap.servers.2 = your-other-server 784 785 ## Connect to the LDAP server using TLS 786 ## 787 # auth_ldap.use_ssl = false 788 789 ## Specify the LDAP port to connect to 790 ## 791 # auth_ldap.port = 389 792 793 ## LDAP connection timeout, in milliseconds or 'infinity' 794 ## 795 # auth_ldap.timeout = infinity 796 797 ## Or number 798 # auth_ldap.timeout = 500 799 800 ## Enable logging of LDAP queries. 801 ## One of 802 ## - false (no logging is performed) 803 ## - true (verbose logging of the logic used by the plugin) 804 ## - network (as true, but additionally logs LDAP network traffic) 805 ## 806 ## Defaults to false. 807 ## 808 # auth_ldap.log = false 809 810 ## Also can be true or network 811 # auth_ldap.log = true 812 # auth_ldap.log = network 813 814 ## 815 ## Authentication 816 ## ============== 817 ## 818 819 ## Pattern to convert the username given through AMQP to a DN before 820 ## binding 821 ## 822 # auth_ldap.user_dn_pattern = cn=${username},ou=People,dc=example,dc=com 823 824 ## Alternatively, you can convert a username to a Distinguished 825 ## Name via an LDAP lookup after binding. See the documentation for 826 ## full details. 827 828 ## When converting a username to a dn via a lookup, set these to 829 ## the name of the attribute that represents the user name, and the 830 ## base DN for the lookup query. 831 ## 832 # auth_ldap.dn_lookup_attribute = userPrincipalName 833 # auth_ldap.dn_lookup_base = DC=gopivotal,DC=com 834 835 ## Controls how to bind for authorisation queries and also to 836 ## retrieve the details of users logging in without presenting a 837 ## password (e.g., SASL EXTERNAL). 838 ## One of 839 ## - as_user (to bind as the authenticated user - requires a password) 840 ## - anon (to bind anonymously) 841 ## - {UserDN, Password} (to bind with a specified user name and password) 842 ## 843 ## Defaults to 'as_user'. 844 ## 845 # auth_ldap.other_bind = as_user 846 847 ## Or can be more complex: 848 # auth_ldap.other_bind.user_dn = User 849 # auth_ldap.other_bind.password = Password 850 851 ## If user_dn and password defined - other options is ignored. 852 853 # ----------------------------- 854 # Too complex section of LDAP 855 # ----------------------------- 856 857 ## 858 ## Authorisation 859 ## ============= 860 ## 861 862 ## The LDAP plugin can perform a variety of queries against your 863 ## LDAP server to determine questions of authorisation. 864 ## 865 ## Related doc guide: http://rabbitmq.com/ldap.html#authorisation. 866 867 ## Following configuration should be defined in additional.config file 868 ## DO NOT UNCOMMENT THIS LINES! 869 870 ## Set the query to use when determining vhost access 871 ## 872 ## {vhost_access_query, {in_group, 873 ## "ou=${vhost}-users,ou=vhosts,dc=example,dc=com"}}, 874 875 ## Set the query to use when determining resource (e.g., queue) access 876 ## 877 ## {resource_access_query, {constant, true}}, 878 879 ## Set queries to determine which tags a user has 880 ## 881 ## {tag_queries, []} 882 # ]}, 883 # -----------------------------
rabbitmq-defaults文件内容如下:
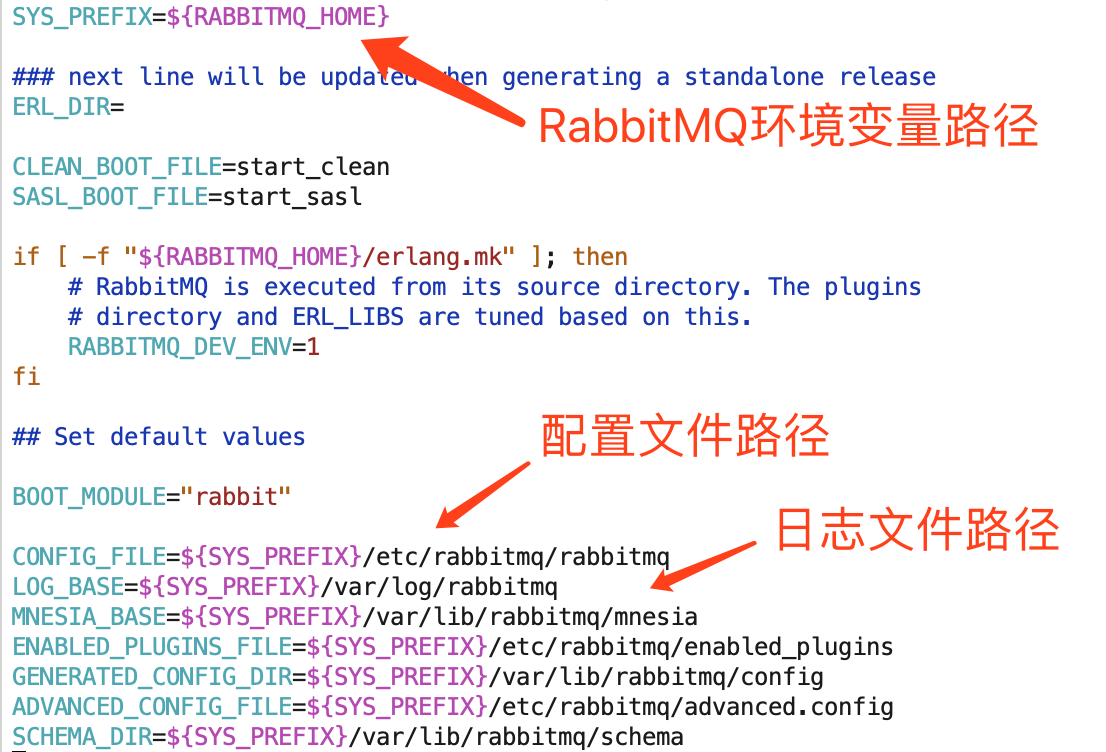
b、RABBITMQ_HOME是环境变量的位置,由上看出配置文件是/data/soft/rabbitmq_server-3.7.9/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf(注意是rabbitmq.conf,不是rabbitmq,不知道为啥rabbitmq-defaults是rabbitmq),将模版改名为rabbitmq.conf,放入/data/soft/rabbitmq_server-3.7.9/etc/rabbitmq/下
c、在配置文件rabbitmq.conf中,增加内容或去掉注,改成为
1 loopback_users.guest = false
9、修改配置文件后重新启动RabbitMQ服务,浏览器输入http://ip:15672,进入web控制台。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号