android JSON解析之JSONObject与GSON
推荐阅读
TensorFlow 2.0 (八) - 强化学习 DQN 玩转 gym Mountain Car
TensorFlow 2.0 (七) - 强化学习 Q-Learning 玩转 OpenAI gym
TensorFlow 2.0 (六) - 监督学习玩转 OpenAI gym game
TensorFlow 2.0 (五) - mnist手写数字识别(CNN卷积神经网络)
TensorFlow入门(四) - mnist手写数字识别(制作h5py训练集)
TensorFlow入门(三) - mnist手写数字识别(可视化训练)
TensorFlow入门(二) - mnist手写数字识别(模型保存加载)
TensorFlow入门(一) - mnist手写数字识别(网络搭建)
1.写在前面
JSON数据是android网络开发中常见的数据格式,JSON最常见的传输方法是使用HTTP协议,关于android开发中HTTP协议的使用方法可参考我的另一篇随笔android网络编程之HTTP,解析JSON数据有多种方法:
- 使用官方自带JSONObject
- 使用第三方开源库,包括但不限于
GSON、FastJSON、Jackson,本文主要介绍由Google提供的GSON库的使用方法。
2.JSONObject的使用方法
2.1 示例代码
//org.json.JSONArray;
//org.json.JSONObject;
private void parseJSONWithJSONObject(String jsonData){
try {
//将json字符串jsonData装入JSON数组,即JSONArray
//jsonData可以是从文件中读取,也可以从服务器端获得
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray(jsonData);
for (int i = 0; i< jsonArray.length(); i++) {
//循环遍历,依次取出JSONObject对象
//用getInt和getString方法取出对应键值
JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
int stu_no = jsonObject.getInt("stu_no");
String stu_name = jsonObject.getString("stu_name");
String stu_sex = jsonObject.getString("stu_sex");
Log.d("MainActivity","stu_no: " + stu_no);
Log.d("MainActivity","stu_name: " + stu_name);
Log.d("MainActivity","stu_sex: " + stu_sex);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
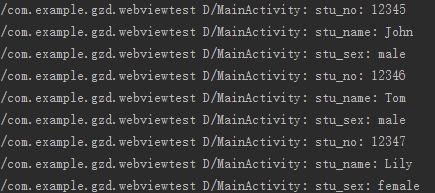
2.2 字符串jsonData如下,图为运行结果
[{ "stu_no":12345,"stu_name":"John","stu_sex":"male"
},{ "stu_no":12346,"stu_name":"Tom","stu_sex":"male"
},{"stu_no":12347,"stu_name":"Lily","stu_sex":"female"}]
3.GSON的使用方法
3.1 下载并安装
- GSON2.6.1下载地址,点击即可下载。
- 将下载的gson-2.6.1.jar复制到
项目目录->app->libs文件夹下
3.2 方法简介
- toJson(params1),将传入对象转换为字符串
- fromJson(params1,params2),传入两个参数,将字符串params1转换为params2指定的数据类型。
3.3 示例代码
3.3.1 单个对象的解析
public class Student {
private int stu_no;
private String stu_name;
private String stu_sex;
Student(int stu_no,String stu_name,String stu_sex){
this.stu_no = stu_no;
this.stu_name = stu_name;
this.stu_sex = stu_sex;
}
}
// 序列化,将Student对象stu转换为字符串str
Student stu = new Student(123,"Tom","male");
Gson gson = new Gson();
String str = gson.toJson(stu);
//反序列化,将字符串转换为Student对象
jsonData = "{ \"stu_no\":12345,\"stu_name\":\"John\",\"stu_sex\":\"male\" }";
Gson gson = new Gson();
Student student = gson.fromJson(jsonData,Student.class);
3.3.2 JSON数组的解析(原生类)
Gson gson = new Gson();
int[] ints = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
String[] strings = {"abc", "def", "ghi"};
//序列化(serialization)
//将整数数组转换为JSON数组
gson.toJson(ints); // ==> [1,2,3,4,5]
//将字符串数组转换为JSON数组
gson.toJson(strings); // ==> ["abc", "def", "ghi"]
// 反序列化(Deserialization)
// 将JSON数组转换为原生类数组
// ints2、string2与ints、strings相等
int[] ints2 = gson.fromJson("[1,2,3,4,5]", int[].class);
String[] strings2 = gson.fromJson("[\"abc\", \"def\", \"ghi\"]",String[].class);
3.3.3 JSON数组的解析(自定义类)
//对于类似于2.2中的jsonData,包含3个Student对象
//与原生类不同,需要借助TypeToken获得期望解析成的数据类型
//下列代码运行后,students包含三个Student对象
Gson gson = new Gson();
List<Student> students;
students = gson.fromJson(jsonData, new TypeToken<List<Student>>(){}.getType()); // ==>[stu0,stu1,stu2]
3.4 更多方法
- GSON的
简便之处在于其可以将字符串自动映射为原生或自定义对象,从而不需要手动编写代码进行解析。- GSON的
更多方法可以阅读GSON在github上的用法介绍,README.md -> user guide。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号