实验3
实验任务1
task1.c源代码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 char score_to_grade(int score); // 函数声明 4 5 int main() { 6 int score; 7 char grade; 8 9 while(scanf("%d", &score) != EOF) { 10 grade = score_to_grade(score); // 函数调用 11 printf("分数: %d, 等级: %c\n\n", score, grade); 12 } 13 14 return 0; 15 } 16 17 // 函数定义 18 char score_to_grade(int score) { 19 char ans; 20 21 switch(score/10) { 22 case 10: 23 case 9: ans = 'A'; break; 24 case 8: ans = 'B'; break; 25 case 7: ans = 'C'; break; 26 case 6: ans = 'D'; break; 27 default: ans = 'E'; 28 } 29 30 return ans; 31 }
运行测试截图:
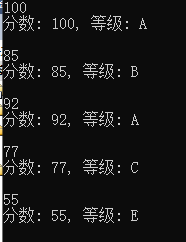
问题1:score_to_grade是用来定义等级,形参类型是整型,返回值类型是字符型
问题2:line3~6 case语句后没有break来终止执行下一个case语句;z字符应该用' '而不是" "
实验任务2
task2.c源代码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int sum_digits(int n); // 函数声明 4 5 int main() { 6 int n; 7 int ans; 8 9 while(printf("Enter n: "), scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { 10 ans = sum_digits(n); // 函数调用 11 printf("n = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, ans); 12 } 13 14 return 0; 15 } 16 17 // 函数定义 18 int sum_digits(int n) { 19 int ans = 0; 20 21 while(n != 0) { 22 ans += n % 10; 23 n /= 10; 24 } 25 26 return ans; 27 }
运行测试截图:
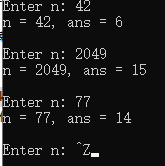
问题1:计算所有位数之和
问题2:能,前迭代,后递归
实验任务3
task3.c源代码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int power(int x, int n); // 函数声明 4 5 int main() { 6 int x, n; 7 int ans; 8 9 while(printf("Enter x and n: "), scanf("%d%d", &x, &n) != EOF) { 10 ans = power(x, n); // 函数调用 11 printf("n = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, ans); 12 } 13 14 return 0; 15 } 16 17 // 函数定义 18 int power(int x, int n) { 19 int t; 20 21 if(n == 0) 22 return 1; 23 else if(n % 2) 24 return x * power(x, n-1); 25 else { 26 t = power(x, n/2); 27 return t*t; 28 } 29 }
运行测试截图:
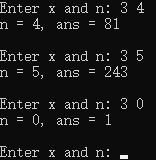
问题1:计算x的n次方
问题2:
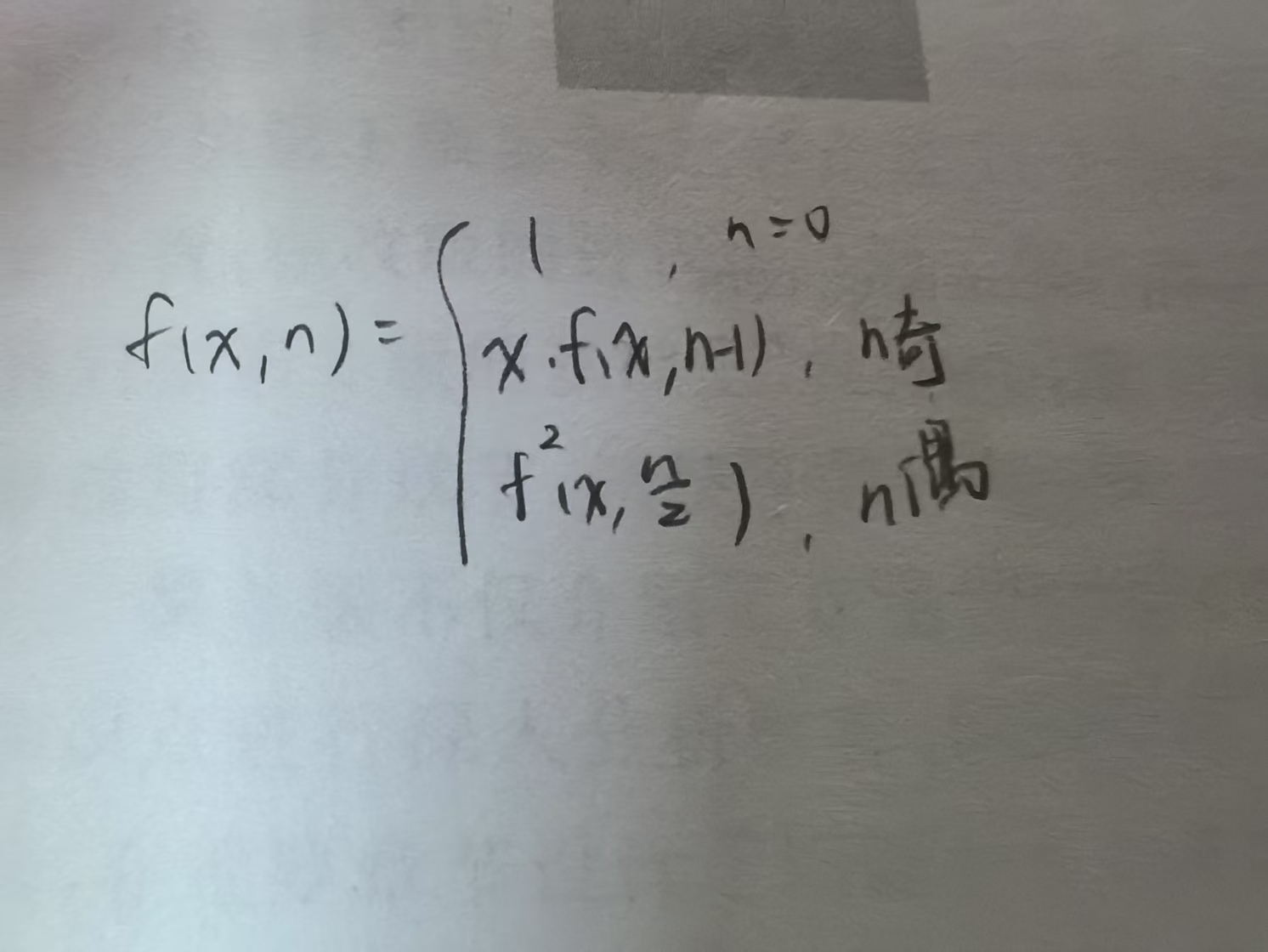
实验任务4
task4.c源代码:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<math.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 int is_prime(int n); 5 int main(){ 6 int i; 7 printf("100以内的孪生素数:\n"); 8 for(i=2;i<=100;++i){ 9 if(is_prime(i)&is_prime(i+2)) 10 printf("%d %d\n",i,i+2); 11 } 12 system("pause"); 13 return 0; 14 } 15 int is_prime(int n){ 16 int k; 17 for(k=2;k<=sqrt(1.0*n);++k) 18 if(n%k==0) 19 return 0; 20 return 1; 21 }
运行测试截图:
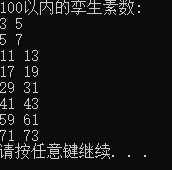
实验任务5
task5.c源代码:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to); 4 void move(unsigned int n,char from,char to);
int count; 5 int main(){ 6 7 int count; 8 while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){ 9 hanoi(n,'A','B','C'); 10 printf("一共移动了%d次",count);
count=0; 11 } 12 system("pause"); 13 return 0; 14 } 15 void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to){ 16 17 if(n==1){ 18 move(n,from,to); 19 20 } 21 else{ 22 hanoi(n-1,from,to,temp); 23 move(n,from,to); 24 25 hanoi(n-1,temp,from,to); 26 } 27 return count; 28 } 29 void move(unsigned int n,char from,char to){ 30 printf("%u:%c-->%c\n",n,from,to);
++count; 31 }
运行测试截图:

实验任务6
task6.c源代码:
#include <stdio.h> int func(int n, int m); // 函数声明 int main() { int n, m; int ans; while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) { ans = func(n, m); // 函数调用 printf("n = %d, m = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, m, ans); } return 0; } int func(int n, int m){ int i,j,k,a=1,b=1,c=1,ans; for(i=1;i<=n;++i) a*=i; for(j=1;j<=m;++j) b*=j; for(k=1;k<=n-m;++k) c*=k; ans=a/b/c; return ans; }
1 int func(int n, int m){ 2 if(n<m||m<0) 3 return 0; 4 else{ 5 if(n==1) 6 return 1; 7 else 8 return func(n-1,m)+func(n-1,m-1); 9 } 10 }
运行测试截图:
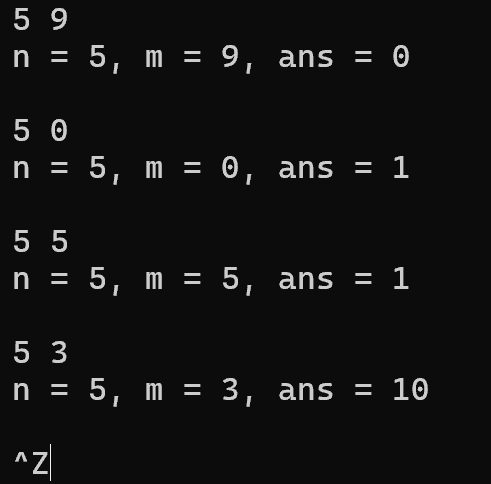
实验任务7
task7.c源代码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int gcd(int a,int b,int c); 4 int main() { 5 int a, b, c; 6 int ans; 7 8 while(scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c) != EOF) { 9 ans = gcd(a, b, c); // 函数调用 10 printf("最大公约数: %d\n\n", ans); 11 } 12 13 return 0; 14 } 15 int gcd(int a,int b,int c){ 16 int i=a,j; 17 if(b<a) 18 i=b; 19 if(c<i) 20 i=c; 21 for(j=i;j>=1;j--){ 22 if(a%j==0&b%j==0&c%j==0) 23 return j; 24 } 25 }
运行测试截图:
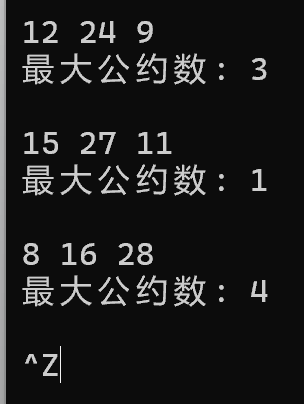




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号