常规算法
贪心算法

找零问题

代码:
def change(n):
t = [100, 50, 20, 5, 1] # 钱的种类
m = [0 for _ in range(len(t))]
for index, monery in enumerate(t):
m[index] = n // monery
n = n % monery
print(m)
return m
if __name__ == '__main__':
change(999) # [9, 1, 2, 1, 4]
change(999) # [1, 0, 1, 0, 3]
背包问题
背包容量50kg,怎么装东西以达到最大的价值?
def backpack(goods, w):
m = [0 for _ in range(len(goods))]
total = 0
for i, (prize, weight) in enumerate(goods):
if w > weight:
m[i] = 1
total += prize # 当前拿到的价值
w -= weight # 背包剩余重量
else:
m[i] = w / weight
total += m[i] * prize
w = 0 # 背包装满
break
return total, m
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 3类物品,价值60元钟10kg,价值100元重20kg,价值120元重30kg
goods = [(60, 10), (100, 20), (120, 30)]
w = 50 # 背包承受重量
a = backpack(goods, w)
print(a)
拼接数字最大问题

代码:
# 例如:32,94,128,1286,6,71
# 拼接最大数字为:94 71 6 32 1286 128
from functools import cmp_to_key
def index(li):
li = list(map(str,li))
print(li)
li.sort(key=cmp_to_key(xy_cmp))
print(li)
return ''.join(li)
def xy_cmp(x,y):
if x+y < y+x:
return 1
elif x+y > y+x:
return -1
else:
return 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
li = [32, 94, 128, 1286, 6, 71]
print(index(li))
活动选择问题


代码:
active = [(1, 4), (0, 6), (5, 9), (8, 12), (2, 14), (12, 16), (3, 5), (6, 10), (8, 11), (5, 7), (3, 9)]
# 保证活动是按结束时间排好序的
active.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
def activtty_selection(active):
res = [active[0]] # 活动列表
for i in range(1, len(active)):
start_time = active[i][0] # 活动开始时间
if res[-1][1] <= start_time: # 当前活动的开始时间小于等于列表中最后一个活动的结束时间
res.append(active[i])
print(res)
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
activtty_selection(active)
动态规划
钢条切割
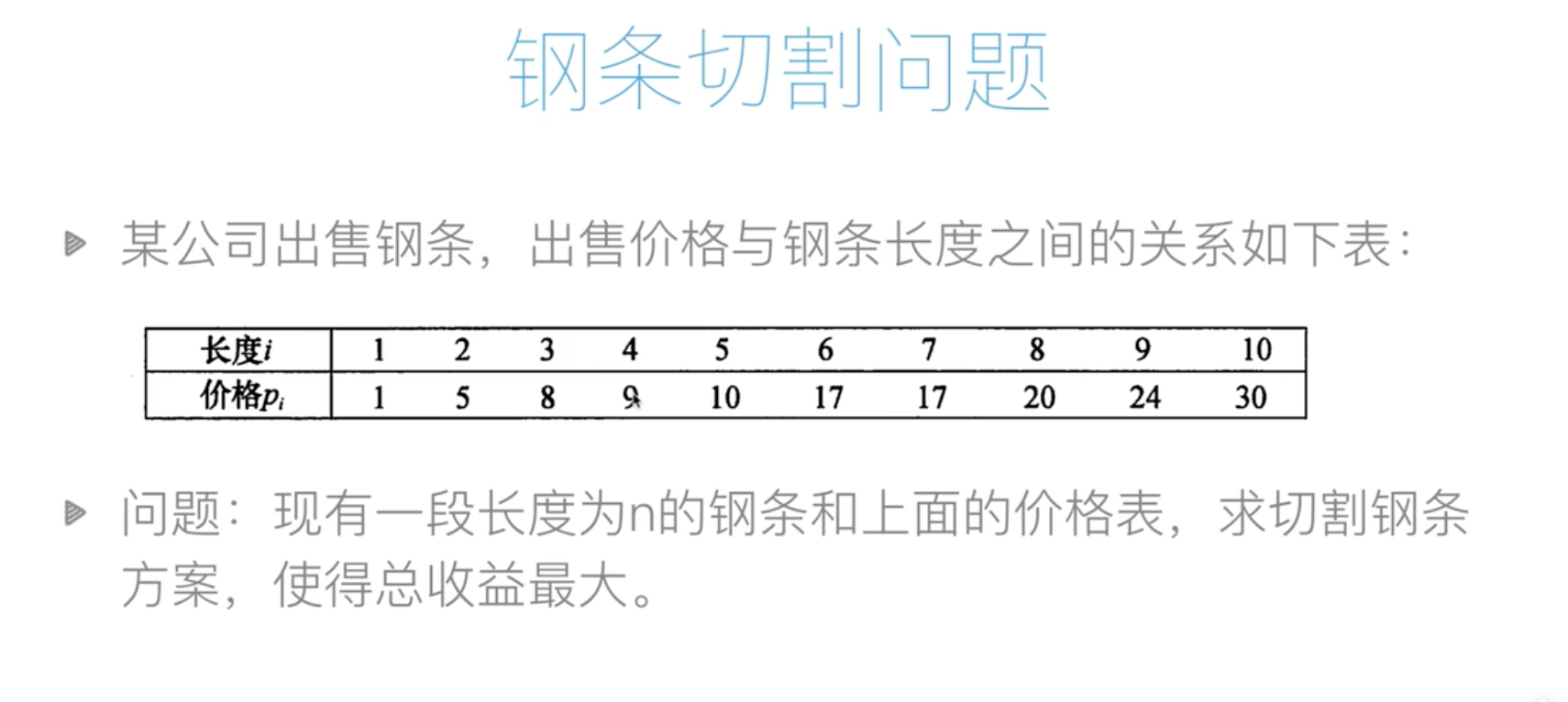
代码:时间复杂度O(n方)
import time
def cal_time(func):
def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
t1 = time.time()
result = func(*args,**kwargs)
t2 = time.time()
print("耗时:", t2-t1)
return result
return wrapper
@cal_time
def cut_rod_dp(p, n):
r = [0]
for i in range(1, n + 1):
res = 0
for j in range(1, i + 1):
res = max(res, p[j] + r[i - j])
r.append(res)
print(r[n])
print(r)
print(len(r))
return r[n]
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = [0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 18, 20, 21, 23, 24, 26, 27, 27, 28, 30, 33, 36, 39, 40]
n = 20 # 钢条长度
cut_rod_dp(p, n)
最长公共子序列


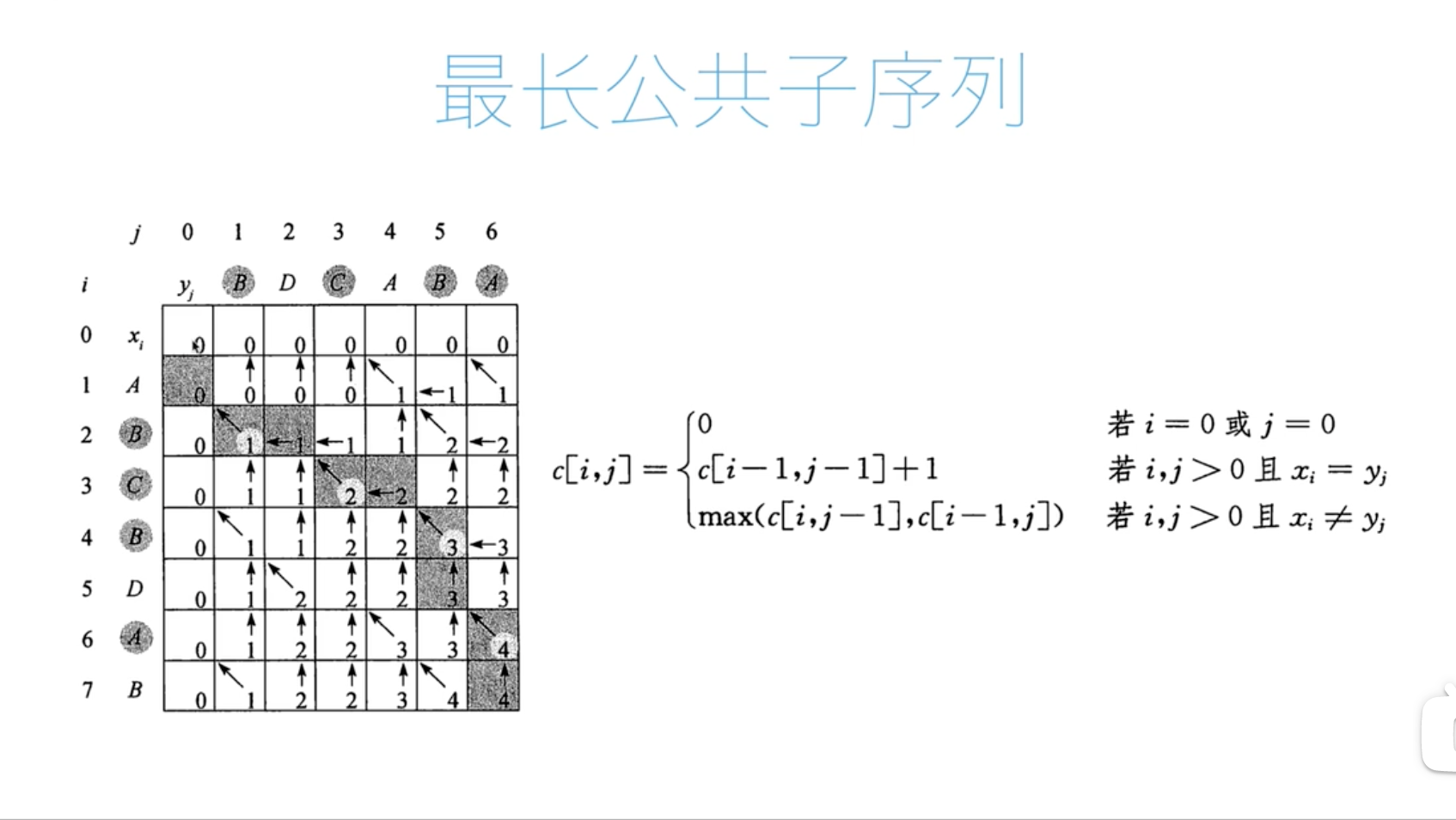
代码:
# 最长公共子序列长度算法
def lcs_length(x, y):
m = len(x)
n = len(y)
c = [[0 for _ in range(n + 1)] for _ in range(m + 1)]
for i in range(1, m + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if x[i - 1] == y[j - 1]: # i j 位置上的自负匹配的时候,来自左上方+1
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
else:
c[i][j] = max(c[i - 1][j], c[i][j - 1])
for _ in c:
print(_)
return c[m][n]
# 最长公共子序列方向算法
def lcs(x, y):
m = len(x)
n = len(y)
c = [[0 for _ in range(n + 1)] for _ in range(m + 1)]
b = [[0 for _ in range(n + 1)] for _ in range(m + 1)]
for i in range(1, m + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if x[i - 1] == y[j - 1]: # i j 位置上的自负匹配的时候,来自左上方+1
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
b[i][j] = 1
elif c[i - 1][j] > c[i][j - 1]: # 来自于上方
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j]
b[i][j] = 2
else:
c[i][j] = c[i][j - 1]
b[i][j] = 3
return c[n][n], b
# 最长公共子序列回溯算法
def lcs_trackback(x, y):
c, b = lcs(x, y)
i = len(x)
j = len(y)
res = []
while i > 0 and j > 0:
if b[i][j] == 1: # 来自左上方=》匹配
res.append(x[i - 1])
i -= 1
j -= 1
elif b[i][j] == 2: # 来自上方=》不匹配
i -= 1
else: # 来自作坊=》不匹配
j -= 1
return "".join(reversed(res))
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = "ABCBDAB"
y = "BDCABA"
res = lcs_trackback(x, y)
print(res)
欧几里得算法


动态演示:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Qv411t7sa?p=95&spm_id_from=pageDriver
代码:
# 循环写法1
def gcd2(x, y):
while True:
a = x % y
if a != 0:
x = y
y = a
else:
return y
# 循环写法2
def gcd3(x, y):
while y > 0:
a = x % y
x = y
y = a
return x
# 递归写法
def gcd(x, y):
if y == 0:
return x
else:
return gcd(y, x % y)
if __name__ == '__main__':
res = gcd2(105, 252)
# res = gcd2(252, 105)
print(res)
# res = gcd2(100,21)
# print(res)
RSA算法过程


选择了IT,必定终身学习


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号