java grpc 简单易懂 ---1
简介:
grpc是谷歌的一个开源的rpc(远程服务调用)框架,可以让各个语言按照指定的规则通过http2协议相互调用,这个规则是用Protocol Buffer(谷歌的一个数据描述语言)写的一个.proto文件,grpc的目的就是为了让服务调用更方便。
目前支持的语言有C, C++,C#,Java, Node.js, Python,Go等,大部分语言都是通过插件根据.proto文件生成对应的代码,用生成好的代码,创建或调用grpc服务。
grpc的接口调用分为四类
1.普通调用
2.请求流调用
3.响应流调用
4.双向流调用
从.proto文件开始
| syntax | 指定语言版本 |
| option | 修改配置选项 |
| service | 声明一个服务 |
| rpc | 声明一个方法 |
| resturns | 方法的返回值 |
| message | 定义一个消息类型 |
| repeated | 数组 |
| stream | 用流来交互 |
一个例子:
syntax = "proto3";
option java_package = "java_test";
option java_multiple_files = true;
service TestService
{
rpc method(Request) returns (Result){}
}
message Request
{
string request1 = 1;
string request2 = 2;
}
message Result
{
string result1 = 1;
string result2 = 2;
}
指定一个版本:
syntax = "proto3";
针对java的代码生成的一些配置
option java_package = "java_test"; option java_multiple_files = true;
用 message 定义了一个请求消息,和一个返回消息
message Request
{
string request1 = 1;
string request2 = 2;
}
message Result
{
string result1 = 1;
string result2 = 2;
}
用 service 声明了一个服务,用 rpc 声明一个方法
service TestService
{
rpc method(Request) returns (Result){}
}
说正经的:
想使用grpc要先做一些配置
添加grpc的包
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-all</artifactId>
<version>1.10.1</version>
</dependency>
添加编译.proto文件用的插件
<plugin>
<groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.5.0</version>
<configuration>
<protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.0.0-beta-4:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact>
<pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:0.15.0:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact>
<pluginId>grpc</pluginId>
<protoSourceRoot>src/main/resources/proto</protoSourceRoot>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>compile-custom</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
添加.proto文件的编译工具
<configuration>
<protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.0.0-beta-4:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact>
<pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:0.15.0:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact>
<pluginId>grpc</pluginId>
<protoSourceRoot>src/main/resources/proto</protoSourceRoot>
</configuration>
protoc工具通过.proto文件生成对应的java对应的类
<protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.0.0-beta-4:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact>
protoc-gen-grpc-java工具通过.proto文件生成grpc的工具类
<pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:0.15.0:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact>
这是生成grpc工具类存放的文件夹的名字
<pluginId>grpc</pluginId>
要编辑的.proto文件的路径
<protoSourceRoot>src/main/resources/proto</protoSourceRoot>
这个是为下载上面工具用的,他可以提供一些变量,
os.detected.classifier变量可以根据当前系统的类型来下载对应的工具
<extension>
<groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1.Final</version>
</extension>
这是上面两个编译工具用到的命令,当用maven编译项目时会执行这两个命令
<goal>compile</goal> <goal>compile-custom</goal>
真的,说正经的:
用maven编译一下

会生成两个文件夹
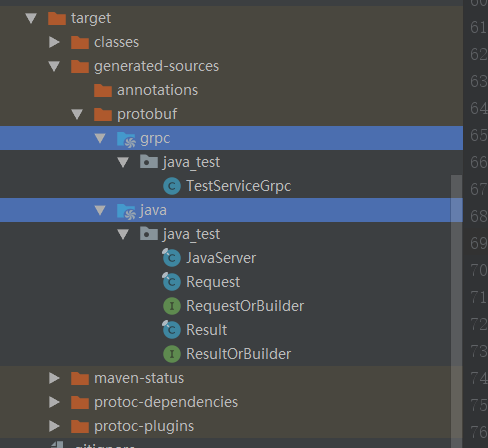
java文件夹是protoc编译工具生成的代码
grpc文件夹是protoc-gen-grpc-java编译工具生成的工具类
这两个文件就是我们在.proto文件中定义的消息类型(经常被用到)
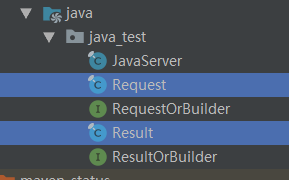
这两个是为消息类型的一个接口,里面有get方法(不会被用到)

这个是对消息的一个描述(更不会被用到)
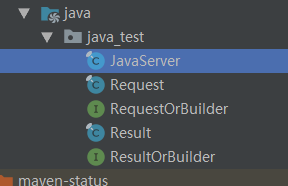
这个是grpc的工具类(会被用到)

这次真的要说正经的了,我们要用这些grpc为我们生成出来的奇怪的东西,写奇怪的东西了:
1.普通接口
1.1.服务端
package com.gutousu.grpc_service_java_test.service;
import io.grpc.ServerBuilder;
import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver;
import java_test.Request;
import java_test.Result;
import java_test.TestServiceGrpc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class JavaGrpcServer extends TestServiceGrpc.TestServiceImplBase implements InitializingBean
{
@Override
public void method(Request request, StreamObserver<Result> responseObserver) {
Result result = Result.newBuilder().setResult1("result1").setResult2("result2").build();
responseObserver.onNext(result);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
ServerBuilder.forPort(2)
.addService(new JavaGrpcServer())
.build()
.start();
}
}
首先建立一个服务类叫JavaGrpcServer 继承 TestServiceGrpc.TestServiceImplBase 重写里面的method方法
public class JavaGrpcServer extends TestServiceGrpc.TestServiceImplBase
TestServiceGrpc.TestServiceImplBase 就是我们在.proto文件中定义的服务
用 ServerBuilder 的 forProt 方法来指定一个端口,用 addService 来添加一个服务类,也就是当前类
ServerBuilder.forPort(2)
.addService(new JavaGrpcServer())
.build()
.start();
grpc生成的消息类有点独特,他们没有set方法,只有get方法,想要赋值,要用他们的一个内部类Builder来间接赋值
Result result = Result.newBuilder().setResult1("result1").setResult2("result2").build();
添加返回值,完成调用
responseObserver.onNext(result); responseObserver.onCompleted();
StreamObserver(流观察者) 这个接口会在后面详细说,这里只需要知道 onNext 是添加返回值,onCompleted 是完成调用即可
这里利用了spring的 InitializingBean 接口和 Component 注解在bean初始化的时候建立服务
好了,服务端搞完了,下一个
1.2.客户端
先写一个叫 Functional 的函数式接口,方便调用
package com.gutousu.grpc_client_java_test;
public interface Functional<Arg,Result>
{
Result run(Arg arg);
}
建一个叫 JavaGrpcClient 的类 来调用接口
package com.gutousu.grpc_client_java_test.client;
import com.gutousu.grpc_client_java_test.Functional;
import io.grpc.Channel;
import io.grpc.ManagedChannelBuilder;
import java_test.TestServiceGrpc;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class JavaGrpcClient
{
private Channel channel = channel();
public <Result> Result run(Functional<TestServiceGrpc.TestServiceBlockingStub,Result> functional)
{
TestServiceGrpc.TestServiceBlockingStub testServiceBlockingStub =
TestServiceGrpc.newBlockingStub(channel);
return functional.run(testServiceBlockingStub);
}
private Channel channel()
{
return ManagedChannelBuilder
.forAddress("192.168.0.31",2)
.usePlaintext(true)
.build();
}
}
用 ManagedChannelBuilder 的 forAddress 方法来连接服务端,usePlaintext的意思是使用明文不加密(应该可以加密)
private Channel channel()
{
return ManagedChannelBuilder
.forAddress("192.168.0.31",2)
.usePlaintext(true)
.build();
}
用 TestServiceGrpc.newBlockingStub 来创建一个实例
TestServiceGrpc.TestServiceBlockingStub testServiceBlockingStub =
TestServiceGrpc.newBlockingStub(channel);
再搞一个测试
package com.gutousu.grpc_client_java_test;
import com.gutousu.grpc_client_java_test.client.JavaGrpcClient;
import java_test.Request;
import java_test.Result;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class GrpcClientJavaTestApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private JavaGrpcClient javaGrpcClient;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
Request request = Request.newBuilder().setRequest1("test1").setRequest2("test2").build();
Result result = javaGrpcClient.run(o -> o.method(request));
}
}
让我们把这两个项目跑起来,看一下
看!断点经过了创建服务那里,而且没有报错,服务端跑起来了!

看!客户端要!

他进来了,连接了服务端,创建了实例,马上就要....
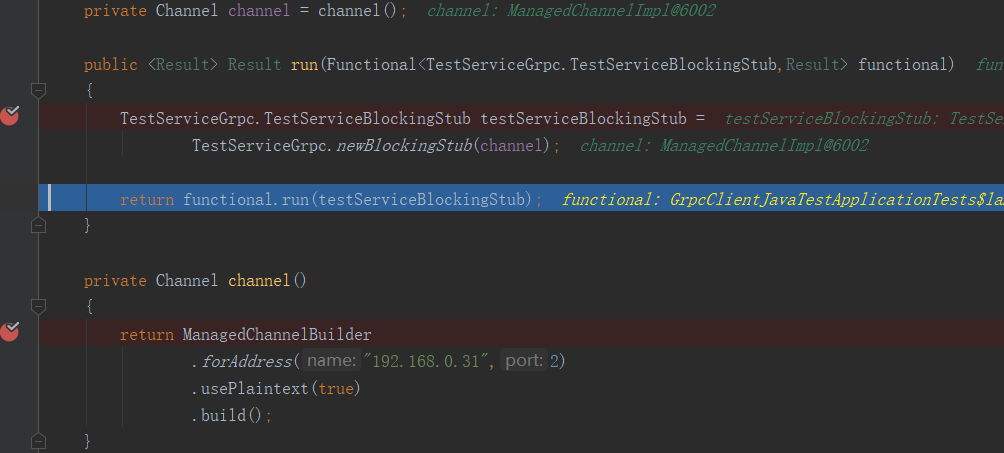
他带着参数过来了,被断点拦住了
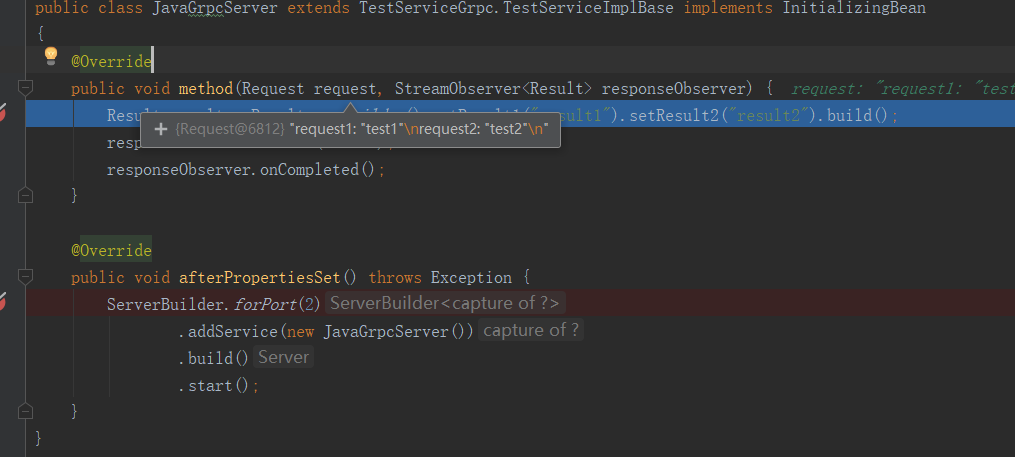
给他一个返回值,结束
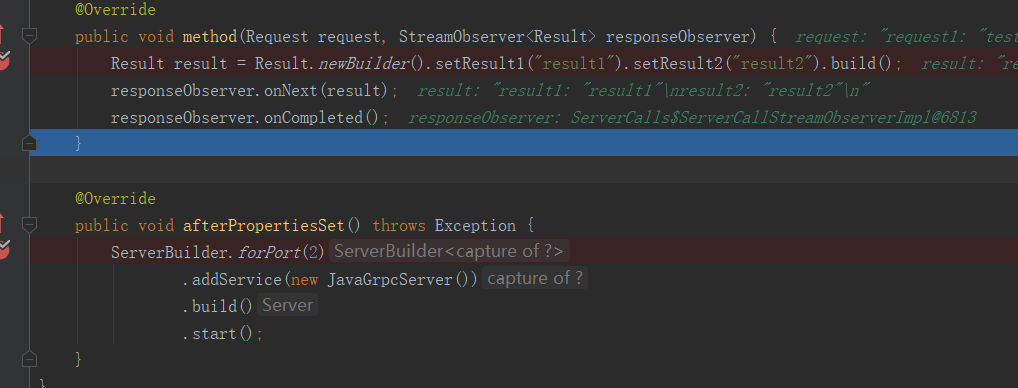
走你!
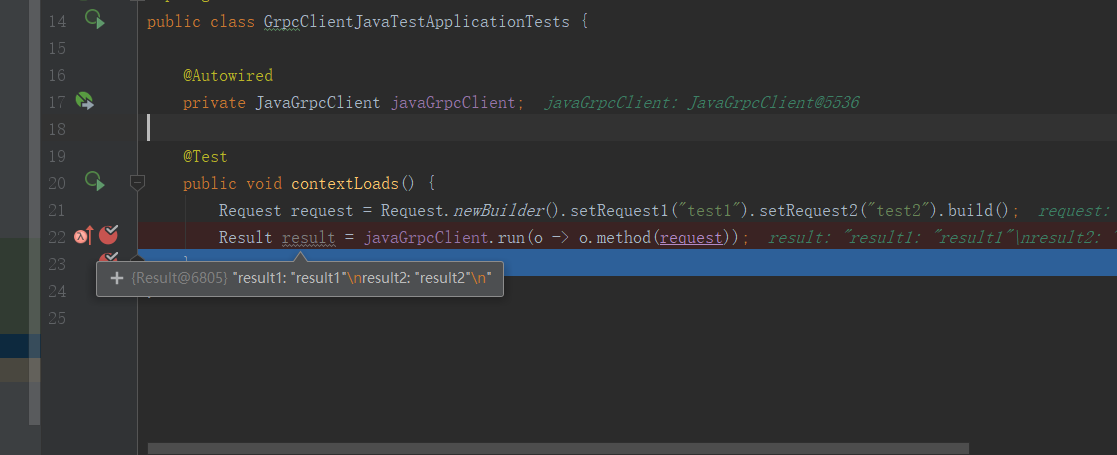
拿到了返回值,完结!撒花!
等等!
这只是普通的接口
还有三种接口呢!
好,那继续
2.请求流接口
等等!
博客写的有点长了,下一篇吧^_^
不要走开,广告之后更精彩!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号