题解:P10279 [USACO24OPEN] The 'Winning' Gene S
思路
建议升蓝。
算法一
考虑暴力。
我们先枚举 \(K,L\),考虑如何求解。
直接枚举每一个 \(K\)-mer,再枚举里面的每一个长度为 \(L\) 的子串,找到最大的子串并在起始部分打一个标记。最后直接看有几个地方被打标记就行。
时间复杂度:\(O(n^4)\)。预计能过测试点 \(1-4\)。
算法二
我们可以把选取子串的过程大概画下来。
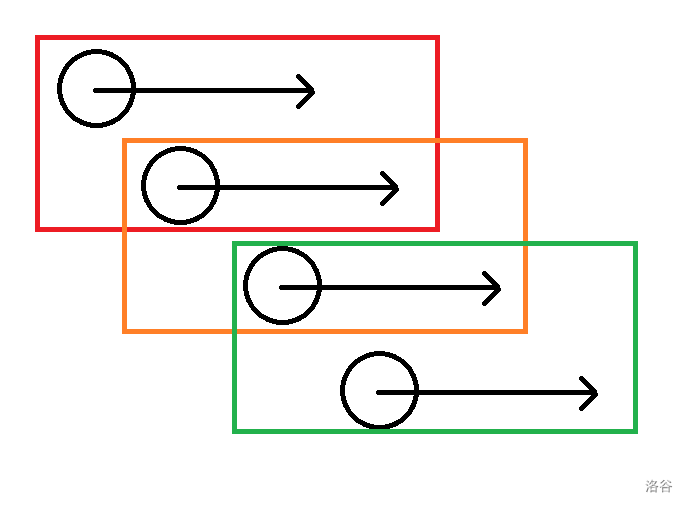
我们发现每一次都会往后面都会多一个子串,我们可以考虑一个数据结构,可以删除最前面的数据,而且可以往后面加入一个数据,并动态求最值。我在这里选择的数据结构为单调队列。
时间复杂度:\(O(n^3)\),预计能过测试点 \(1-7\)。
代码
实践后:

(常数写大了,超了 0.07秒)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
//#define int long long
namespace gtx{
// Fast IO
void read(int &x){
x = 0;int h = 1;char tmp;
do{tmp=getchar();if(tmp=='-')h*=-1;}while(!isdigit(tmp));
while(isdigit(tmp)) x*=10,x+=tmp-'0',tmp=getchar();
x*=h;
}
void read(char &x){do{x=getchar();}while(x==' '||x=='\n'||x=='\r');}
void write(char x){putchar(x);}
void write(int x){
if(x<0) putchar('-'),x=-x;int st[200]={0},tot=0;
do{st[++tot]=x%10,x/=10;} while(x);
while(tot){putchar(st[tot--]+'0');};
}
void write(int x,char y){write(x);write(y);}
const int MAXN = 3100;
int n,ans,t[MAXN];
char a[MAXN];
signed main(){
read(n);
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) read(a[i]);
for(int K = 1;K<=n;K++){
for(int L = 1;L<=K;L++){
deque<pair<int,string>> st;
string now;
for(int i = 1;i<=L;i++) now += a[i];
st.push_back({1,now});
for(int i = 2;i<=K-L+1;i++){
now.erase(now.begin());
now += a[i+L-1];
while(!st.empty()&&st.back().second>now) st.pop_back();
st.push_back({i,now});
}
bitset<MAXN> b;
b.set(st.front().first);
for(int i = K-L+2;i<=n-L+1;i++){
if(st.front().first==i-(K-L)-1) st.pop_front();
now.erase(now.begin());
now += a[i+L-1];
while(!st.empty()&&st.back().second>now) st.pop_back();
st.push_back({i,now});
b.set(st.front().first);
}
t[b.count()]++;
}
}
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) write(t[i],'\n');
return 0;
}
}
signed main(){
// freopen("gene.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("gene.ans","w",stdout);
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// gtx::read(T);
while(T--) gtx::main();
return 0;
}
算法三
我们在上面的代码中发现其实 \(K\) 有没有都几乎没有什么区别,于是可以想一想定长的 \(L\) 可以对哪些答案产生的贡献。
记录前面第一个比这个子串大的子串的起始位置为 \(left_i\),后面第一个比这个子串大的子串的起始位置为 \(right_i\)。那么对于一个子串来说,如果这个子串能产生贡献 \(K\) 最大应该的值的区间应该是这样的:
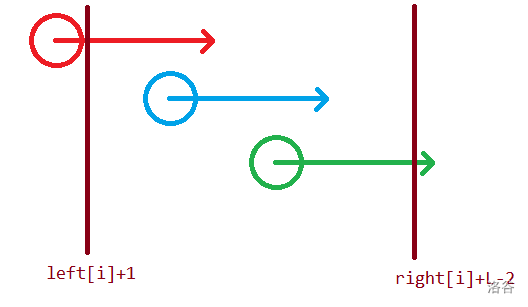
所以产生的最大的 \(K\) 为 \(right_i+L-2-left_i\)。最小的 \(K\) 应该就是这个子串的长度,那么这个子串就会对这些 \(K\) 产生答案。我们可以用差分解决。
至于维护 \(left_i\) 和 \(right_i\) 可以使用单调队列。
时间复杂度:\(O(n^2)\)。预计得分:\(100pts\)。
AC代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
//#define int long long
namespace gtx{
// Fast IO
void read(int &x){
x = 0;int h = 1;char tmp;
do{tmp=getchar();if(tmp=='-')h*=-1;}while(!isdigit(tmp));
while(isdigit(tmp)) x*=10,x+=tmp-'0',tmp=getchar();
x*=h;
}
void read(char &x){do{x=getchar();}while(x==' '||x=='\n'||x=='\r');}
void write(char x){putchar(x);}
void write(int x){
if(x<0) putchar('-'),x=-x;int st[200]={0},tot=0;
do{st[++tot]=x%10,x/=10;} while(x);
while(tot){putchar(st[tot--]+'0');};
}
void write(int x,char y){write(x);write(y);}
const int MAXN = 3100;
int n,t[MAXN],ans[MAXN][MAXN],left[MAXN],right[MAXN];
char a[MAXN];
signed main(){
read(n);
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) read(a[i]);
for(int L = 1;L<=n;L++){
stack<pair<int,string>> st;
string now;
for(int i = 1;i<=L;i++) now += a[i];
st.push({1,now});
for(int i = 1;i<=n-L+1;i++) left[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n-L+1;i++) right[i] = 0;
left[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2;i<=n-L+1;i++){
now.erase(now.begin());
now += a[i+L-1];
while(!st.empty()&&st.top().second>now) st.pop();
left[i] = st.empty()?1:st.top().first+1;
st.push({i,now});
}
while(!st.empty()) st.pop();
now="";
for(int i = n-L+1;i<=n;i++) now+=a[i];
right[n-L+1] = n;
st.push({n-L+1,now});
for(int i = n-L;i>=1;i--){
now.erase(--now.end());
now = a[i]+now;
while(!st.empty()&&st.top().second>=now) st.pop();
right[i] = st.empty()?n:st.top().first+L-2;
st.push({i,now});
}
for(int i = 1;i<=n-L+1;i++){
if(right[i]-left[i]+1<L) continue;
ans[L][L]++;
ans[right[i]-left[i]+2][L]--;
}
// cout << L << endl;
// for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) cout << left[i] << " " << right[i] << endl;
}
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++){
for(int i = j;i<=n;i++){
ans[i][j] += ans[i-1][j];
t[ans[i][j]]++;
}
}
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++) write(t[i],'\n');
return 0;
}
}
signed main(){
// freopen("gene.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("gene.out","w",stdout);
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// gtx::read(T);
while(T--) gtx::main();
return 0;
}
tag
USACO
单调栈、思维、单调队列、差分




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号