Mybatis
第1章 框架概述
1.1 软件开发常用结构
1.1.1 三层架构
三层架构包含的三层:
界面层(User Interface layer)、业务逻辑层(Business Logic Layer)、数据访问层(Data access layer)
三层的职责
- 界面层(表示层,视图层):主要功能是接受用户的数据,显示请求的处理结果。使用 web 页面和
用户交互,手机 app 也就是表示层的,用户在 app 中操作,业务逻辑在服务器端处理。 - 业务逻辑层:接收表示传递过来的数据,检查数据,计算业务逻辑,调用数据访问层获取数据。
- 数据访问层:与数据库打交道。主要实现对数据的增、删、改、查。将存储在数据库中的数据提交
给业务层,同时将业务层处理的数据保存到数据库.
三层的处理请求的交互:
用户---> 界面层--->业务逻辑层--->数据访问层--->DB 数据库
如图:
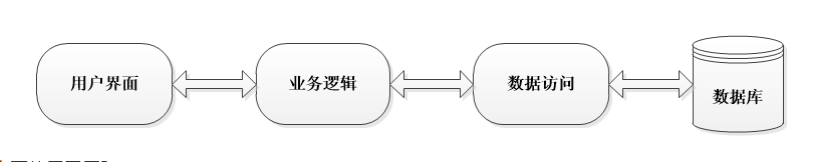
为什么要使用三层?
- 结构清晰、耦合度低, 各层分工明确,
- 可维护性高 可扩展性高
- 有利于标准化
- 开发人员可以只关注整个结构中的其中某一层的功能实现
- 有利于各层逻辑的复用
1.1.2 常用框架
常见的 J2EE 中开发框架:
MyBatis 框架:
MyBatis 是一个优秀的基于 java 的持久层框架,内部封装了 jdbc,开发者只需要关注 sql 语句
本身,而不需要处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建 statement、关闭连接,资源等繁杂的过程。
MyBatis 通过 xml 或注解两种方式将要执行的各种 sql 语句配置起来,并通过 java 对象和 sql 的动态参数进行映射生成最终执行的 sql 语句,最后由 mybatis 框架执行 sql 并将结果映射为 java
对象并返回。
Spring 框架:
Spring 框架为了解决软件开发的复杂性而创建的。Spring 使用的是基本的 JavaBean 来完成以前
非常复杂的企业级开发。Spring 解决了业务对象,功能模块之间的耦合,不仅在 javase,web 中使用,
大部分 Java 应用都可以从 Spring 中受益。
Spring 是一个轻量级控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器。
SpringMVC 框架
Spring MVC 属于 SpringFrameWork 3.0 版本加入的一个模块,为 Spring 框架提供了构建 Web
应用程序的能力。现在可以 Spring 框架提供的 SpringMVC 模块实现 web 应用开发,在 web 项目中
可以无缝使用 Spring 和 Spring MVC 框架。
1.2 框架是什么
1.2.1 框架定义
框架(Framework)是整个或部分系统的可重用设计,表现为一组抽象构件及构件实例间交互的方
法;另一种认为,框架是可被应用开发者定制的应用骨架、模板。
简单的说,框架其实是半成品软件,就是一组组件,供你使用完成你自己的系统。从另一个角度来
说框架一个舞台,你在舞台上做表演。在框架基础上加入你要完成的功能。
框架安全的,可复用的,不断升级的软件。
1.2.2 框架解决的问题
框架要解决的最重要的一个问题是技术整合,在 J2EE 的 框架中,有着各种各样的技术,不同的应
用,系统使用不同的技术解决问题。需要从 J2EE 中选择不同的技术,而技术自身的复杂性,有导致更
大的风险。企业在开发软件项目时,主要目的是解决业务问题。 即要求企业负责技术本身,又要求解
决业务问题。这是大多数企业不能完成的。框架把相关的技术融合在一起,企业开发可以集中在业务领
域方面。
另一个方面可以提供开发的效率。
1.3 JDBC 编程
1.3.1 用 使用 JDBC 编程的回顾
public void findStudent() {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//注册 mysql 驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//连接数据的基本信息 url ,username,password
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//创建连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//保存查询结果
List<Student> stuList = new ArrayList<>();
//创建 Statement, 用来执行 sql 语句
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//执行查询,创建记录集,
rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from student");
while (rs.next()) {
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
stu.setName(rs.getString("name"));
stu.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
//从数据库取出数据转为 Student 对象,封装到 List 集合
stuList.add(stu);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//关闭资源
if (rs != null) ;
{
rs.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.3.2 用 使用 JDBC 的缺陷
- 代码比较多,开发效率低
- 需要关注 Connection ,Statement, ResultSet 对象创建和销毁
- 对 ResultSet 查询的结果,需要自己封装为 List
- 重复的代码比较多些
- 业务代码和数据库的操作混在一起
1.4 MyBatis 框架概述
MyBatis 框架:
MyBatis 本是 apache 的一个开源项目 iBatis, 2010 年这个项目由 apache software foundation 迁移到了 google code,并且改名为 MyBatis 。2013 年 11 月迁移到 Github。
iBATIS 一词来源于“internet”和“abatis”的组合,是一个基于 Java 的持久层框架。iBATIS 提供的
持久层框架包括 SQL Maps 和 Data Access Objects(DAOs)
当前,最新版本是 MyBatis 3.5.1 ,其发布时间是 2019 年 4 月 8 日。
1.4.1 MyBatis 解决的主要问题
减轻使用 JDBC 的复杂性,不用编写重复的创建 Connetion , Statement ; 不用编写关闭资源代码。
直接使用 java 对象,表示结果数据。让开发者专注 SQL 的处理。 其他分心的工作由 MyBatis 代劳.
MyBatis 可以完成:
- 注册数据库的驱动,例如 Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”))
- 创建 JDBC 中必须使用的 Connection , Statement, ResultSet 对象
- 从 xml 中获取 sql,并执行 sql 语句,把 ResultSet 结果转换 java 对象
List<Student> list = new ArrayLsit<>();
ResultSet rs = state.executeQuery(“select * from student”);
while(rs.next){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(rs.getString(“name”));
student.setAge(rs.getInt(“age”));
list.add(student);
}
4.关闭资源
ResultSet.close() , Statement.close() , Conenection.close()
第2章 MyBatis 框架快速入门
内容列表:
◼ 快速开始一个 MyBatis
◼ 基本 CURD 的操作
◼ MyBatis 内部对象分析
◼ 使用 Dao 对象
2.1 入门案例
MyBatis 开发准备
搭建 MyBatis 开发环境,实现第一个案例
2.1.1 使用 Mybatis 准备
下载 mybatis
https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/releases
2.1.2 搭建 MyBatis 开发环境
1. 创建 mysql 数据库和表
数据库名 ssm ;表名 student
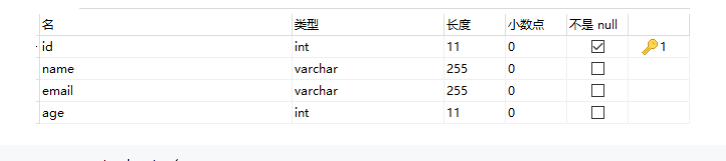
CREATE TABLE student (
id int(11) NOT NULL ,
name varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
email varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
age int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
2. 创建 maven 工程
创建 maven 工程,信息如下:
模板:
工程坐标:
3. 删除默认创建的 App 类文件
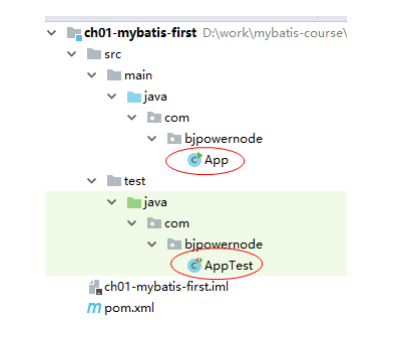
4. 加入 maven 坐标
pom.xml 加入 maven 坐标:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
5. 加入 maven 插件
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory><!--所在的目录-->
<includes><!--包括目录下的.properties,.xml 文件都会扫描到-->
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>false</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
6. 编写 Student 实体类
创建包 com.g0rez.domain, 包中创建 Student 类
package com.g0rez.domain;
/**
* <p>Description: 实体类 </p>
*/
public class Student {
// 属性名和列名一样
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
private Integer age;
// set ,get , toString
}
7.编写 Dao接口StudentDao
创建 com.g0rez.dao 包,创建 StudentDao 接口
package com.g0rez.dao;
import com.g0rez.domain.Student;
import java.util.List;
/*
* <p>Description: Dao 接口 </p>
*/
public interface StudentDao {
/* 查询所有数据*/
List<Student> selectStudents();
}
8.编写Dao接口Mapper映射文件StudentDao.xml
要求:
- 在 dao 包中创建文件 StudentDao.xml
- 要 StudentDao.xml 文件名称和接口 StudentDao 一样,区分大小写的一样。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
namespace :必须有值,自定义的唯一字符串
推荐使用: dao 接口的全限定名称
-->
<mapper namespace="com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao">
<!--
<select>: 查询数据, 标签中必须是 select 语句
id: sql 语句的自定义名称,推荐使用 dao 接口中方法名称,
使用名称表示要执行的 sql 语句
resultType: 查询语句的返回结果数据类型,使用全限定类名
-->
<select id="selectStudents" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
<!-- 要执行的 sql 语句 -->
select id,name,email,age from student
</select>
</mapper>
9.创建MyBatis主配置文件
项目 src/main 下创建 resources 目录,设置 resources 目录为 resources root
创建主配置文件:名称为 mybatis.xml
说明:主配置文件名称是自定义的,内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 配置 mybatis 环境 -->
<environments default="mysql">
<!--id: 数据源的名称 -->
<environment id="mysql">
<!-- 配置事务类型:使用 JDBC 事务(使用 Connection 的提交和回滚) -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 数据源 dataSource :创建数据库 Connection 对象
type: POOLED 使用数据库的连接池
-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 连接数据库的四个要素 -->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!-- 告诉 mybatis 要执行的 sql 语句的位置 -->
<mapper resource="com/g0rez/dao/StudentDao.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
10.创建测试类MyBatisTest
src/test/java/com/g0rez/ 创建 MyBatisTest.java 文件
/*
* mybatis 入门
*/
@Test
public void testStart() throws IOException {
//1.mybatis 主配置文件
String config = "mybatis-config.xml";
//2. 读取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
//3. 创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象, , 目的是获取 Sql Session
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//4. 获取 SqlSession,SqlSession 能执行 sql 语句
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//5. 执行 SqlSession 的 selectList()
List<Student> studentList =
session.selectList("com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.selectStudents");
//6. 循环输出查询结果
studentList.forEach( student -> System.out.println(student));
//7. 关闭 SqlSession ,释放资源
session.close();
}
List<Student> studentList =
session.selectList("com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.selectStudents");
//近似等价的 jdbc 代码
Connection conn = 获取连接对象
String sql=” select id,name,email,age from student”
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
11.配置日志功能
mybatis.xml 文件加入日志配置,可以在控制台输出执行的 sql 语句和参数
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING" />
</settings>
2.2 基本的 CURD
查询一个用selectOne
insert ,update ,delete
2.2.1 insert
1.StudentDao 接口中增加方法
int insertStudent(Student student);
2.StudentDao.xml 加入sql 语句
<insert id="insertStudent">
insert into student(id,name,email,age)
values(#{id},#{name},#{email},#{age})
</insert>
3.增加测试方法
@Test
public void testInsert() throws IOException {
//1.mybatis 主配置文件
String config = "mybatis-config.xml";
//2. 读取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
//3. 创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//4. 获取 SqlSession
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//5. 创建保存数据的对象
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1005);
student.setName(" 张丽");
student.setEmail("zhangli@163.com");
student.setAge(20);
//6. 执行插入 insert
int rows = session.insert(
"com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.insertStudent",student);
//7. 提交事务
session.commit();
System.out.println(" 增加记录的行数:"+rows);
//8. 关闭 SqlSession
session.close();
}
2.2.2 update
1.StudentDao 接口中增加方法
int updateStudent(Student student);
2.StudentDao.xml 增加 sql 语句
<update id="updateStudent">
update student set age = #{age} where id=#{id}
</update>
3.增加测试方法
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws IOException {
//1.mybatis 主配置文件
String config = "mybatis-config.xml";
//2. 读取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
//3. 创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//4. 获取 SqlSession
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//5. 创建保存数据的对象
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1005);// 要修改的 id
student.setAge(30); // 要修改的年龄值
//6. 执行 更新 update
int rows = session.update(
"com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.updateStudent",student);
//7. 提交事务
session.commit();
System.out.println(" 修改记录的行数:"+rows);
//8. 关闭 SqlSession
session.close();
}
2.2.3 delete
1.StudentDao 接口中增加方法
int deleteStudent(int id);
2.StudentDao.xml增加sql语句
<delete id="deleteStudent">
delete from student where id=#{studentId}
</delete>
3.增加测试方法
@Test
public void testDelete() throws IOException {
//1.mybatis 主配置文件
String config = "mybatis-config.xml";
//2. 读取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
//3. 创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//4. 获取 SqlSession
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//5. 删除的 id
int id = 1001;
//6. 执行删除 delete
int rows = session.delete(
"com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.deleteStudent",id);
//7. 提交事务
session.commit();
System.out.println(" 修改记录的行数:"+rows);
//8. 关闭 SqlSession
session.close();
}
2.3 MyBatis 对象分析
2.3.1 对象使用
SqlSession , SqlSessionFactory 等
1.Resources类
Resources 类,顾名思义就是资源,用于读取资源文件。其有很多方法通过加载并解析资源文件,返
回不同类型的 IO 流对象。
2.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类
SqlSessionFactory 的 创 建 , 需 要 使 用 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 对 象 的 build() 方 法 。 由 于
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 对象在创建完工厂对象后,就完成了其历史使命,即可被销毁。所以,一般会将
该 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 对象创建为一个方法内的局部对象,方法结束,对象销毁。
3.SqlSessionFactory接口
SqlSessionFactory 接口对象是一个重量级对象(系统开销大的对象),是线程安全的,所以一个应用
只需要一个该对象即可。创建 SqlSession 需要使用 SqlSessionFactory 接口的的 openSession()方法。
openSession(true):创建一个有自动提交功能的 SqlSession
openSession(false):创建一个非自动提交功能的 SqlSession,需手动提交
openSession():同 openSession(false)
4.SqlSession接口
SqlSession 接口对象用于执行持久化操作。一个 SqlSession 对应着一次数据库会话,一次会话以
SqlSession 对象的创建开始,以 SqlSession 对象的关闭结束。
SqlSession 接口对象是线程不安全的,所以每次数据库会话结束前,需要马上调用其 close()方法,将
其关闭。再次需要会话,再次创建。 SqlSession 在方法内部创建,使用完毕后关闭。
2.3.2 创建工具类
1.创建 MyBatisUtil 类
package com.g0rez.common;
/**
* <p>Description: 实体类 </p>
*/
public class MyBatisUtil {
// 定义 SqlSessionFactory
private static SqlSessionFactory factory = null;
static {
// 使用 静态块 创建一次 SqlSessionFactory
try{
String config = "mybatis-config.xml";
// 读取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
// 创建 SqlSessionFactory 对象
factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
}catch (Exception e){
factory = null;
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/* 获取 SqlSession 对象 */
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
SqlSession session = null;
if( factory != null){
session = factory.openSession();
}
return session;
}
}
2.使用MyBatisUtil类
@Test
public void testUtils() throws IOException {
SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession();
List<Student> studentList = session.selectList(
"com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.selectStudents");
studentList.forEach( student -> System.out.println(student));
session.close();
}
2.4 MyBatis 使用传统 Dao 开发方式
使用 Dao 的实现类,操作数据库
2.4.1 Dao 开发
1.创建 Dao 接口实现类
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao
2.实现接口中 select 方法
public List<Student> selectStudents() {
SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession();
List<Student> studentList = session.selectList(
"com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.selectStudents");
session.close();
return studentList;
}
测试查询操作:
MyBatisTest 类中创建 StudentDaoImpl 对象
public class MyBatisTest {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDaoImpl();
}
@Test
public void testSelect() throws IOException {
final List<Student> studentList = studentDao.selectStudents();
studentList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
3.实现接口中 insert 方法
public int insertStudent(Student student) {
SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession();
int nums = session.insert(
"com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.insertStudent",student);
session.commit();
session.close();
return nums;
}
测试 insert
@Test
public void testInsert() throws IOException {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1006);
student.setName(" 林浩");
student.setEmail("linhao@163.com");
student.setAge(26);
int nums = studentDao.insertStudent(student);
System.out.println(" 使用 Dao 添加数据:"+nums);
}
4.实现接口中 update 方法
public int updateStudent(Student student) {
SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession();
int nums = session.insert(
"com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.updateStudent",student);
session.commit();
session.close();
return nums;
}
测试 update
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws IOException {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1006);
student.setAge(28);
int nums = studentDao.updateStudent(student);
System.out.println(" 使用 Dao 修改数据:"+nums);
}
5.实现接口中 delete 方法
public int deleteStudent(int id) {
SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession();
int nums = session.insert(
"com.g0rez.dao.StudentDao.deleteStudent",1006);
session.commit();
session.close();
return nums;
}
测试 delete
@Test
public void testDelete() throws IOException {
int nums = studentDao.deleteStudent(1006);
System.out.println(" 使用 Dao 修改数据:"+nums);
}
2.4.2传统 Dao 开发方式的分析
在前面例子中自定义 Dao 接口实现类时发现一个问题:Dao 的实现类其实并没有干什么实质性的工作,它仅仅就是通过 SqlSession 的相关 API 定位到映射文件 mapper 中相应 id 的 SQL 语句,真正对 DB 进行操作的工作其实是由框架通过 mapper 中的 SQL 完成的。
所以,MyBatis 框架就抛开了 Dao 的实现类,直接定位到映射文件 mapper 中的相应 SQL 语句,对DB 进行操作。这种对 Dao 的实现方式称为 Mapper 的动态代理方式。
Mapper 动态代理方式无需程序员实现 Dao 接口。接口是由 MyBatis 结合映射文件自动生成的动态代理实现的。
第3 章 MyBatis框架Dao代理
内容列表
◼ Dao 接口动态代理
◼ 参数传递
◼ 处理查询结果
◼ like 和主键
3.1 Dao 代理实现 CURD
3.1.1 步骤
1.去掉 Dao 接口实现类
2.getMapper 获取代理对象
只需调用 SqlSession 的 getMapper()方法,即可获取指定接口的实现类对象。该方法的参数为指定 Dao接口类的 class 值。
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
StudentDao dao = session.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
使用工具类:
StudentDao studentDao =MyBatisUtil.getSqlSession().getMapper(StudentDao.class);
3.使用 Dao 代理对象方法执行 sql 语句
select 方法:
@Test
public void testSelect() throws IOException {
final List<Student> studentList = studentDao.selectStudents();
studentList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
insert 方法:
@Test
public void testInsert() throws IOException {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1006);
student.setName(" 林浩");
student.setEmail("linhao@163.com");
student.setAge(26);
int nums = studentDao.insertStudent(student);
System.out.println(" 使用 Dao 添加数据:"+nums);
}
update 方法
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws IOException {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1006);
student.setAge(28);
int nums = studentDao.updateStudent(student);
System.out.println(" 使用 Dao 修改数据:"+nums);
}
delete 方法
@Test
public void testDelete() throws IOException {
int nums = studentDao.deleteStudent(1006);
System.out.println(" 使用 Dao 修改数据:"+nums);
}
3.1.2 原理
动态代理
MapperProxy 类定义:
invoke()方法:
重点方法:
3.2 深入理解参数
3.2.1 parameterType
parameterType: 接口中方法参数的类型, 类型的完全限定名或别名。这个属性是可选的,因为 MyBatis可以推断出具体传入语句的参数,默认值为未设置(unset)。接口中方法的参数从 java 代码传入到mapper 文件的 sql 语句。
int 或 java.lang.Integer
hashmap 或 java.util.HashMap
list 或 java.util.ArrayList
student 或 com.g0rez.domain.Student
更多看课件资源中的有关别名的文件或者 mybatis-3.5.1.pdf 的 15 页。
<select>,<insert>,<update>,<delete>都可以使用 parameterType 指定类型
例如:
<delete id="deleteStudent" parameterType="int">
delete from student where id=#{studentId}
</delete>
等同于
<delete id="deleteStudent" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from student where id=#{studentId}
</delete>
3.2.2 MyBatis 传递参数
从 java 代码中把参数传递到 mapper.xml 文件。
3.2.3 一个简单参数
Dao 接口中方法的参数只有一个简单类型(java 基本类型和 String),占位符 #{ 任意 字符 },和方法的参数名无关。
接口方法:
Student selectById(int id);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
{studentId} , studentId 是自定义的变量名称,和方法参数名无关。
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
// 一个参数
Student student = studentDao.selectById(1005);
System.out.println(" 查询 id 是 1005 的学生:"+student);
}
3.2.4 多个参数- 使用@Param
当 Dao 接口方法多个参数,需要通过名称使用参数。 在方法形参前面加入@Param(“自定义参数名”),
mapper 文件使用#{自定义参数名}。
例如定义
List<Student> selectStudent( @Param(“personName”) String name ) { … }
mapper 文件 select * from student where name = #{ personName}
接口方法:
List<Student> selectMultiParam(@Param("personName") String name,@Param("personAge") int age);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectMultiParam" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{personName} or age=#{personAge}
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectMultiParam(){
List<Student> stuList = studentDao.selectMultiParam(" 李力",20);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
3.2.5 多个参数- 使用对象
使用 java 对象传递参数, java 的属性值就是 sql 需要的参数值。 每一个属性就是一个参数。
语法格式: #{ property,javaType=java 中数据类型名,jdbcType=数据类型名称 }
javaType, jdbcType 的类型 MyBatis 可以检测出来,一般不需要设置。常用格式 #{ property }
mybatis-3.5.1.pdf 第 43 页 4.1.5.4 小节:
创建保存参数值的对象 QueryParam
package com.g0rez.vo;
public class QueryParam {
private String queryName;
private int queryAge;
//set , get 方法
}
接口方法:
List<Student> selectMultiObject(QueryParam queryParam);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectMultiObject" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{queryName} or age=#{queryAge}
</select>
或
<select id="selectMultiObject" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student
where name=#{queryName,javaType=string,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
or age =#{queryAge,javaType=int,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void selectMultiObject(){
QueryParam qp = new QueryParam();
qp.setQueryName(" 李力");
qp.setQueryAge(20);
List<Student> stuList = studentDao.selectMultiObject(qp);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
3.2.6 多个参数- 按位置
参数位置从 0 开始, 引用参数语法 #{ arg 位置 } , 第一个参数是#{arg0}, 第二个是#{arg1}
注意:mybatis-3.3 版本和之前的版本使用#{0},#{1}方式, 从 mybatis3.4 开始使用#{arg0}方式。
接口方法:
List<Student> selectByNameAndAge(String name,int age);
mapper 文件
<select id="selectByNameAndAge" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{arg0} or age =#{arg1}
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectByNameAndAge(){
// 按位置参数
List<Student> stuList = studentDao.selectByNameAndAge(" 李力",20);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
3.2.7 多个参数- 使用 Map
Map集合可以存储多个值,使用Map向mapper文件一次传入多个参数。Map集合使用String的key,
Object 类型的值存储参数。 mapper 文件使用 # { key } 引用参数值。
例如:
Map<String,Object> data = new HashMap<String,Object>();
data.put(“myname”,”李力”);
data.put(“myage”,20);
接口方法:
List<Student> selectMultiMap(Map<String,Object> map);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectMultiMap" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{myname} or age =#{myage}
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectMultiMap(){
Map<String,Object> data = new HashMap<>();
data.put("myname"," 李力");// #{myname}
data.put("myage",20); // #{myage}
List<Student> stuList = studentDao.selectMultiMap(data);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
3.2.8 #和$:
占位符,告诉 mybatis 使用实际的参数值代替。并使用 PrepareStatement 对象执行 sql 语句, #{…}代替
sql 语句的“?”。这样做更安全,更迅速,通常也是首选做法,
mapper 文件
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
转为 MyBatis 的执行是:
String sql=” select id,name,email,age from student where id=?”;
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setInt(1,1005);
解释:
where id=? 就是 where id=#{studentId}
ps.setInt(1,1005) , 1005 会替换掉 #{studentId}
$ 字符串替换, ,告诉 mybatis 使用$包含的“字符串”替换所在位置。使用 Statement 把 sql 语句和${}的
内容连接起来。主要用在替换表名,列名,不同列排序等操作。
例 1: 分别使用 id , email 列查询 Student
接口方法:
Student findById(int id);
Student findByEmail(String email);
mapper 文件:
<select id="findById" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select * from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
<select id="findByEmail" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select * from student where email=#{stuentEmail}
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testFindStuent(){
Student student1 = studentDao.findById(1002);
System.out.println("findById:"+student1);
Student student2 = studentDao.findByEmail("zhou@126.net");
System.out.println("findByEmail:"+student2);
}
例 2:通用方法,使用不同列作为查询条件
接口方法:
Student findByDiffField(@Param("col") String colunName,@Param("cval") Object value);
mapper 文件:
<select id="findByDiffField" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select * from student where ${col} = #{cval}
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testFindDiffField(){
Student student1 = studentDao.findByDiffField("id",1002);
System.out.println("按 按 id 列查询:"+student1);
Student student2 = studentDao.findByDiffField("email","zhou@126.net");
System.out.println("按 按 email 列查询:"+student2);
}
3.3 封装 MyBatis 输出结果
3.3.1 resultType
resultType: 执行 sql 得到 ResultSet 转换的类型,使用类型的完全限定名或别名。 注意如果返回的是集合,那应该设置为集合包含的类型,而不是集合本身。resultType 和 resultMap,不能同时使用。
A 、 简单类型
接口方法:
int countStudent();
mapper 文件:
<select id="countStudent" resultType="int">
select count(*) from student
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testRetunInt(){
int count = studentDao.countStudent();
System.out.println(" 学生总人数:"+ count);
}
B 、 对象类型
接口方法:
Student selectById(int id);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id=#{studentId}
</select>
框架的处理: 使用构造方法创建对象。调用 setXXX 给属性赋值。
Student student = new Student();
注意:Dao 接口方法返回是集合类型,需要指定集合中的类型,不是集合本身.
C 、 Map
sql 的查询结果作为 Map 的 key 和 value。推荐使用 Map<Object,Object>。
注意:Map 作为接口返回值,sql 语句的查询结果最多只能有一条记录。大于一条记录是错误。
接口方法:
Map<Object,Object> selectReturnMap(int id);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectReturnMap" resultType="java.util.HashMap">
select name,email from student where id = #{studentId}
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testReturnMap(){
Map<Object,Object> retMap = studentDao.selectReturnMap(1002);
System.out.println(" 查询结果是 Map:"+retMap);
}
3.3.2 resultMap
resultMap 可以自定义 sql 的结果和 java 对象属性的映射关系。更灵活的把列值赋值给指定属性。
常用在列名和 java 对象属性名不一样的情况。
使用方式:
1.先定义 resultMap,指定列名和属性的对应关系。
2.在select中把 resultType 替换为 resultMap。
接口方法:
List<Student> selectUseResultMap(QueryParam param);
mapper 文件:
<!-- 创建 resultMap
id: 自定义的唯一名称,在 <select> 使用
type: 期望转为的 java 对象的全限定名称或别名
-->
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
<!-- 主键字段使用 id -->
<id column="id" property="id" />
<!-- 非主键字段使用 result-->
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="email" property="email" />
<result column="age" property="age" />
</resultMap>
<!--resultMap: resultMap 标签中的 id 属性值 -->
<select id="selectUseResultMap" resultMap="studentMap">
select id,name,email,age from student where name=#{queryName} or age=#{queryAge}
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectUseResultMap(){
QueryParam param = new QueryParam();
param.setQueryName(" 李力");
param.setQueryAge(20);
List<Student> stuList = studentDao.selectUseResultMap(param);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
3.3.3 实体类属性名和列名不同的处理方式
(1 ) 使用列别名 和
步骤:
- 创建新的实体类 PrimaryStudent
package com.g0rez.domain;
-
Description: 实体类
-
public class PrimaryStudent { private Integer stuId; private String stuName; private Integer stuAge; // set , get 方法 }
- 接口方法
List<PrimaryStudent> selectUseFieldAlias(QueryParam param);
- mapper 文件:
<select id="selectUseFieldAlias"
resultType="com.g0rez.domain.PrimaryStudent">
select id as stuId, name as stuName,age as stuAge
from student where name=#{queryName} or age=#{queryAge}
</select>
4.测试方法
@Test
public void testSelectUseFieldAlias(){
QueryParam param = new QueryParam();
param.setQueryName(" 李力");
param.setQueryAge(20);
List<PrimaryStudent> stuList;
stuList = studentDao.selectUseFieldAlias(param);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
(2 ) 使用
步骤:
- 接口方法
List<PrimaryStudent> selectUseDiffResultMap(QueryParam param);
- mapper 文件:
<!-- 创建 resultMap
id: 自定义的唯一名称,在 <select> 使用
type: 期望转为的 java 对象的全限定名称或别名
-->
<resultMap id="primaryStudentMap"
type="com.g0rez.domain.PrimaryStudent">
<!-- 主键字段使用 id -->
<id column="id" property="stuId" />
<!-- 非主键字段使用 result-->
<result column="name" property="stuName"/>
<result column="age" property="stuAge" />
</resultMap>
<!--resultMap: resultMap 标签中的 id 属性值 -->
<select id="selectUseDiffResultMap" resultMap="primaryStudentMap">
select id,name,email,age from student
where name=#{queryName} or age=#{queryAge}
</select>
- 测试方法
@Test
public void testSelectUseDiffResultMap(){
QueryParam param = new QueryParam();
param.setQueryName(" 李力");
param.setQueryAge(20);
List<PrimaryStudent> stuList;
stuList = studentDao.selectUseDiffResultMap(param);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
3.4 模糊 like
模糊查询的实现有两种方式, 一是 java 代码中给查询数据加上“%” ; 二是在 mapper 文件 sql 语句的
条件位置加上“%”
需求:查询姓名有“力”的
例 例 1: java 代码中提供要查询的 “%力% ”
接口方法:
List<Student> selectLikeFirst(String name);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectLikeFirst" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student
where name like #{studentName}
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectLikeOne(){
String name="% 力%";
List<Student> stuList = studentDao.selectLikeFirst(name);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
例 2:mapper 文件中使用 like name "%" #{xxx} "%"
接口方法:
List<Student> selectLikeSecond(String name);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectLikeSecond" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student
where name like "%" #{studentName} "%"
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectLikeSecond(){
String name=" 力";
List<Student> stuList = studentDao.selectLikeSecond(name);
stuList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
第4章 MyBatis框架动态SQL
内容列表
◼ 动态 SQL-if
◼ 动态 SQL-where
◼ 动态 SQL-foreach
◼ 动态 SQL- 片段
动态SQL,通过 MyBatis 提供的各种标签对条件作出判断以实现动态拼接 SQL 语句。这里的条件判断使用的表达式为 OGNL 表达式。常用的动态 SQL 标签有
动态SQL,主要用于解决查询条件不确定的情况:在程序运行期间,根据用户提交的查询条件进行查询。提交的查询条件不同,执行的 SQL 语句不同。若将每种可能的情况均逐一列出,对所有条件进行排列组合,将会出现大量的 SQL 语句。此时,可使用动态 SQL 来解决这样的问题
4.1 环境准备
创建新的 maven 项目,加入 mybatis , mysql 驱动依赖
创建实体类 Student , StudentDao 接口,StudentDao.xml , mybatis.xml , 测试类
使用之前的表 student。
在 mapper 的动态 SQL 中若出现大于号(>)、小于号(<)、大于等于号(>=),小于等于号(<=)等符号,最好将其转换为实体符号。否则,XML 可能会出现解析出错问题。
特别是对于小于号(<),在 XML 中是绝不能出现的。否则解析 mapper 文件会出错。
实体符号:
< 小于 <
> 大于 >
>= 大于等于 >=
<= 小于等于 <=
4.2 动态 SQL 之
对于该标签的执行,当 test 的值为 true 时,会将其包含的 SQL 片断拼接到其所在的 SQL 语句中。
语法:
接口方法:
List<Student> selectStudentIf(Student student);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectStudentIf" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student
where 1=1
<if test="name != null and name !='' ">
and name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age > 0 ">
and age > #{age}
</if>
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelect() throws IOException {
Student param = new Student();
param.setName(" 李力");
param.setAge(18);
List<Student> studentList = studentDao.selectStudentIf(param);
studentList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
4.3 动态 SQL 之
使用
where 子句。需要注意的是,第一个
语法:
<where> 其他动态 sql </where>
接口方法:
List<Student> selectStudentWhere(Student student);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectStudentWhere" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student
<where>
<if test="name != null and name !='' ">
and name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age > 0 ">
and age > #{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectWhere() throws IOException {
Student param = new Student();
param.setName(" 李力");
param.setAge(18);
List<Student> studentList = studentDao.selectStudentWhere(param);
studentList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
4.4 动态 SQL 之
➢ collection 表示要遍历的集合类型, list ,array 等。
➢ open、close、separator 为对遍历内容的 SQL 拼接。
语法:
<foreach collection=" 集合类型" open=" 开始的字符" close=" 结束的字符"
item=" 集合中的成员" separator=" 集合成员之间的分隔符">
#{item 的值}
</foreach>
(1)遍历 List< 简单类型>
表达式中的 List 使用 list 表示,其大小使用 list.size 表示。
需求:查询学生 id 是 1002,1005,1006
接口方法:
List<Student> selectStudentForList(List<Integer> idList);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectStudentForList" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student
<if test="list !=null and list.size > 0 ">
where id in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" item="stuid" separator=",">
#{stuid}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectForList() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1002);
list.add(1005);
list.add(1006);
List<Student> studentList = studentDao.selectStudentForList(list);
studentList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
(2)遍历 List< 对象类型>
接口方法:
List<Student> selectStudentForList2(List<Student> stuList);
mapper 文件:
<select id="selectStudentForList2" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student
<if test="list !=null and list.size > 0 ">
where id in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" item="stuobject" separator=",">
#{stuobject.id}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectForList2() {
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setId(1002);
list.add(s1);
s1 = new Student();
s1.setId(1005);
list.add(s1);
List<Student> studentList = studentDao.selectStudentForList2(list);
studentList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
4.5 动态 SQL 之代码片段
接口方法:
List<Student> selectStudentSqlFragment(List<Student> stuList);
mapper 文件:
<!-- 创建 sql 片段 id: 片段的自定义名称 -->
<sql id="studentSql">
select id,name,email,age from student
</sql>
<select id="selectStudentSqlFragment" resultType="com.g0rez.domain.Student">
<!-- 引用 sql 片段 -->
<include refid="studentSql"/>
<if test="list !=null and list.size > 0 ">
where id in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" item="stuobject" separator=",">
#{stuobject.id}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
测试方法:
@Test
public void testSelectSqlFragment() {
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setId(1002);
list.add(s1);
s1 = new Student();
s1.setId(1005);
list.add(s1);
List<Student> studentList = studentDao.selectStudentSqlFragment(list);
studentList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
第5 章 MyBatis 配置文件
内容列表
◼ 主配置文件
◼ dataSource 标签
◼ 事务
◼ 别名
◼ mapper 文件
5.1 主配置文件
之前项目中使用的 mybatis.xml 是主配置文件。
主配置文件特点:
1. xml 文件,需要在头部使用约束文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
2.根元素,
3.主要包含内容:
➢ 定义别名
➢ 数据源
➢ mapper 文件
5.2 dataSource 标签
Mybatis 中访问数据库,可以连接池技术,但它采用的是自己的连接池技术。在 Mybatis 的 mybatis.xml配置文件中,通过
5.2.1 dataSource 类型
上图看出 Mybatis 将数据源分为三类:
UNPOOLED 不使用连接池的数据源
POOLED 使用连接池的数据源
JNDI 使用 JNDI 实现的数据源
其中 UNPOOLED ,POOLED 数据源实现了 javax.sq.DataSource 接口, JNDI 和前面两个实现方式不同,了解可以。
5.2.2 dataSource 配置
在 MyBatis.xml 主配置文件,配置 dataSource:
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 连接数据库的四个要素 -->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm?charset=utf-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
MyBatis 在初始化时,根据
type=”POOLED”:MyBatis 会创建 PooledDataSource 实例
type=”UNPOOLED” : MyBatis 会创建 UnpooledDataSource 实例
type=”JNDI”:MyBatis 会从 JNDI 服务上查找 DataSource 实例,然后返回使用
5.3 事务
(1)默认需要手动提交事务
Mybatis 框架是对 JDBC 的封装,所以 Mybatis 框架的事务控制方式,本身也是用 JDBC 的 Connection对象的 commit(), rollback() .
Connection 对象的 setAutoCommit()方法来设置事务提交方式的。自动提交和手工提交、
该标签用于指定MyBatis所使用的事务管理器。MyBatis支持两种事务管理器类型:JDBC 与MANAGED。
➢ JDBC:使用 JDBC 的事务管理机制。即,通过 Connection 的 commit()方法提交,通过 rollback()方法回滚。但默认情况下,MyBatis 将自动提交功能关闭了,改为了手动提交。即程序中需要显式的对事务进行提交或回滚。从日志的输出信息中可以看到。
MANAGED:由容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(如 Spring 容器).
(2)自动提交事务
设置自动提交的方式,factory 的 openSession() 分为有参数和无参数的。
有参数为 true,使用自动提交,可以修改 MyBatisUtil 的 getSqlSession()方法。
session = factory.openSession(true);
再执行 insert 操作,无需执行 session.commit(),事务是自动提交的
5.4 使用数据库属性配置文件
为 了方便对数据库连接的管理,DB 连接四要素数据一般都是存放在一个专门的属性文件中的。MyBatis
主配置文件需要从这个属性文件中读取这些数据。
步骤:
(1)在 classpath 路径下,建 创建 properties 文件
在 resources 目录创建 jdbc.properties 文件,文件名称自定义。
(2)使用 properties 标签
修改主配置文件,文件开始位置加入:
(3) 使用 key 指定值
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 使用 properties 文件 : 语法 ${key}-->
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
5.5 typeAliases (类型别名)
Mybatis 支持默认别名,我们也可以采用自定义别名方式来开发,主要使用在 select resultType="别名"
mybatis.xml 主配置文件定义别名:
<typeAliases>
<!--
定义单个类型的别名
type: 类型的全限定名称
alias: 自定义别名
-->
<typeAlias type="com.g0rez.domain.Student" alias="mystudent"/>
<!--
批量定义别名,扫描整个包下的类,别名为类名(首字母大写或小写都可以)
name: 包名
-->
<package name="com.g0rez.domain"/>
<package name="... 其他包"/>
</typeAliases>
mapper.xml 文件,使用别名表示类型
<select id="selectStudents" resultType="mystudent">
select id,name,email,age from student
</select>
5.6 mappers (映射器)
(1)mapper resource=" " /
使用相对于类路径的资源,从 classpath 路径查找文件
例如:
<mapper resource="com/g0rez/dao/StudentDao.xml" />
(2)package name=""/
指定包下的所有 Dao 接口
如:
<package name="com.g0rez.dao"/>
注意:此种方法要求 Dao 接口名称和 mapper 映射文件名称相同,且在同一个目录中。
第6 章 扩展
内容列表
◼ PageHelper
6.1 PageHelper
6.1.1 Mybatis 通用分页插件
https://github.com/pagehelper/Mybatis-PageHelper
PageHelper 支持多种数据库:
-
Oracle
-
Mysql
-
MariaDB
-
SQLite
-
Hsqldb
-
PostgreSQL
-
DB2
-
SqlServer(2005,2008)
-
Informix
-
H2
-
SqlServer2012
-
Derby
-
Phoenix
6.1.2 于 基于 PageHelper 分页: :
实现步骤:
(1)maven 坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.1.10</version>
</dependency>
(2)加入 plugin 配置
在
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor" />
</plugins>
(3)PageHelper 对象
查询语句之前调用 PageHelper.startPage 静态方法。
除了 PageHelper.startPage 方法外,还提供了类似用法的 PageHelper.offsetPage 方法。在你需要进行分页的 MyBatis 查询方法前调用 PageHelper.startPage 静态方法即可,紧跟在这个方法后的第一个 MyBatis 查询方法会被进行分页。
@Test
public void testSelect() throws IOException {
// 获取第 1 页,3 条内容
PageHelper.startPage(1,3);
List<Student> studentList = studentDao.selectStudents();
studentList.forEach( stu -> System.out.println(stu));
}
本文来自博客园,作者:guoyuxin3,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/guoyuxin3/p/15374297.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号