近期总结
总结
一.近期学习总结:
1:从刚开始的java学习中,大多数的语法均是从c语言中照搬过来,其中最开始不同的是java语言的输入与输出。
Java语言的输出分为:第一种:System.out.print 第二种:System.out.println 第三种:System.out.printf。这三种的区别如下:
第一种为一般的标准输出,输出会自动将括号中的内容转换成字符串输出,如果括号中是一个对象的话,就会自动调用toString()方法。该输出方式不会换行。如:
public class Main{
Public static void main(String[] args){
int a = 2;
System.out.print(a);
System.out.print(“a”);
System.out.print(“a”);
System.out.print(“Hello World”);
}
}
输出结果:2aHello World
第二种System.out.println为一般的标准输出和在输出末尾加换行,其用法和System.out.print相同,只是在末尾加个换行符。如:
public class Main{
Public static void main(String[] args){
int a = 2;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(“a”);
System.out.println(“Hello World”);
}
}
输出结果:2
a
System.out.print(“Hello World”);
第三种System.out.printf为格式化输出,其输出基本沿用c语言,如:
public class Main{
Public static void main(String[] args){
int A = 65;
System.out.printf("%d",A);
System.out.printf("%c",A);
System.out.printf("Hello World");
}
}
输出结果:65AHello World。
Java语言的输入则更为复杂一点如下
1:首先导入Scanner包:import java.util.Scanner;
2:创建Scanner对象,实现从控制台获取信息:
Scanner input/*自己定义的名字*/ = new Scanner(System.in);
3:选择需要输入的类型
1:int: int a = input.nextInt();
2:float: float a = input.nextFloat():
3:double double a = input.nextDouble();
4:String: String sc = input.nextLine();
5:char: char c = input.next().charAt(0);
实例如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = input.nextInt();
float b = input.nextFloat();
double c = input.nextDouble();
String sc = input.nextLine();
char e = input.next().charAt(0);
System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"-"+c+"-"+sc+"-"+e);
}
}
输入:1 2.1 2.22 345
A
输出:1-2.1-2.22- 345-A
- 在java学习中与c语言不同的是c语言是面向过程的编程语言而java是面向对象的语言其中最有特点的是java语言中的类和对象。关于类和对象,其中类包括属性和方法,属性是指一些常量或者变量,而方法为在函数实行一定目的的行为。对象,就是在主函数中创建的特定的对象,而这个对象有具有在类中定义的属性和方法。
例:雨刷类
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {//主类
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Driver driver = new Driver();
driver.work();
}
}
Lever类

View类

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Driver {
private View view = new View();
private Agent agent = new Agent();
public Driver() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
Driver类
public Driver(View view, Agent agent) {
super();
this.view = view;
this.agent = agent;
}
public void work() {
int choice = 0;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
view.menu();
choice = input.nextInt();
switch(choice) {
case 1:this.agent.getLever().upPos();break;
case 2:this.agent.getLever().downPos();break;
case 3:this.agent.getDial().upPos();break;
case 4:this.agent.getDial().downPos();break;
case 0:System.exit(0);
}
this.agent.processSpeed();
view.display(this.agent.getLever().getPos(),
this.agent.getDial().getPos(),
this.agent.getBrush().getSpeed());
}
}
}
Dial类

Brush类

Agent类
public class Agent {//关联
private Lever lever;
private Dial dial;
private Brush brush;
public Agent() {
super();
lever = new Lever(1);
dial = new Dial(1);
brush = new Brush(0);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Agent(Lever lever, Dial dial, Brush brush) {
super();
this.lever = lever;
this.dial = dial;
this.brush = brush;
}
public Lever getLever() {
return lever;
}
public void setLever(Lever lever) {
this.lever = lever;
}
public Dial getDial() {
return dial;
}
public void setDial(Dial dial) {
this.dial = dial;
}
public Brush getBrush() {
return brush;
}
public void setBrush(Brush brush) {
this.brush = brush;
}
public void processSpeed() {
int speed = 0;
switch(this.lever.getPos()) {
case 1:speed = 0;break;//停止档位
case 2: //间歇档位
switch(this.dial.getPos()) {
case 1:speed = 4;break;//刻度盘为1
case 2:speed = 6;break;//刻度盘为2
case 3:speed = 12;break;//刻度盘为3
}break;
case 3:speed = 30;break;//低速档位
case 4:speed = 60;break;//高速档位
}
this.brush.setSpeed(speed);
}
}
在上述雨刷类中其中包括主类共有7个类
2.1主类主要是创建了一个对象,调用对象里面的work方法。
2.2Lever类创建了一个pos属性,并创建了构造方法,get,set,升档,降档的方法
2.3Brush类创建了speed属性,创建构造方法,get,set方法
2.4Dial类创建了一个pos属性,创建构造方法,get,set,升降刻度盘的方法
2.5View类 创建了一个输出方法和一个菜单方法
2.6Agent类 主要作用为解耦
2.7Driver类 主要作用为调用之前所创建的方法来实现对雨刷正常工作的需求
- java语言的三大特性;封装,继承,多态。
3.1:封装性:就是把类的属性私有化,再通过公有方法进行访问和修改
具体实现方法 将变量定义为私有及在变量前用private修饰,如后续想要调用或修改该属性则可以用get,set方法。
实例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Students stu = new Students(221112);
stu.print();
}
}
class Students{
private int id;
public Students(int id) {
super();
this.id = id;
}
public Students() {
super();
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void print() {
System.out.println(id);
}
}
输出221112
假如要更改id,在Students stu = new Students(221112);下面一行直接调用stu.id = 222222;编译器会报错。除非将Students中的private int id 改为 int id。
3.2:实现封装的好处
3.2.1:提高代码的安全性
3.2.2:隐藏代码的细节
3.2.3:便于修改代码和后续代码的维护
3.2继承性: 继承就是子类继承父类的特征和行为,使得子类对象具有父类的实例域和方法,或子类从父类继承方法,使得子类具有父类相同的行为,并且子类只能有一个父类,java的继承只能进行单继承(摒弃了c++的多继承),子类不能直接调用除了父类的私有属性之外的方法(也可间接的调用方法来调用父类属性)。继承的重写:对父类中的方法进行重写。
实例:如
import java.util.Scanner;
class Animal{
private char[] name = new char[10];
public Animal() {
super();
}
public Animal(char[] name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public char[] getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(char[] name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("动物睡觉");
}
}
class Sheep extends Animal{
}
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sheep sheep = new Sheep();
sheep.sleep();
}
}
输出:动物睡觉
重写:
@Override
class Sheep extends Animal{
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("羊吃草");
}
}
输出:羊吃草
3.3多态性:同一操作作用于不同的对象,可以有不同的解释,产生不同的执行结果。多态中有两种情况,向上转型和向下转型,向上转型是子类到父类,向下转型是父类到子类,两种情况都要有继承。Java里的程序分为编译阶段和运行阶段,当有了对象的多态性以后,我们在编译期,只能调用父类中声明的方法,但在运行期,我们实际执行的是子类重写父类的方法。
实例:如
import java.util.Scanner;
class Animal{
private char[] name = new char[10];
public Animal() {
super();
}
public Animal(char[] name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public char[] getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(char[] name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("动物睡觉");
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("动物进食");
}
}
class Sheep extends Animal{
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("羊睡觉");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("羊吃草");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("狗睡觉");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("狗吃肉");
}
}
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal1 = new Sheep();
animal1.sleep();
animal1.eat();
Animal animal2 = new Dog();
animal2.sleep();
animal2.eat();
}
}
输出:
羊睡觉
羊吃草
狗睡觉
狗吃肉
该例子为向上转型。
二.题目集总结
前言:知识点:java的基本的语法如:if—else,for、while循环,输入输出,String函数,类和对象,引用的使用。
设计与分析:
第二次题目集第二个:本题首先进行一个for循环判断1的个数,并将输入的每一个数字存入数组中,其次根据1的个数和输入字符串的长度判断是否满足null date的情况,如满足则输出null date 不满足则进行下一步判断,首先判断起始点0,在将之后的值全部加起来判断是否是奇校验在用if-else将每一种情况输出。
第三次题目集的第一个:首先根据题目要求写出类QusdraticEquation,根据类图
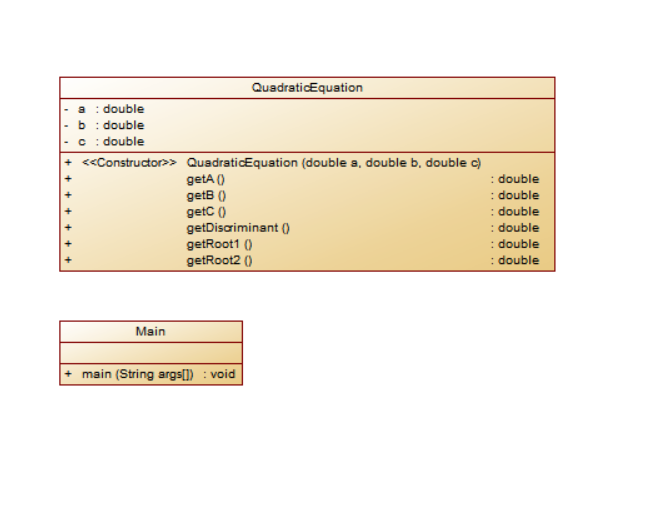
写出其三个私有属性构造方法,get,set方法,以及判断能否有根的方法getDiscriminant,以及两个获取根的函数。
第三次题目集的第二个:首先根据题目要求并根据主函数写出另一个Dateutil类,在这个类中根据类图
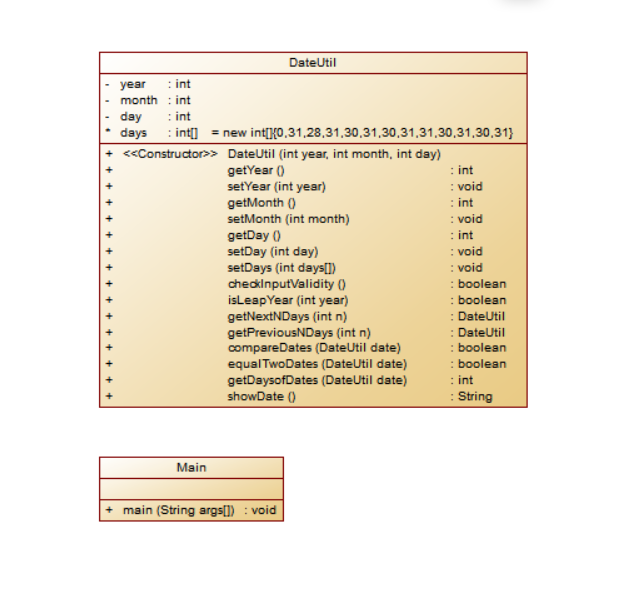
首先创建三个私有属性的year,month,day,在根据类图将各个方法写出来,其中最重要为求前n天方法,后n天方法,和两个日期相距的天数,在求前n天方法中,先判断是否是大于365天,在将每一种情况用if-else列出来,然后将剩余的天数进入for循环中,一天天的减,在用if-else进行枚举。其中求后n天算法基本与求前n天一致,也是先判断是否是大于365天,在将每一种情况用if-else列出来,然后将剩余的天数进入for循环中,一天天的加,在用if-else进行枚举。求相差n天时,用日期小的一天天加到日期大的,然后输出增加的天数即为相差天数。
第三次题目集的第三个:
其主要方法与第二题无异议,基本套用第二题的算法,只是因为增加了几个类,每次改值的时候均需要引用,根据类图
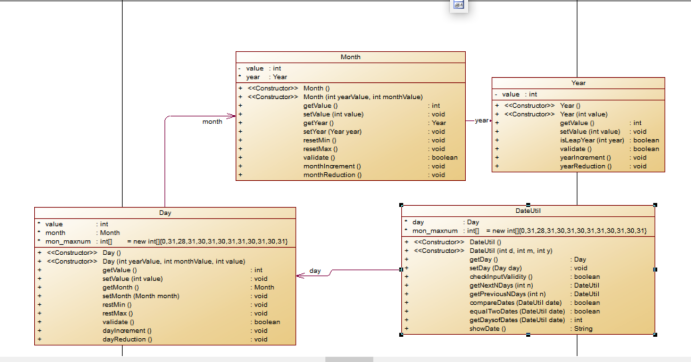
来设计每一个类所要的属性与方法。
踩坑心得:
题目集2第二题:
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String sc = input.nextLine();
int count = 0;
int num = 1;
int check = 0;
int sum = 0;
char[] a = new char[100];
for(int i=0;i<sc.length();i++) {
a[i] = sc.charAt(i);
if(sc.charAt(i)=='1') {
count++;
}
}
if(sc.length()<11||count==sc.length()){
System.out.println("null data");
}
else{
for(int i=0;i<sc.length();i++){
if(a[i]=='0'){
for(int j=i+1;j<i+10;j++){
sum = sum + a[j];
}
check = sum % 2;
sum = 0;
if(check==1){
if(a[i+10]=='1'){
System.out.println(num+":"+sc.substring(i+1,i+9));
num = num + 1;
}
else {
System.out.println(num+":"+"validate error");
num = num + 1;
}
}
if(check==0){
if(a[i+10]=='1'){
System.out.println(num+":"+"parity check error");
num = num + 1;
}
else if (a[i+10]=='0'){
System.out.println(num+":"+"validate error");
num = num + 1;
}
}
i = i + 10;
}
}
}
}
}
该题在提交过程最大的一个错误是对于奇校验的判断,奇校验判断是输入所需要的11个数里面全部的1的个数加起来是否为奇数而不是最后一位为奇数。
第三次题目集第一题:
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = Double.parseDouble(input.next());
double b = Double.parseDouble(input.next());
double c = Double.parseDouble(input.next());
if(a == 0){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
//create a QuadraticEquation object
QuadraticEquation equation = new QuadraticEquation(a, b, c);
//get value of b * b - 4 * a * c
double discriminant = equation.getDiscriminant();
System.out.println("a=" + equation.getA() +
",b=" + equation.getB() +
",c=" + equation.getC()+":");
if (discriminant < 0) {
System.out.println("The equation has no roots.");
}
else if (discriminant == 0)
{
System.out.println("The root is " +
String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1()));
}
else // (discriminant >= 0)
{
System.out.println("The roots are " +
String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1())
+ " and " + String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot2()));
}
}
}
class QuadraticEquation{
//your code
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
public QuadraticEquation(double a,double b,double c) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
public double getA() {
return a;
}
public double getB() {
return b;
}
public double getC() {
return c;
}
public double getDiscriminant() {
double dealt = 0;
dealt = b * b - 4 * a * c;
return dealt;
}
public double getRoot1() {
double root1 = 0;
root1 = (-b + Math.sqrt(getDiscriminant())) / 2 * a;
return root1;
}
public double getRoot2() {
double root2 = 0;
root2 = (-b - Math.sqrt(getDiscriminant())) / 2 * a;
return root2;
}
}
该题并没有什么踩坑的地方,只需要注意求根公式是否出错。
第三次题目集第二题:
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(
date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class DateUtil{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
int[] days = new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public DateUtil(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
public void setDays(int[] days) {
this.days = days;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){
boolean checkInputValidity;
int[] days = new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(isLeapYear(year))
days[2] = 29;
checkInputValidity=(year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>0&&month<=12&&day<=days[month]&&day>0);
return checkInputValidity;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year){
boolean isLeapYear;
isLeapYear = (year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0;
return isLeapYear;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {
while(n>365) {
if(isLeapYear(year) && month <= 2 || isLeapYear(year+1) && month > 2){
if(month == 2 && day == 29){
day = 1;
month = month + 1;
}
year = year + 1;
n = n - 366;
}
else{
year++;
n = n - 365;
}
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
day++;
if(isLeapYear(year)) {
days[2] = 29;
}
if(day > days[month]) {
if(month<12) {
month = month + 1;
day = 1;
}
else {
month = 1;
year = year + 1;
day = 1;
}
}
}
return this;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {
while(n > 365){
if(isLeapYear(year)) {
year = year - 1;
n = n - 366;
}
if(!isLeapYear(year)) {
year = year - 1;
n = n - 365;
}
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
if(isLeapYear(year)) {
days[2] = 29;
}
day--;
if(day <= 0) {
month = month - 1;
day = days[month];
if(month <= 0) {
day = 31;
month = 12;
year = year - 1;
}
}
}
return this;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
if(year > date.getYear()) {
return true;
}
else if(year == date.getYear() && month > date.getMonth()) {
return true;
}
else if(year == date.getYear() && month == date.getMonth() && day > date.getDay()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
if(year == date.getYear()) {
if(month == date.getMonth()) {
if(day == date.getDay()) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) {
int sum = 0;
if(!compareDates(date)) {
while(true) {
day++;
sum++;
if(isLeapYear(year)) {
days[2] = 29;
}
else {
days[2] = 28;
}
if(day > days[month]) {
if(month < 12) {
month++;
day = 1;
}
else {
month = 1;
day = 1;
year++;
}
}
if(equalTwoDates(date)){
break;
}
}
}
return sum;
}
public String showDate(){
return year + "-" + month + "-" + day;
}
}
该题在提交过程中出现较大问题主要为求前n天,求相差天数,在求后n天时,因为未对最后一年有没有过2月做校验,导致了天数多一天,求相差天数的过程中,最开始的想法是用大的时间减去小的时间,因为未考虑周全导致算出答案错误,后改变算法从小的时间一天天加到大的时间,增加的天数即为相差的天数。
第三次第三次题目:
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println( fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class Year{
private int value;
public Year() {
}
public Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year){
boolean isLeapYear;
isLeapYear = (year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0;
return isLeapYear;
}
public boolean validate() {
boolean validate;
validate = (value>=1900&&value<=2050);
return validate;
}
public void yearIncrement() {
this.value = value + 1;
}
public void yearReduction() {
this.value = value - 1;
}
}
class Month{
private int value;
Year year ;
public Month() {
super();
}
public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){
this.year=new Year(yearValue);
this.value=monthValue;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void resetMin(){
value=1;
}
public void resetMax(){
value=12;
}
public boolean validate(){
boolean validate;
validate = (value>=1&&value<=12);
return validate;
}
public void monthIncrement(){
value=value+1;
}
public void monthReduction(){
value=value-1;
}
}
class Day{
int value;
Month month;
int[] mon_maxnum = new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public Day() {
super();
}
public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int value){
this.month=new Month(yearValue,monthValue);
this.value=value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public void restMin() {
value = 1;
}
public void restMax() {
value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()];
}
public boolean validate() {
boolean validate;
if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(this.getMonth().getYear().getValue()))
mon_maxnum[2]=29;
validate = (value>=1&&value<=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]);
return validate;
}
public void dayIncrement() {
value=value+1;
}
public void dayReduction() {
value=value-1;
}
}
class DateUtil{
Day day;
int[] mon_maxnum = new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public DateUtil() {
super();
}
public DateUtil(int d,int m,int y){
this.day=new Day(d,m,y);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){
boolean checkInputValidity;
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())) {
mon_maxnum[2] = 29;
}
checkInputValidity = (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().validate()&&this.getDay().getMonth().validate()&&this.day.getValue()>=1&&this.day.getValue()<=mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]);
return checkInputValidity;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {
while(n>365) {
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) && this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() <= 2||this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1) && this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() > 2){
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == 2 && this.day.getValue() == 29){
this.getDay().setValue(1);
this.getDay().getMonth().setValue(3);
}
this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
n = n - 366;
}
else{
this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
n = n - 365;
}
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
this.day.dayIncrement();
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())) {
mon_maxnum[2] = 29;
}
else{
mon_maxnum[2] = 28;
}
if(this.day.getValue() > mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]) {
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==12) {
this.getDay().getMonth().setValue(1);
this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
this.day.setValue(1);
}
else {
this.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement();
this.day.setValue(1);
}
}
}
return this;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) {
int[] mon_maxnum = new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
while(n > 365){
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())) {
this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
n = n - 366;
}
if(!this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())) {
this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
n = n - 365;
}
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())) {
mon_maxnum[2] = 29;
}
else{
mon_maxnum[2] = 28;
}
this.day.dayReduction();
if(this.day.getValue() <= 0) {
this.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction();
this.day.setValue(mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]);
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() <= 0) {
this.day.setValue(31);
this.getDay().getMonth().setValue(12);
this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();
}
}
}
return this;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return true;
}
else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) {
return true;
}
else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() && this.getDay().getValue() > date.day.getValue()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) {
if(this.getDay().getValue() == date.getDay().getValue()) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) {
int sum = 0;
while(true) {
if(equalTwoDates(date)){
sum = 0;
break;
}
if(!compareDates(date)) {
day.dayIncrement();
sum++;
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())) {
mon_maxnum[2] = 29;
}
else {
mon_maxnum[2] = 28;
}
if(day.getValue()>mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]) {
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() < 12) {
this.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement();
this.getDay().setValue(1);
}
else {
this.getDay().getMonth().setValue(1);
this.getDay().setValue(1);
this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();
}
}
if(equalTwoDates(date)){
break;
}
}
else {
if(equalTwoDates(date)){
sum = 0;
break;
}
date.getDay().dayIncrement();
sum++;
if(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())) {
mon_maxnum[2] = 29;
}
else {
mon_maxnum[2] = 28;
}
if(date.getDay().getValue()>mon_maxnum[date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]) {
if(date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() < 12) {
date.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement();
date.day.setValue(1);
}
else {
date.getDay().getMonth().setValue(1);
date.getDay().setValue(1);
date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();;
}
}
if(equalTwoDates(date)){
break;
}
}
}
return sum;
}
public String showDate(){
return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + "-" + this.getDay().getValue();
}
}
关于该题的最大的难点为怎么引用,要更改年份必须得从day,在到month,最后才到年份,该题的算法基本还是与第二题一致,直接将第二题的代码改为引用的格式。
改进建议:
对于第二次题目集的第二次作业,因其仅需实现一个功能,就是对输入字符串进行判断其是否满足哪种情况,所以我认为该题没有什么改进建议。
对于第三次题目集第一次作业:该题只是简单的类的应用,其主函数在给出的前提下,里面的属性与方法均已固定所以并不需要对改题目进行什么改进。
对于第三次题目集第二次作业:该题除了主类之外,仅有一个Dateutil类,未能完全的体现出java面向对象的特性,所以要将该代码修改出多个类,并解除代码的耦合性。
对于第三次题目集第三次作业:该题目虽然除了主类之后还有四个类,但是该题类设计的非常繁琐,要想修改或查看年份,月份,必须从day开始,这样仅会增加工程量,对其他的并没有什么很大的帮助,应该将类与类之间的耦合性解除,使得单个类能独立处理东西。
总结:通过这三次题目集的练习,实现了从c语言到java 语言的简单过渡。从第一次题目集基本与c语言的写法一致,只是输入和输出不一样,到第二次题目集比第一次更复杂的算法,再到最后一次题目集对类的创建及对类与类之间方法的调用,这三次题目集一步一步的将我从c语言的面向程序的思想调整为java语言面向对象的思想。对于这几次代码的编写,老师引导我们使用业界里阿里巴巴的代码格式,我也尽力的转变自己的代码格式,以及对编写代码后注释的编写,现在对我来说,对于多态的理解远远不到位,应该多去学习和领悟,对于java这么语言仅仅依靠课上学习,课后的pta作业是远远不够的,我还应该多去学习后续的课程。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号