前言
此篇博客演示可以移动的View
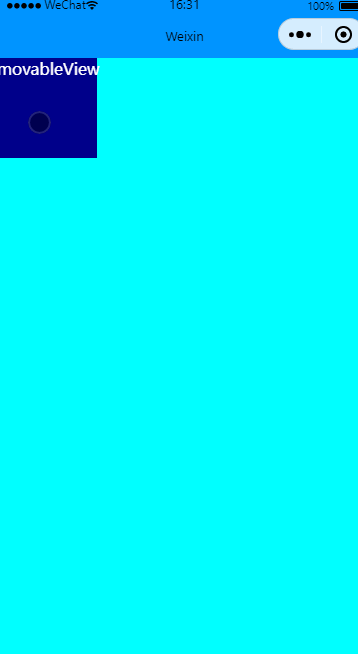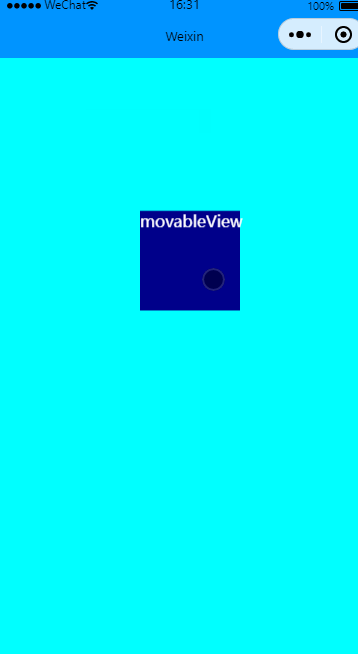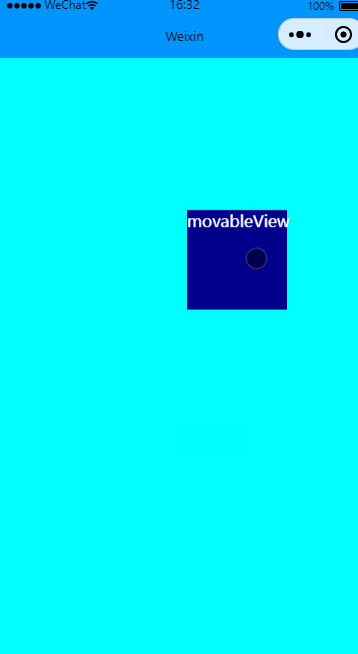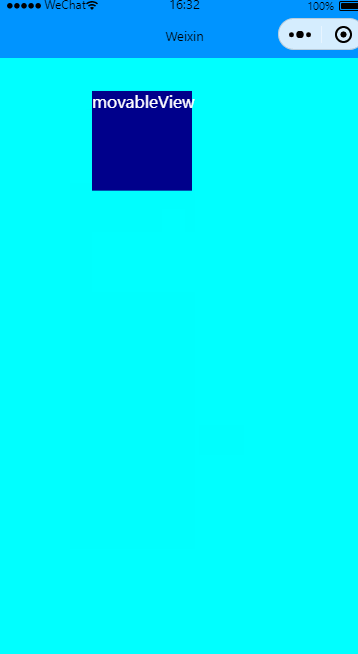
全方向移动
效果图
.js
Page({ /** * 页面的初始数据,这里需要提供x和y2个数据 */ data: { x:0, y:0 }, })
.wxml
<movable-area class="myMovableStyle"> <movable-view class="myMvableView" x="{{x}}" y="{{y}}" direction="all">movableView</movable-view> </movable-area>
.wxss
.myMovableStyle{ /* position属性用于指定一个元素在文档中的定位方式,因为这里设置了absolute 才让宽度与高度的百分比有功能 */ position: absolute; background-color: cyan; width: 100%; height: 100%; } .myMvableView{ position: absolute; background-color:darkblue; color: white; width: 200rpx; height: 200rpx; }
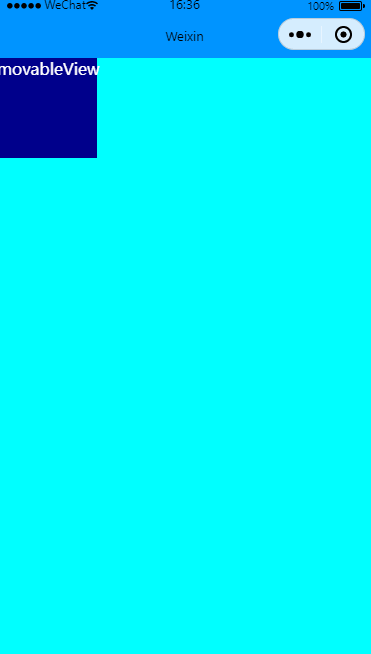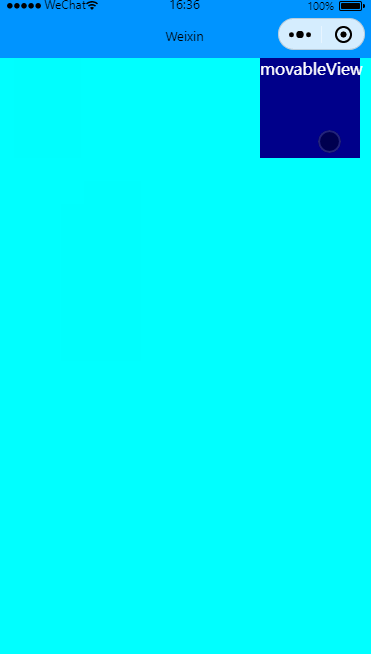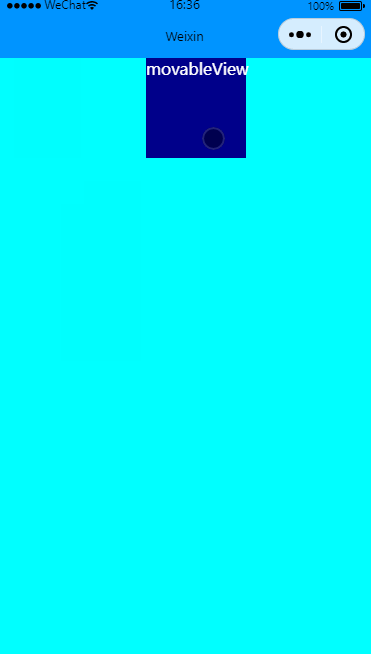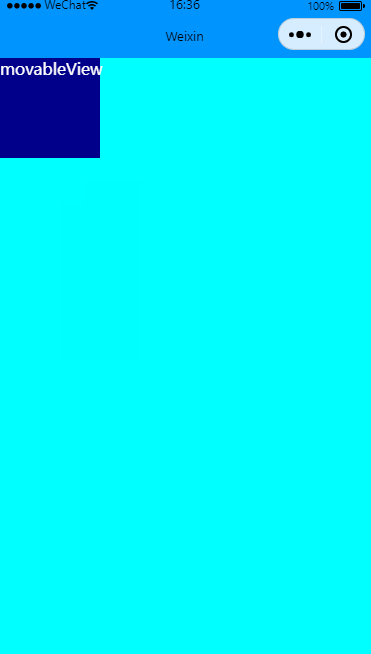
限制横竖方向移动
效果图:
.wxml
关键修改direction
<movable-area class="myMovableStyle"> <!--direction方向设置为横向horizontal 竖向为vertical --> <movable-view class="myMvableView" x="{{x}}" y="{{y}}" direction="vertical">movableView</movable-view> </movable-area>
可超出边界移动
效果图:

.wxml
在movable-view里增加out-of-bounds实现
<movable-area class="myMovableStyle"> <movable-view class="myMvableView" x="{{x}}" y="{{y}}" direction="all" out-of-bounds>movableView</movable-view> </movable-area>
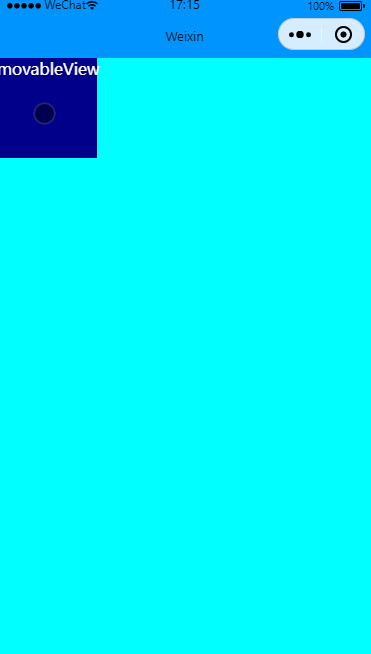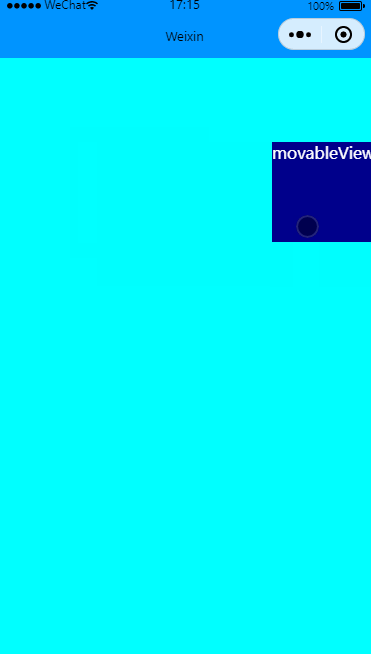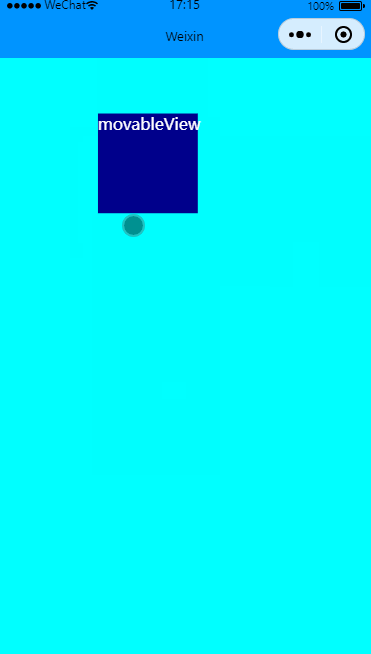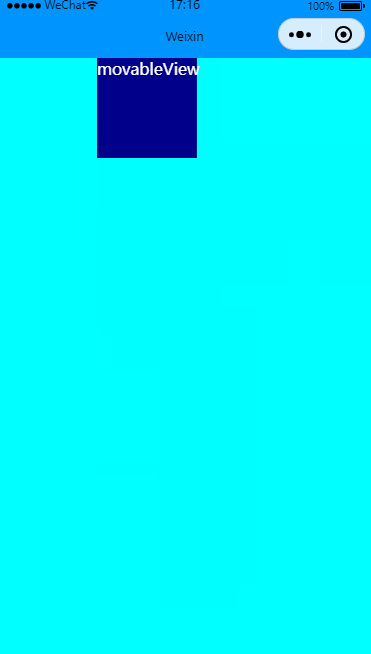
有惯性移动
效果图:
.wxml
在movable-view里增加inertia实现
<movable-area class="myMovableStyle"> <movable-view class="myMvableView" x="{{x}}" y="{{y}}" direction="all" inertia>movableView</movable-view> </movable-area>
缩放
效果图:

.js
// pages/demo/demo.js Page({ data: { scale: 0, }, onChange(e) { console.log(e.detail) }, onScale(e) { console.log(e.detail) }, //放大 enlargeBtn: function () { this.setData( { scale: this.data.scale + 1 }) }, //缩小 narrowBtn: function () { this.setData( { scale: this.data.scale - 1 }) } })
.wxml
<!--pages/demo/demo.wxml--> <movable-area class="myMovableStyle"> <movable-view class="myMvableView" x="{{x}}" y="{{y}}" direction="all" bindchange="onChange" bindscale="onScale" scale scale-min="0.5" scale-max="4" scale-value="{{scale}}">movableView</movable-view> </movable-area> <view class="myButtonParentView"> <button bindtap="enlargeBtn" class="myButton">放大</button> <button bindtap="narrowBtn" class="myButton">缩小</button> </view>
.wxss
/* pages/demo/demo.wxss */ .myMovableStyle { /* position属性用于指定一个元素在文档中的定位方式,因为这里设置了absolute 才让宽度与高度的百分比有功能 */ position: absolute; background-color: cyan; width: 100%; height: 100%; } .myMvableView { position: absolute; top: 40%; left: 40%; background-color: darkblue; color: white; width: 200rpx; height: 200rpx; } .myButtonParentView { display: flex; position: absolute; bottom: 0%; width: 100%; height: 100rpx; } /* 指定某个child view的风格 */ .myButtonParentView button:nth-child(1) { display: flex; /* align-items 属性将所有直接子节点上的 align-self 值设置为一个组。align-self 属性设置项目在其包含块中在交叉轴方向上的对齐方式。 */ align-items: center; /* justify-content 属性定义了浏览器之间,如何分配顺着弹性容器主轴 (或者网格行轴) 的元素之间及其周围的空间。 */ justify-content: center; background-color: lightskyblue; color: tomato; } .myButtonParentView button:nth-child(2) { display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center; background-color: lightgreen; color: tomato; }
End
本文来自博客园,作者:观心静 ,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/guanxinjing/p/16555017.html
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但必须给出原文链接,并保留此段声明,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号