在应用开过程中,我们常常会有一些加解密的场景需求,如API接口返回一个加密字符串,在下次调用时将加密字符串带入请求,进行解密验证并拿到加密内容。ASP.NET CORE提供了一个通用加解密组件 Data Protection。
设计原则
Data Protection的设计思路主要基于以下几个原则:
- 尽可能简化配置,默认情况下零配置即可正常运行。
- 提供简单可用的API
- 加密密钥的管理机制应该是隐蔽的,加密的算法选择和生存周期由系统选择
- 加密密钥尽可能得到保护,默认情况下,保护机制由系统提供
简单说就是 组件尽可能使用简单。实现的算法和保护机制不向开发人员公开,避免泄露问题。
主要的Package
Data Protection涉及到的主要Package如下,根据需要引用。
Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection.Abstractions标准的.NET CORE抽象层组件包命名方式。包含IDataProtectionProvider、IDataProtector等主要的接口服务。Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection上一个抽象包的具体实现包,包括核心加密操作、密钥管理、配置和扩展性。Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection.Extensions扩展包。提供了创建实例的工厂方法、密钥的存储扩展方法。在非DI模式下会用到这个包。Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection.SystemWeb实现对ASP.NET4.x中的<machineKey>加解密机制的兼容。Microsoft.AspNetCore.Cryptography.KeyDerivation提供 PBKDF2 密码哈希例程的实现。在需要使用Hash加密的时候使用。
简单使用
那么,我们现在看看 Data Protection 组件到底是怎样的一个使用方便~~
来自官方文档的案例:
using System;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// add data protection services
var serviceCollection = new ServiceCollection();
serviceCollection.AddDataProtection();
var services = serviceCollection.BuildServiceProvider();
// create an instance of MyClass using the service provider
var instance = ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance<MyClass>(services);
instance.RunSample();
}
public class MyClass
{
IDataProtector _protector;
// the 'provider' parameter is provided by DI
public MyClass(IDataProtectionProvider provider)
{
_protector = provider.CreateProtector("Contoso.MyClass.v1");
}
public void RunSample()
{
Console.Write("Enter input: ");
string input = Console.ReadLine();
// protect the payload
string protectedPayload = _protector.Protect(input);
Console.WriteLine($"Protect returned: {protectedPayload}");
// unprotect the payload
string unprotectedPayload = _protector.Unprotect(protectedPayload);
Console.WriteLine($"Unprotect returned: {unprotectedPayload}");
}
}
}
/*
* SAMPLE OUTPUT
*
* Enter input: Hello world!
* Protect returned: CfDJ8ICcgQwZZhlAlTZT...OdfH66i1PnGmpCR5e441xQ
* Unprotect returned: Hello world!
*/
确实很简单啊!!核心步骤:
- 注入,serviceCollection.AddDataProtection();
- 创建,IDataProtector _protector =provider.CreateProtector("Contoso.MyClass.v1");
太多真相被掩盖,加密方式是什么?有过期时间吗?有密钥吗?
我们继续往下。。
IDataProtectionProvider IDataProtector
- IDataProtectionProvider 看名字可知是基于微软的Provider模式,用于提供创建实例的策略。通过调用
IDataProtectionProvider.CreateProtector(purpose)方法创建 IDataProtector 对象。 - IDataProtector 则是负责加解密的服务,它主要提供了protect、Unprotect两类方法(每类都有很多重载和扩展方法)。简单理解即 protect 用于加密,unprotect用于解密。
IDataProtectionProvider的Create方法参数是一个字符串,用于提供隔离性功能。通过不通的字符串创建的 IDataProtector 即使对同一个对象加密,得到的加密结果也是不同的。同时 IDataProtector 本身也是隐式的IDataProtectionProvider,同样提供的 CreateProtector(purpose) 方法。这意味着可以方便的实现多租户应用模式。
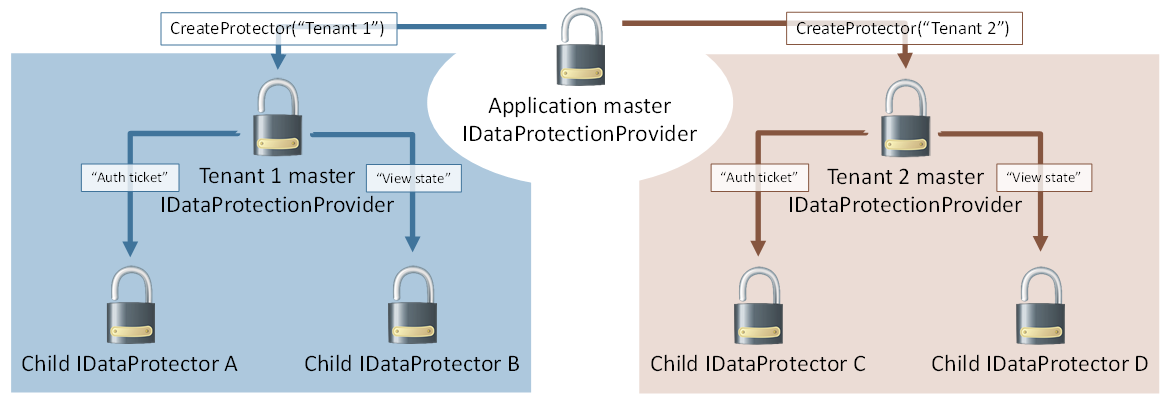
这里有几个注意点:
- IDataProtectionProvider、IDataProtector的实例都是线程安全的。
- unprotect方法是通过抛出异常的方式来告知调用者解密失败。异常类为
CryptographicException。
生存周期
如果像对加密设置生存周期,则需要使用 ITimeLimitedDataProtector 接口。它的实现存在于 Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection.Extensions 包中。它的实例创建方式也很简单,可以直接通过可以直接通过IDataProtector转换: IDataProtector.ToTimeLimitedDataProtector 。
ITimeLimitedDataProtector 提供的API和IDataProtector类似,只是多了一个生存周期参数。
- Protect(byte[] plaintext, DateTimeOffset expiration) : byte[]
- Protect(byte[] plaintext, TimeSpan lifetime) : byte[]
- Protect(byte[] plaintext) : byte[]
- Protect(string plaintext, DateTimeOffset expiration) : string
- Protect(string plaintext, TimeSpan lifetime) : string
- Protect(string plaintext) : string
哈希密码
Data Protection同样也提供了Hash加密的机制。算法采用 PBKDF2 algorithm ,据说比.net framework的实现算法性能好很多。
具体使用方式如下:
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Cryptography.KeyDerivation;
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("Enter a password: ");
string password = Console.ReadLine();
// generate a 128-bit salt using a secure PRNG
byte[] salt = new byte[128 / 8];
using (var rng = RandomNumberGenerator.Create())
{
rng.GetBytes(salt);
}
Console.WriteLine($"Salt: {Convert.ToBase64String(salt)}");
// derive a 256-bit subkey (use HMACSHA1 with 10,000 iterations)
string hashed = Convert.ToBase64String(KeyDerivation.Pbkdf2(
password: password,
salt: salt,
prf: KeyDerivationPrf.HMACSHA1,
iterationCount: 10000,
numBytesRequested: 256 / 8));
Console.WriteLine($"Hashed: {hashed}");
}
}
/*
* SAMPLE OUTPUT
*
* Enter a password: Xtw9NMgx
* Salt: NZsP6NnmfBuYeJrrAKNuVQ==
* Hashed: /OOoOer10+tGwTRDTrQSoeCxVTFr6dtYly7d0cPxIak=
*/
说好的更加简单的API呢?现在需要你自己去选择HASH算法、加盐、迭代次数!!
IPersistedDataProtector
IPersistedDataProtector是一个特殊的解密接口服务,在某些场景下如我们希望解密一些已经过期或者密钥已经被销毁的加密字符串时,可以使用以下方法:
IPersistedDataProtector.DangerousUnprotect(byte[] protectedData, bool ignoreRevocationErrors,out bool requiresMigration, out bool wasRevoked)
来自官方的示例代码:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection.KeyManagement;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var serviceCollection = new ServiceCollection();
serviceCollection.AddDataProtection()
// point at a specific folder and use DPAPI to encrypt keys
.PersistKeysToFileSystem(new DirectoryInfo(@"c:\temp-keys"))
.ProtectKeysWithDpapi();
var services = serviceCollection.BuildServiceProvider();
// get a protector and perform a protect operation
var protector = services.GetDataProtector("Sample.DangerousUnprotect");
Console.Write("Input: ");
byte[] input = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Console.ReadLine());
var protectedData = protector.Protect(input);
Console.WriteLine($"Protected payload: {Convert.ToBase64String(protectedData)}");
// demonstrate that the payload round-trips properly
var roundTripped = protector.Unprotect(protectedData);
Console.WriteLine($"Round-tripped payload: {Encoding.UTF8.GetString(roundTripped)}");
// get a reference to the key manager and revoke all keys in the key ring
var keyManager = services.GetService<IKeyManager>();
Console.WriteLine("Revoking all keys in the key ring...");
keyManager.RevokeAllKeys(DateTimeOffset.Now, "Sample revocation.");
// try calling Protect - this should throw
Console.WriteLine("Calling Unprotect...");
try
{
var unprotectedPayload = protector.Unprotect(protectedData);
Console.WriteLine($"Unprotected payload: {Encoding.UTF8.GetString(unprotectedPayload)}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{ex.GetType().Name}: {ex.Message}");
}
// try calling DangerousUnprotect
Console.WriteLine("Calling DangerousUnprotect...");
try
{
IPersistedDataProtector persistedProtector = protector as IPersistedDataProtector;
if (persistedProtector == null)
{
throw new Exception("Can't call DangerousUnprotect.");
}
bool requiresMigration, wasRevoked;
var unprotectedPayload = persistedProtector.DangerousUnprotect(
protectedData: protectedData,
ignoreRevocationErrors: true,
requiresMigration: out requiresMigration,
wasRevoked: out wasRevoked);
Console.WriteLine($"Unprotected payload: {Encoding.UTF8.GetString(unprotectedPayload)}");
Console.WriteLine($"Requires migration = {requiresMigration}, was revoked = {wasRevoked}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{ex.GetType().Name}: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
/*
* SAMPLE OUTPUT
*
* Input: Hello!
* Protected payload: CfDJ8LHIzUCX1ZVBn2BZ...
* Round-tripped payload: Hello!
* Revoking all keys in the key ring...
* Calling Unprotect...
* CryptographicException: The key {...} has been revoked.
* Calling DangerousUnprotect...
* Unprotected payload: Hello!
* Requires migration = True, was revoked = True
*/
这里,
- requiresMigration,true表示密钥已过期或已回滚,不是当前默认的密钥。
- wasRevoked,true表示密钥已被销毁。
配置
ASP.NET CORE 提供了丰富的Api支持密码持久化配置和自定义功能。
-
PersistKeysToAzureBlobStorage、ProtectKeysWithAzureKeyVault。Azure云存储方案。
-
PersistKeysToFileSystem。本地文件系统存储方案,配置大概长下面这样,记录了加密算法、密钥以及依赖项
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <key id="7ae2f1e3-27ed-4148-9375-48035300c447" version="1"> <creationDate>2020-10-16T02:51:58.4681047Z</creationDate> <activationDate>2020-10-16T02:51:58.4559376Z</activationDate> <expirationDate>2021-01-14T02:51:58.4559376Z</expirationDate> <descriptor deserializerType="Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection.AuthenticatedEncryption.ConfigurationModel.AuthenticatedEncryptorDescriptorDeserializer, Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection, Version=3.1.6.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=adb9793829ddae60"> <descriptor> <encryption algorithm="AES_256_CBC" /> <validation algorithm="HMACSHA256" /> <masterKey p4:requiresEncryption="true" xmlns:p4="http://schemas.asp.net/2015/03/dataProtection"> <!-- Warning: the key below is in an unencrypted form. --> <value>8L1/o/JFl+nVOdxykHTbAs25PORJhLFyi2IdvdDTGTBFU+33d+v05YjykP9OdeWpl9ArI1BKN9bBk0qDfGLH+g==</value> </masterKey> </descriptor> </descriptor> </key> -
ProtectKeysWith*。通过该命名方式的扩展提供加密方式。例如
ProtectKeysWithCertificate -
SetDefaultKeyLifetime。 设置密钥生存周期,默认为90天。
-
SetApplicationName。设置应用名。默认情况下数据保护机制对各个应用是绝对隔离的。通过设置相同的应用名可以实现应用之间的密钥共享。
-
DisableAutomaticKeyGeneration。禁止密钥自动回滚。很多时候我们其实不希望密码发生变化或是在一个集群服务中,我们有专门的一台服务负责密钥的更新回滚,其他负载只要从共享的地方获取就好了。
-
UseCryptographicAlgorithms。使用自定义的加解密算法,例如
services.AddDataProtection() .UseCryptographicAlgorithms( new AuthenticatedEncryptorConfiguration() { EncryptionAlgorithm = EncryptionAlgorithm.AES_256_CBC, ValidationAlgorithm = ValidationAlgorithm.HMACSHA256 }); -
如果在Docker中配置,千万要将密钥配置放置公共区域,而非Docker容器内。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号