时间和日期相关函数
在编程中,程序员会经常使用到日期相关的函数,比如:统计某段代码执行话费的时间等等。
1)时间和日期相关函数,需要导入time包
2)time.Time 类型,用于表示时间
3)获取到当前时间的方法:
now := time.Now() //now 的类型就是time.Time
func main() {
//1.获取当前时间
now := time.Now()
fmt.Printf("now=%v now type=%T \n", now, now)
}

4)如何获取到其它的日期信息
func main() {
now := time.Now()
//2.通过now可以获取到年月日,时分秒
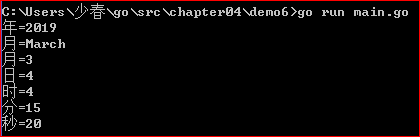
fmt.Printf("年=%v\n", now.Year())
fmt.Printf("月=%v\n", now.Month())
fmt.Printf("月=%v\n", int(now.Month()))
fmt.Printf("日=%v\n", now.Day())
fmt.Printf("时=%v\n", now.Hour())
fmt.Printf("分=%v\n", now.Minute())
fmt.Printf("秒=%v\n", now.Second())
}
5)格式化日期时间
(1)格式化的第一种方式:就是使用 Printf 或者Sprintf
func main() {
//格式化日期时间
now := time.Now()
fmt.Printf("当前年月日 %02d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d \n", now.Year(),
now.Month(), now.Day(), now.Hour(), now.Minute(), now.Second())
fmt.Printf("当前年月日 %d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d \n", now.Year(),
now.Month(), now.Day(), now.Hour(), now.Minute(), now.Second())
dateStr := fmt.Sprintf("当前年月日 %02d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d \n", now.Year(),
now.Month(), now.Day(), now.Hour(), now.Minute(), now.Second())
fmt.Printf("dateStr=%v \n", dateStr )
}

(2)格式化的第二种方式:使用 time.Format() 方法完成。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
now := time.Now()
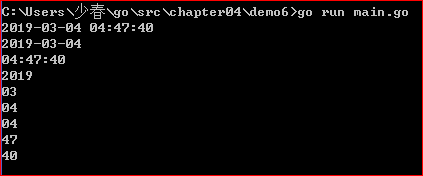
fmt.Printf(now.Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05"))
fmt.Println()
fmt.Printf(now.Format("2006-01-02"))
fmt.Println()
fmt.Printf(now.Format("15:04:05"))
fmt.Println()
fmt.Printf(now.Format("2006")) //打印年
fmt.Println()
fmt.Printf(now.Format("01")) //打印月
fmt.Println()
fmt.Printf(now.Format("02")) //打印日
fmt.Println()
fmt.Printf(now.Format("15")) //打印小时
fmt.Println()
fmt.Printf(now.Format("04")) //打印分
fmt.Println()
fmt.Printf(now.Format("05")) //打印秒
fmt.Println()
}
结果是:
对上面代码的说明:
"2006/01/02 15:04:05" 这个字符串的各个数字是固定的,必须这样写。
"2006/01/02 15:04:05" 这个字符串各个数字可以自由的组合,这样可以按程序需求来返回时间和日期
6)时间的常量
const (
Nanosecond Duration = 1 //纳秒
Microsecond = 1000 * Nanosecond //微秒
Millisecond = 1000 * Microsecond //毫秒
second = 1000 * Millisecond //秒
Minute = 60 * Second //分钟
Hour = 60 * Minute //小时
)
常量的作用:在程序中可用于获取指定时间单位的时间,比如想得到100毫秒 100 * time.Millisecond
7)休眠
func Sleep(d Duration)
案例:time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond) //休眠100毫秒
6和7一起组合的案例:
func main() {
//需求,每隔1秒钟打印一个数字,打印到100时就退出
//需求2:每隔0.1秒钟打印一个数字,打印到100时就退出
i := 0
for {
i++
fmt.Println(i)
//休眠
//time.Sleep(time.Second)
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 100)
if i == 100 {
break
}
}
}
8)获取当前unix 时间戳 和 unixnano 时间戳。(作用是可以获取随机数字)
案例:
func main() {
now := time.Now()
fmt.Printf("unix时间戳=%v unixnano时间戳=%v \n", now.Unix(), now.UnixNano())
}
得到的结果是:

最佳实践案例:
编写一段代码来统计 函数test03 执行的时间
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"strconv"
)
func test03() {
str := ""
for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ {
str += "hello" + strconv.Itoa(i) //i是int类型的,需要转换成string类型的。
}
}
func main() {
//在执行test03前,先获取到当前的unix时间戳,
start := time.Now().Unix()
start1 := time.Now().UnixNano()
test03()
end := time.Now().Unix()
end1 := time.Now().UnixNano()
fmt.Printf("执行test03()耗费时间为%v秒\n", end-start)
fmt.Printf("执行test03()耗费时间为%v纳秒\n", end1-start1)
}
输出的结果是:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号