异步编程(三)委托-Action
action实现异步处理
1.实现
class Async { public void DoSomething(string name) { Console.WriteLine($"{name}开始工作;线程:【{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}】;{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); long result = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000_000; i++) { result += i; } Console.WriteLine($"{name}结束工作;线程:【{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}】;{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")};result:{result}"); } public void AsyncCall() { Console.WriteLine($"异步执行,线程:【{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}】,【 {DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}】"); Action<string> action = this.DoSomething; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { string name = string.Format($"id_{i}"); Console.WriteLine($"我在这儿检测线程{i}"); action.BeginInvoke(name, null, null); } Console.WriteLine($"执行结束,线程ID:【{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}】,【 {DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}】"); } }
运行结果如下
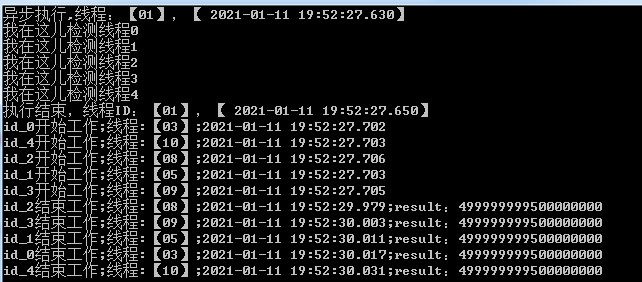
其实很清晰了,dosomething是一种类似于后台运行的状态,并不影响主程序的接续执行,因此“我在这儿检测线程4”打印到工作台时,甚至线程0都还没有开始工作。
2.扩展
(1)invoke和begininvoke
使用Invoke完成一个委托方法的封送,就类似于使用SendMessage方法来给界面线程发送消息,是一个同步方法。也就是说在Invoke封送的方法被执行完毕前,Invoke方法不会返回,从而调用者线程将被阻塞。
使用BeginInvoke方法封送一个委托方法,类似于使用PostMessage进行通信,这是一个异步方法。也就是该方法封送完毕后马上返回,不会等待委托方法的执行结束,调用者线程将不会被阻塞。但是调用者也可以使用EndInvoke方法或者其它类似WaitHandle机制等待异步操作的完成。
如果你的后台线程在更新一个UI控件的状态后不需要等待,而是要继续往下处理,那么你就应该使用BeginInvoke来进行异步处理。
如果你的后台线程需要操作UI控件,并且需要等到该操作执行完毕才能继续执行,那么你就应该使用Invoke。否则,在后台线程和主截面线程共享某些状态数据的情况下,如果不同步调用,而是各自继续执行的话,可能会造成执行序列上的问题,虽然不发生死锁,但是会出现不可预料的显示结果或者数据处理错误。
(2)begininvoke的参数跟随Action变化
①如果Action是无参的,那么begininvoke只有两个参数
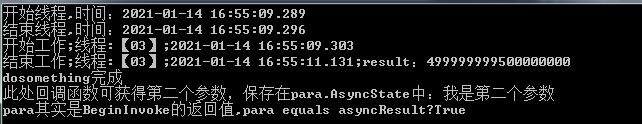
public void DoSomething() { Console.WriteLine($"开始工作;线程:【{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}】;{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); long result = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000_000; i++) { result += i; } Console.WriteLine($"结束工作;线程:【{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}】;{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")};result:{result}"); } public void FirstWay() { Console.WriteLine($"开始线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); Action action = this.DoSomething; IAsyncResult asyncResult = null; AsyncCallback callback = new AsyncCallback(para => { Console.WriteLine($"dosomething完成,此处回调函数可获得第二个参数,保存在para.AsyncState中:{para.AsyncState},而para其实是BeginInvoke的返回值,para equals asyncResult?{para.Equals(asyncResult)}"); }); asyncResult = action.BeginInvoke(callback, "我是第二个参数"); Console.WriteLine($"结束线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}**"); }
- 第一个参数表示一个委托,需要传递一个方法,当该线程结束时会调用这个方法;
- 第二个参数可以设置为任意对象,以便在回调函数中访问它;
②如果Action是有参的,那么begininvoke有三个参数
public void DoSomething(string name) { Console.WriteLine($"{name}开始工作;线程:【{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}】;{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); long result = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000_000; i++) { result += i; } Console.WriteLine($"{name}结束工作;线程:【{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString("00")}】;{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")};result:{result}"); } public void FirstWay() { Console.WriteLine($"开始线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); Action<string> action = this.DoSomething; IAsyncResult asyncResult = null; AsyncCallback callback = new AsyncCallback(para => { Console.WriteLine($"dosomething完成\n此处回调函数可获得第三个参数,保存在para.AsyncState中:{para.AsyncState}\npara其实是BeginInvoke的返回值,para equals asyncResult?{para.Equals(asyncResult)}"); }); asyncResult = action.BeginInvoke("异步线程", callback, "我是第三个参数"); Console.WriteLine($"结束线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); }
- 第一个参数是传递给Action事件,可以在DoSomething中访问;
- 第二个参数表示一个委托,需要传递一个方法,当该线程结束时会调用这个方法;
- 第三个参数可以设置为任意对象,以便在回调函数中访问它;
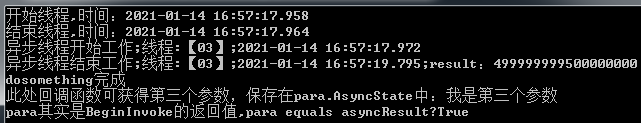
执行顺序是:先执行Action函数,然后执行完返回一个IAsyncResult结果asyncResult,然后把asyncResult作为参数传入到AsyncCallback这个委托中,最后再执行AsyncCallback委托。
(3)异步方法如何控制顺序
①begininvoke中第二个参数:回调函数,该参数指向操作完成后要处理的函数的地址,因此可形成一个操作链。
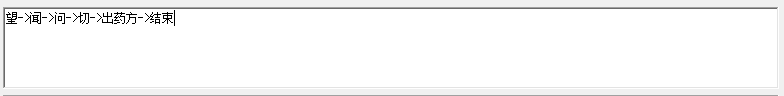
以中医望闻问切为例
private void 望() { ac1.BeginInvoke("望->", 闻, null); } private void 闻(object ob) { ac2.BeginInvoke("闻->", 问, null); } private void 问(object ob) { ac3.BeginInvoke("问->", 切, null); } private void 切(object ob) { ac4.BeginInvoke("切->", 出药方, null); } private void 出药方(object ob) { ac5.BeginInvoke("出药方->结束", null, null); } private void 诊断(string str) { Action ac = () => { inputtb.AppendText(str); }; ac.Invoke(); } private void InitialActions() { ac1 = 诊断; ac2 = 诊断; ac3 = 诊断; ac4 = 诊断; ac5 = 诊断; 望(); }
由此形成一个操作步骤链,执行结果如下
②begininvoke的返回值
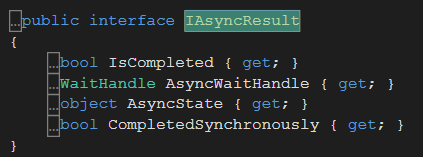
其中,IsCompleted可以标志当前Action是否已经执行完毕,从而可以控制下一个任务的开启。不过这种方式需要不停轮询状态,并不是一个十分完美的解决方案,不过这个返回值可以在许多场景下使用。
public void SecondWay() { Console.WriteLine($"开始线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); Action<string> action = this.DoSomething; IAsyncResult asyncResult = action.BeginInvoke("异步线程", null, null); while (!asyncResult.IsCompleted) { //wait Console.WriteLine("Runnning......"); Thread.Sleep(300); } Console.WriteLine($"结束线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); }
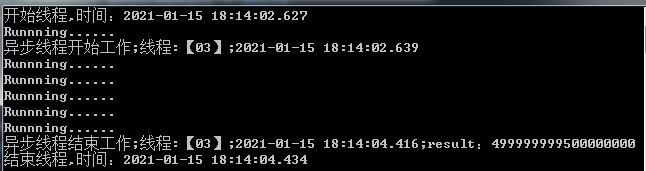
③上述方法虽然可以实现异步线程的等待,但是While循环的方法并不美好,微软为我们提供了更完备的额解决方案:WaitOne
public void ThirdWay() { Console.WriteLine($"开始线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); Action<string> action = this.DoSomething; IAsyncResult asyncResult = action.BeginInvoke("异步线程", null, null); asyncResult.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(); Console.WriteLine($"结束线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); }
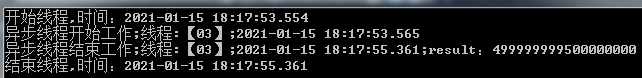
④EndInvoke也可以等待线程完成
public void ForthWay() { Console.WriteLine($"开始线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); Action<string> action = this.DoSomething; IAsyncResult asyncResult = action.BeginInvoke("异步线程", null, null); action.EndInvoke(asyncResult); Console.WriteLine($"结束线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); }
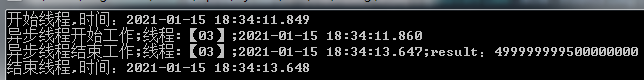
waitone和endinvoke的实现方案的原理都是等待线程完成之后再处理接下来的操作,如果去掉这部分操作,那么【结束线程】就会在线程开始工作之前就被打印到工作区。
以此为例,如下:
public void ForthWay() { Console.WriteLine($"开始线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); Action<string> action = this.DoSomething; IAsyncResult asyncResult = action.BeginInvoke("异步线程", null, null); //action.EndInvoke(asyncResult); Console.WriteLine($"结束线程,时间:{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff")}"); }
参考博客:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号