实验三
任务一
![]() point.hpp
point.hpp
![]() task1.cpp
task1.cpp
![]() point.hpp
point.hpp
![]() vectorPoint.hpp
vectorPoint.hpp
![]() task2.cpp
task2.cpp
![]() point.hpp
point.hpp
![]() vectorPoint.hpp
vectorPoint.hpp
![]() task3.cpp
task3.cpp
![]() task4_1.cpp
task4_1.cpp
![]() task4_2.cpp
task4_2.cpp
![]() task4_3.cpp
task4_3.cpp
![]() task5.cpp
task5.cpp

#pragma once #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Point { public: Point(int x0 = 0, int y0 = 0); ~Point() = default; int get_x() const; int get_y() const; void show() const; void move(int new_x, int new_y); private: int x, y; }; Point::Point(int x0, int y0): x{x0}, y{y0} { } int Point::get_x() const { return x; } int Point::get_y() const { return y; } void Point::show() const { cout << "(" << x << ", " << y << ")" << endl; } void Point::move(int new_x, int new_y) { x = new_x; y = new_y; }

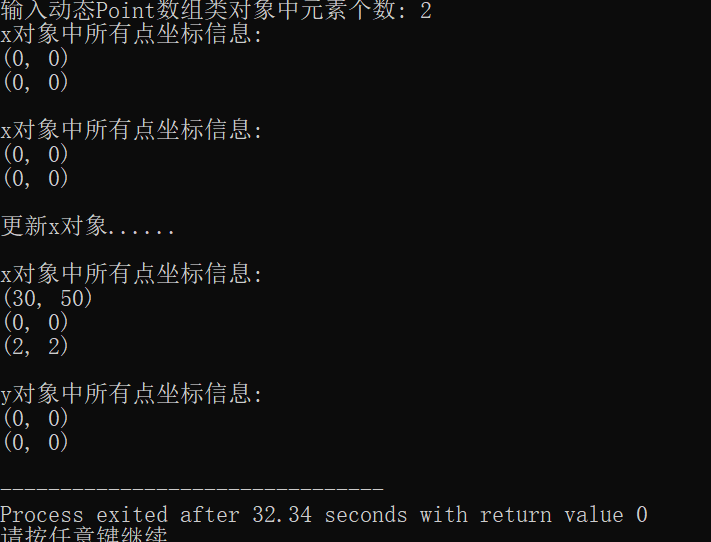
#include "vectorPoint.hpp" #include <iostream> void output(const vectorPoint &v) { for(auto i = 0; i < v.get_size(); ++i) v.at(i).show(); } void test() { using namespace std; int n; cout << "输入vectorPoint对象中元素个数: "; cin >> n; vectorPoint x(n); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); vectorPoint y(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; 复制代码 t { cout << "(" << x << ", " << y << ")" << endl;} void Point::move(int new_x, int new_y) { x = new_x; y = new_y;}
任务二

#pragma once #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Point { public: Point(int x0 = 0, int y0 = 0); ~Point() = default; int get_x() const; int get_y() const; void show() const; void move(int new_x, int new_y); private: int x, y; }; Point::Point(int x0, int y0): x{x0}, y{y0} { } int Point::get_x() const { return x; } int Point::get_y() const { return y; } void Point::show() const { cout << "(" << x << ", " << y << ")" << endl; } void Point::move(int new_x, int new_y) { x = new_x; y = new_y; }

#pragma once #include "point.hpp" #include <cassert> #include <iostream> class vectorPoint{ public: vectorPoint(int n); ~vectorPoint(); int get_size() const; // 获得当前动态数组内元素个数 Point& at(int index); // 返回下标为index的元素引用 Point& at(int index) const; // 返回下标为index的元素const引用 private: int size; // 动态数组的大小 Point *ptr; }; vectorPoint::vectorPoint(int n) : size{n} { ptr = new Point[n]; } vectorPoint::~vectorPoint() { delete[] ptr; } int vectorPoint::get_size() const { return size; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); // 宏,在测试模式下工作。如果不满足条件, 则程序终止 return ptr[index]; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) const { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return ptr[index]; }

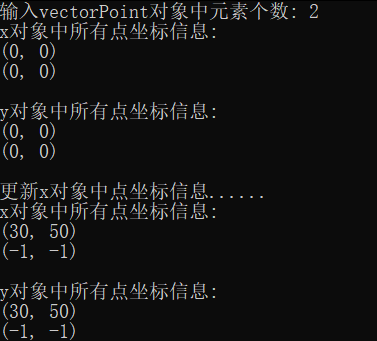
#include "vectorPoint.hpp" #include <iostream> // 输出vectorPoint对象内的所有数据 void output(const vectorPoint &v) { for(auto i = 0; i < v.get_size(); ++i) v.at(i).show(); } // 测试vectorPoint类:构造对象、复制构造对象 void test() { using namespace std; int n; cout << "输入vectorPoint对象中元素个数: "; cin >> n; vectorPoint x(n); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); vectorPoint y(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); cout << "\n更新x对象中点坐标信息......" << endl; x.at(0).move(30, 50); x.at(1).move(-1, -1); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); } int main() { test(); }
任务三

#pragma once #include "point.hpp" #include <cassert> #include <iostream> class vectorPoint{ public: vectorPoint(int n); vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp); ~vectorPoint(); int get_size() const; // 获得当前动态数组内元素个数 Point& at(int index); // 返回下标为index的元素引用 Point& at(int index) const; // 返回下标为index的元素const引用 private: int size; // 动态数组的大小 Point *ptr; }; vectorPoint::vectorPoint(int n) : size{n} { ptr = new Point[n]; } vectorPoint::vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp): size{vp.size}, ptr{new Point[size]} { for(auto i = 0; i < size; ++i) ptr[i] = vp.ptr[i]; } vectorPoint::~vectorPoint() { delete[] ptr; } int vectorPoint::get_size() const { return size; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); // 宏,在测试模式下工作。如果不满足条件, 则程序终止 return ptr[index]; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) const { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return ptr[index]; }

#pragma once #include "point.hpp" #include <cassert> #include <iostream> class vectorPoint{ public: vectorPoint(int n); vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp); ~vectorPoint(); int get_size() const; // 获得当前动态数组内元素个数 Point& at(int index); // 返回下标为index的元素引用 Point& at(int index) const; // 返回下标为index的元素const引用 private: int size; // 动态数组的大小 Point *ptr; }; vectorPoint::vectorPoint(int n) : size{n} { ptr = new Point[n]; } vectorPoint::vectorPoint(const vectorPoint &vp): size{vp.size}, ptr{new Point[size]} { for(auto i = 0; i < size; ++i) ptr[i] = vp.ptr[i]; } vectorPoint::~vectorPoint() { delete[] ptr; } int vectorPoint::get_size() const { return size; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); // 宏,在测试模式下工作。如果不满足条件, 则程序终止 return ptr[index]; } Point& vectorPoint::at(int index) const { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return ptr[index]; }

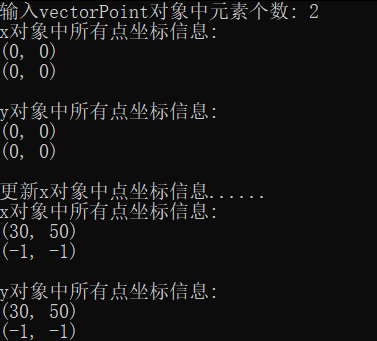
#include "vectorPoint.hpp" #include <iostream> // 输出vectorPoint对象内的所有数据 void output(const vectorPoint &v) { for(auto i = 0; i < v.get_size(); ++i) v.at(i).show(); } // 测试vectorPoint类:构造对象、复制构造对象 void test() { using namespace std; int n; cout << "输入vectorPoint对象中元素个数: "; cin >> n; vectorPoint x(n); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); vectorPoint y(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); cout << "\n更新x对象中点坐标信息......" << endl; x.at(0).move(30, 50); x.at(1).move(-1, -1); cout << "x对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(x); cout << "\ny对象中所有点坐标信息: " << endl; output(y); } int main() { test(); }
任务四

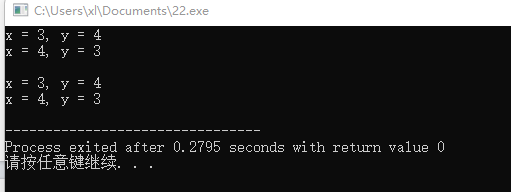
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // 函数声明 void swap1(int &rx, int &ry); // 引用作为形参 void swap2(int *px, int *py); // 指针作为形参 void print(int x, int y); // 普通变量作为形参 // 测试代码 void test() { int x = 3, y = 4; print(x, y); swap1(x, y); // 函数调用,注意:引用作为形参时,实参形式 print(x, y); cout << endl; x = 3, y = 4; print(x, y); swap2(&x, &y); // 函数调用,注意:指针作为形参时,实参形式 print(x, y); } int main() { test(); } // 函数定义:交换两个变量(引用变量作为形参) void swap1(int &rx, int &ry) { int t; t = rx; rx = ry; ry = t; } // 函数定义:交换两个变量(指针变量作为形参) void swap2(int *px, int *py) { int t; t = *px; *px = *py; *py = t; } // 函数定义:输出两个变量(普通变量作为形参) void print(int x, int y) { std::cout << "x = " << x << ", y = " << y << "\n"; }

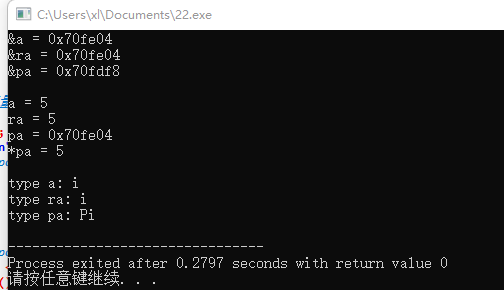
#include <iostream> #include <typeinfo> using namespace std; int main() { int a; int &ra = a; ra = 4; int *pa = &a; *pa = 5; // 以十六进制形式输出普通变量a, 引用变量ra,指针变量pa的地址 cout << "&a = " << hex << &a << endl; cout << "&ra = " << hex << &ra << endl; cout << "&pa = " << hex << &pa << "\n\n"; // 输出普通变量a, 引用变量ra,指针变量pa的值 cout << "a = " << a << endl; cout << "ra = " << a << endl; cout << "pa = " << hex << pa << endl; // 输出指针变量pa指向的变量的值 cout << "*pa = " << *pa << "\n\n"; // 输出普通变量a,引用变量ra, 指针变量pa的类型信息 cout << "type a: " << typeid(a).name() << endl; cout << "type ra: " << typeid(ra).name() << endl; cout << "type pa: " << typeid(pa).name() << endl; }

#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; template<typename T> void output(const T &x) { for(auto i: x) std::cout << i << ", "; std::cout << "\b\b \n"; } template<typename T> void square1(T &x) { for(auto i: x) // i是普通类型 i *= i; } template<typename T> void square2(T &x) { for(auto &i: x) // i是引用类型 i *= i; } void test1() { vector<int> x {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; cout << "动态int型数组对象x内的元素值: "; output(x); cout << "调用函数square1()......" << endl; square1(x); cout << "动态int型数组对象x内的元素值: "; output(x); } void test2() { vector<int> x {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; cout << "动态int型数组对象x内的元素值: "; output(x); cout << "调用函数square2()......" << endl; square2(x); cout << "动态int型数组对象x内的元素值: "; output(x); } int main() { cout << "测试1: " << endl; test1(); cout << "\n测试2: " << endl; test2(); }

任务五

#include "vectorInt.hpp" #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl; class vectorInt { std::vector<int> vec; public: vectorInt(int n) : vec(n) {} // 初始化为n个元素,值未初始化 vectorInt(const vectorInt &other) : vec(other.vec) {} // 使用其他vectorInt对象构造 void at(int i, int val) { vec.at(i) = val; } // 设置元素值 int at(int i) const { return vec.at(i); } // 获取元素值 }; // 函数output()的定义:遍历输出vectorInt对象内的所有元素 void output(const vectorInt &vi) { for (int i = 0; i < vi.vec.size(); ++i) { cout << vi.vec.at(i) << " "; } cout << endl; } void test() { int n; cout << "输入vectorInt对象中元素个数: "; cin >> n; vectorInt x1(n); // 构造动态int数组对象x1,包含n个元素,不对元素初始化 for (auto i = 0; i < n; ++i) { x1.at(i) = i * i; } cout << "vectorInt对象x1: "; output(x1); vectorInt x2(n, 42); // 构造动态int数组对象x1,包含n个元素,每个元素初始值为42 cout << "vectorInt对象x2: "; output(x2); vectorInt x3(x2); // 使用x2构造x3 cout << "vectorInt对象x3: "; output(x3); cout << "更新vectorInt对象x2......\n"; x2.at(0) = 77; x2.at(1) = -999; cout << "vectorInt对象x2: "; output(x2); cout << "vectorInt对象x3: "; output(x3); } int main() { test(); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号