C++ unordered_map 实现
unordered_map是 C++ STL 中的关联容器,它存储键值对,使用哈希表实现,提供平均 O(1) 时间复杂度的查找、插入和删除操作。
1基本用法
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
int main() {
// 创建一个 unordered_map
std::unordered_map<std::string, int> wordCount;
// 插入元素
wordCount["apple"] = 5;
wordCount["banana"] = 3;
wordCount.insert({"orange", 2});
// 访问元素
std::cout << "apple count: " << wordCount["apple"] << std::endl;
// 检查元素是否存在
if (wordCount.find("banana") != wordCount.end()) {
std::cout << "banana exists" << std::endl;
}
// 遍历所有元素
for (const auto& pair : wordCount) {
std::cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << std::endl;
}
// 删除元素
wordCount.erase("orange");
return 0;
}
2 unordered_map默认支持那些数据?
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
int main() {
// 默认支持的键类型示例
std::unordered_map<std::string, int> stringMap; // OK
std::unordered_map<int, double> intMap; // OK
std::unordered_map<char*, bool> ptrMap; // OK(但需注意指针比较)
// 需要自定义哈希的示例(编译错误)
// std::unordered_map<std::pair<int, int>, int> pairMap; // 错误:没有默认哈希
}
在 C++ 中,std::unordered_map默认支持以下类型的键(Key):
1. 基本数据类型
-
int -
unsigned int -
short -
long -
long long -
float -
double -
char -
bool -
std::string(来自<string>)
2. 标准库类型
-
std::string_view(C++17 起) -
std::bitset -
std::vector<bool> -
std::pair(但需要自定义哈希函数,除非使用 C++11 的std::hash特化)
3. 指针类型
-
原始指针(如
int*,char*) -
std::shared_ptr -
std::unique_ptr
4. C++11 标准哈希支持
C++11 标准库已经为以下类型提供了 std::hash特化:
-
所有整数类型(
int,long, 等) -
所有浮点类型(
float,double) -
指针类型(
T*) -
std::string -
std::wstring -
std::u16string -
std::u32string -
std::string_view(C++17) -
std::error_code -
std::thread::id
5. 不支持的默认类型
以下类型 不能直接 作为 unordered_map的键,除非自定义哈希函数和相等比较:
-
自定义结构体/类
-
std::pair(除非使用 C++11 的std::hash特化) -
std::vector(除非自定义哈希) -
std::list -
std::map -
其他没有
std::hash特化的类型
3如何支持自定义类型?
如果想用自定义类型作为键,需要:
-
自定义哈希函数(可以是函数对象或 lambda)
-
重载
operator== 或提供比较函数
示例:自定义类型作为键
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
struct Point {
int x, y;
// 必须定义相等运算符
bool operator==(const Point& other) const {
return x == other.x && y == other.y;
}
};
// 自定义哈希函数
struct PointHash {
std::size_t operator()(const Point& p) const {
return std::hash<int>()(p.x) ^ std::hash<int>()(p.y);
}
};
int main() {
std::unordered_map<Point, std::string, PointHash> pointMap;
pointMap[{1, 2}] = "A";
pointMap[{3, 4}] = "B";
std::cout << pointMap[{1, 2}] << std::endl; // 输出 "A"
}
必须定义相等运算符,为什么?
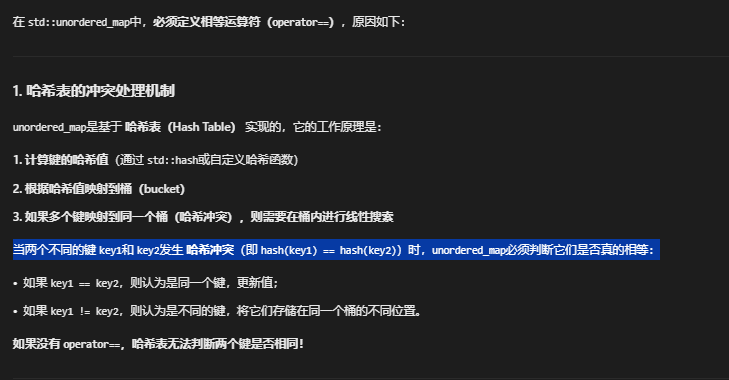
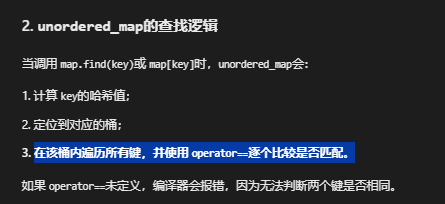

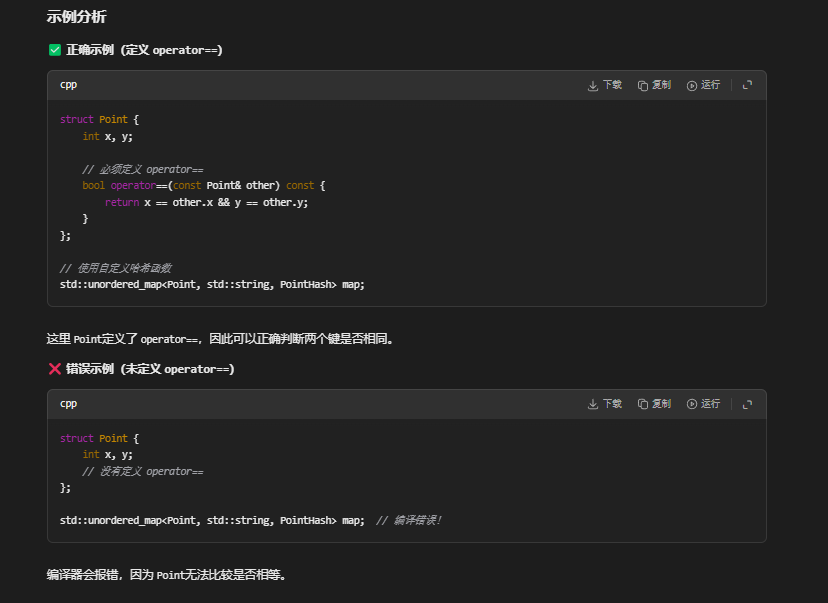
替代方案:自定义比较函数
如果不想重载 operator==,可以通过 自定义比较函数 实现:
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
// 自定义比较函数
struct PointEqual {
bool operator()(const Point& a, const Point& b) const {
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
};
// 在 unordered_map 中传入自定义比较函数
std::unordered_map<Point, std::string, PointHash, PointEqual> map;
源码实现
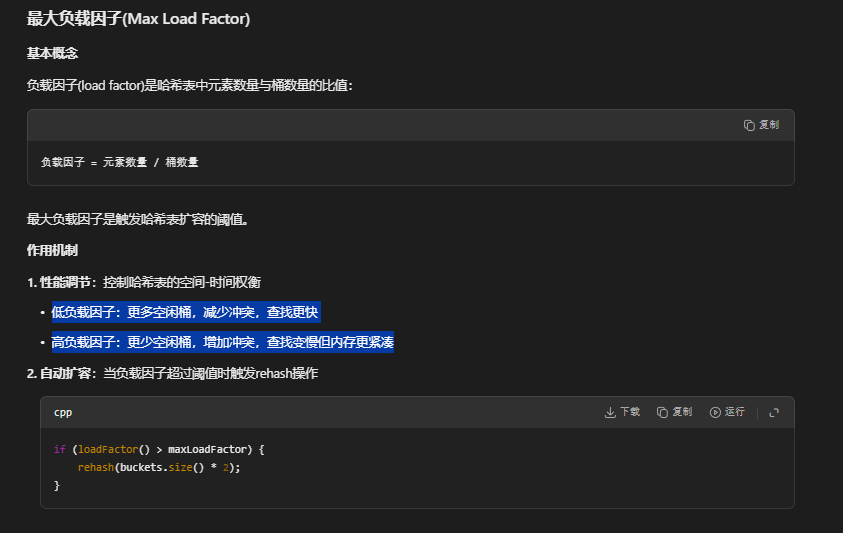
std::hash默认支持的参数


使用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
int main() {
// 整数哈希
std::hash<int> intHash;
std::cout << "Hash of 42: " << intHash(42) << "\n";
// 浮点数哈希
std::hash<double> doubleHash;
std::cout << "Hash of 3.14: " << doubleHash(3.14) << "\n";
// 字符串哈希
std::hash<std::string> stringHash;
std::cout << "Hash of 'hello': " << stringHash("hello") << "\n";
// 指针哈希
int x = 10;
std::hash<int*> ptrHash;
std::cout << "Hash of &x: " << ptrHash(&x) << "\n";
return 0;
}
自定义类型支持
对于用户自定义类型,需要特化 std::hash 模板:
#include <functional>
struct Person {
std::string name;
int age;
};
// 特化 std::hash 模板
namespace std {
template<>
struct hash<Person> {
size_t operator()(const Person& p) const {
return hash<string>()(p.name) ^ hash<int>()(p.age);
}
};
}
// 使用示例
int main() {
Person alice{"Alice", 30};
std::hash<Person> personHash;
std::cout << "Hash of Alice: " << personHash(alice) << "\n";
return 0;
}
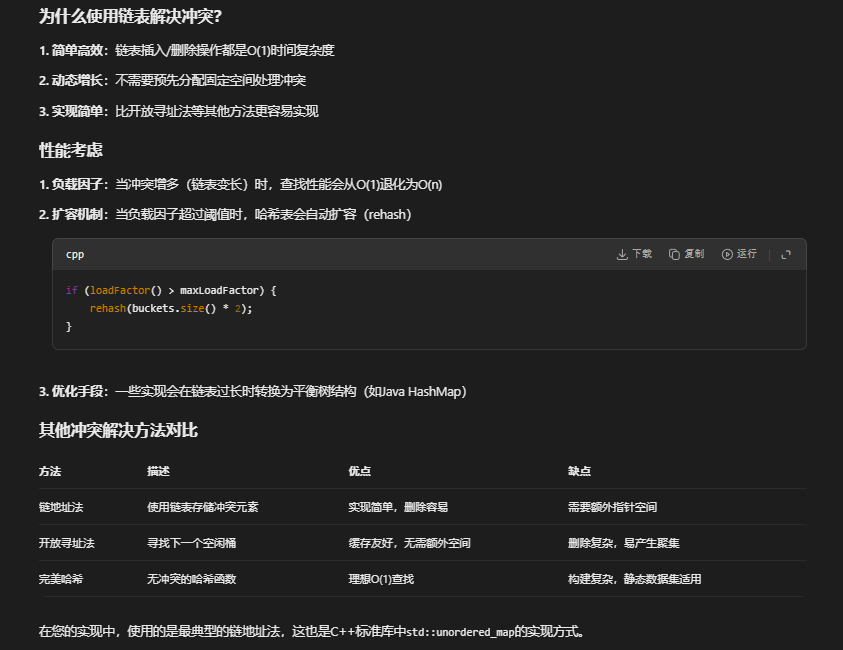
单向链表实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
template<typename Key, typename Value>
class CloserToOriginalUnorderedMap {
private:
// 哈希节点结构(使用单向链表)
struct HashNode {
Key key; // 存储的键
Value value; // 存储的值
HashNode* next; // 指向下一个节点的指针
// 构造函数:创建一个新的哈希节点
// @param k 要存储的键
// @param v 要存储的值
// @param n 下一个节点的指针(默认为空)
HashNode(const Key& k, const Value& v, HashNode* n = nullptr)
: key(k), // 初始化键
value(v), // 初始化值
next(n) // 初始化下一个节点指针
{} // 空函数体
};
// 桶数组存储链表头指针
std::vector<HashNode*> buckets;
// 哈希函数
std::hash<Key> hashFunction;
// 元素计数
size_t numElements = 0;
// 最大负载因子
const float maxLoadFactor = 1.0f;
// 获取桶索引
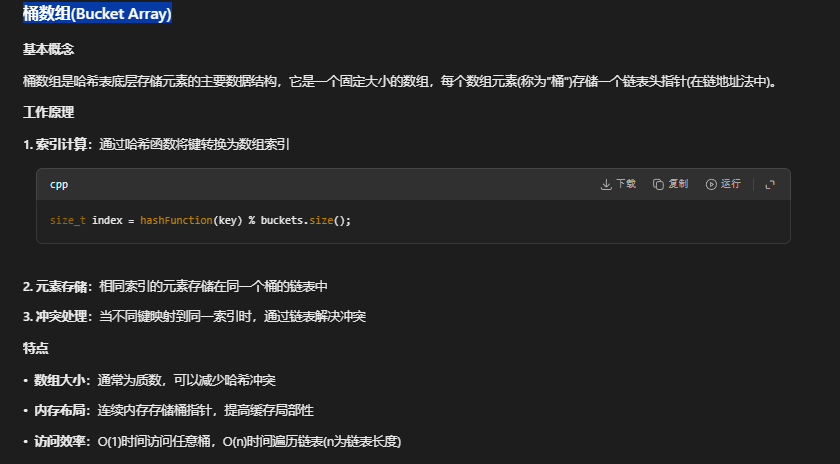
size_t getBucketIndex(const Key& key) const {
std::cout<< "哈希索引计算 key: "<< key << " 原始哈希值hashFunction(key):" << hashFunction(key) << " 桶大小 buckets.size(): " << buckets.size() << " 分配的索引(存在第几个桶)"<< hashFunction(key) % buckets.size() << std::endl;
return hashFunction(key) % buckets.size();
}
// 重新哈希(扩容)
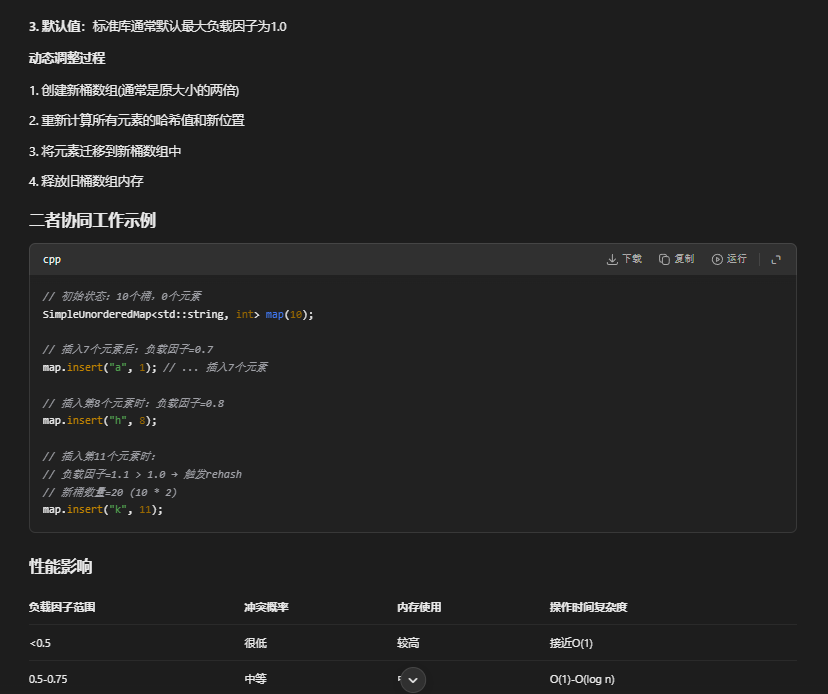
void rehash(size_t newSize) {
std::vector<HashNode*> newBuckets(newSize, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < buckets.size(); ++i) {
HashNode* node = buckets[i];
while (node != nullptr) {
HashNode* next = node->next;
size_t newIndex = hashFunction(node->key) % newSize;
// 插入到新桶的链表头部
node->next = newBuckets[newIndex];
newBuckets[newIndex] = node;
node = next;
}
}
buckets = std::move(newBuckets);
}
public:
CloserToOriginalUnorderedMap(size_t initialSize = 10) {
buckets.resize(initialSize, nullptr);
}
~CloserToOriginalUnorderedMap() {
clear();
}
// 清空哈希表
void clear() {
for (size_t i = 0; i < buckets.size(); ++i) {
HashNode* node = buckets[i];
while (node != nullptr) {
HashNode* next = node->next;
delete node;
node = next;
}
buckets[i] = nullptr;
}
numElements = 0;
}
// 插入元素
void insert(const Key& key, const Value& value) {
// 检查是否需要扩容
if (loadFactor() > maxLoadFactor) {
rehash(buckets.size() * 2);
}
size_t index = getBucketIndex(key);
HashNode* node = buckets[index];// 取出目标位置的数据
// 1-1检查是否已存在该键
while (node != nullptr) {
// 1-1-1 存在 不允许相同的多个,直接更新数值
if (node->key == key) {
node->value = value; // 更新值
return;
}
// 1-1-2 不存在
node = node->next; // 检查下一个节点
}
// 1-2插入新节点到链表头部
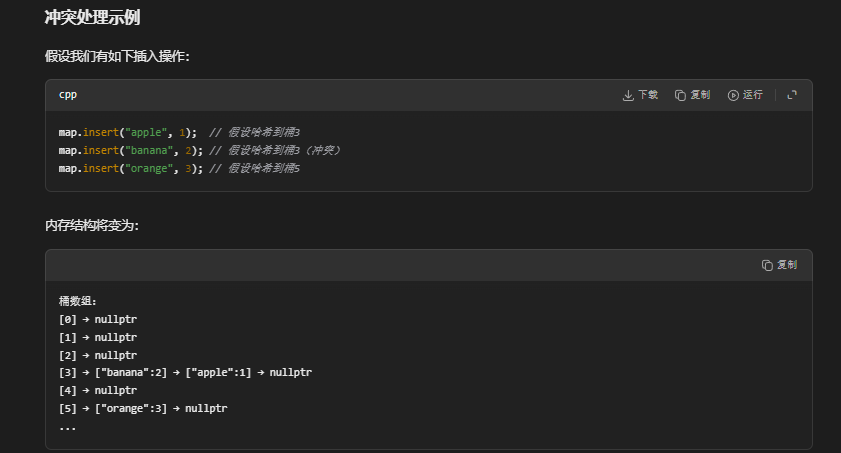
/*
*
map.insert("apple", 1); // 假设哈希到桶3
map.insert("banana", 2); // 假设哈希到桶3(冲突)
map.insert("orange", 3); // 假设哈希到桶5
桶数组:
[0] → nullptr
[1] → nullptr
[2] → nullptr
banana插入前
[3] → ["apple":1] → nullptr
banana插入后
[3] → ["banana":2] → ["apple":1] → nullptr
[4] → nullptr
[5] → ["orange":3] → nullptr
...
*/
buckets[index] = new HashNode(key, value, buckets[index]);
numElements++;
std::cout << "加入数据 key: " << key << " value:" << value << " " << " 哈希索引:" << index << std::endl;
}
// 查找元素
Value* find(const Key& key) {
size_t index = getBucketIndex(key);
HashNode* node = buckets[index];
while (node != nullptr) {
if (node->key == key) {
return &node->value;
}
node = node->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
// 删除元素
bool erase(const Key& key) {
size_t index = getBucketIndex(key);
HashNode* node = buckets[index];
HashNode* prev = nullptr;
while (node != nullptr) {
if (node->key == key) {
if (prev == nullptr) {
// 删除的是链表头节点
buckets[index] = node->next;
}
else {
prev->next = node->next;
}
delete node;
numElements--;
return true;
}
prev = node;
node = node->next;
}
return false;
}
// 获取当前负载因子
float loadFactor() const {
return static_cast<float>(numElements) / buckets.size();
}
// 打印哈希表状态(用于调试)
void printStats() const {
std::cout << "\n Hash Table Stats:\n";
std::cout << " Buckets: " << buckets.size() << "\n";
std::cout << " Elements: " << numElements << "\n";
std::cout << " Load Factor: " << loadFactor() << "\n";
size_t emptyBuckets = 0;
size_t maxChainLength = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < buckets.size(); ++i) {
size_t chainLength = 0;
HashNode* node = buckets[i];
if (node == nullptr) {
emptyBuckets++;
}
while (node != nullptr) {
chainLength++;
node = node->next;
}
if (chainLength > maxChainLength) {
maxChainLength = chainLength;
}
}
std::cout << " Empty Buckets: " << emptyBuckets << "\n";
std::cout << " Max Chain Length: " << maxChainLength << "\n";
}
};
int main() {
CloserToOriginalUnorderedMap<std::string, int> map;
map.insert("apple", 1);
map.insert("banana", 2);
map.insert("orange", 3);
map.insert("apple", 4); // 更新已有的键
// 查找测试
if (auto ptr = map.find("banana")) {
std::cout << "Found banana: " << *ptr << "\n";
}
// 删除测试
map.erase("orange");
// 打印哈希表状态
map.printStats();
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号