https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ie4y1f7XG/?spm_id_from=333.788&vd_source=f88ed35500cb30c7be9bbe418a5998ca

(图中少了个尺度s)


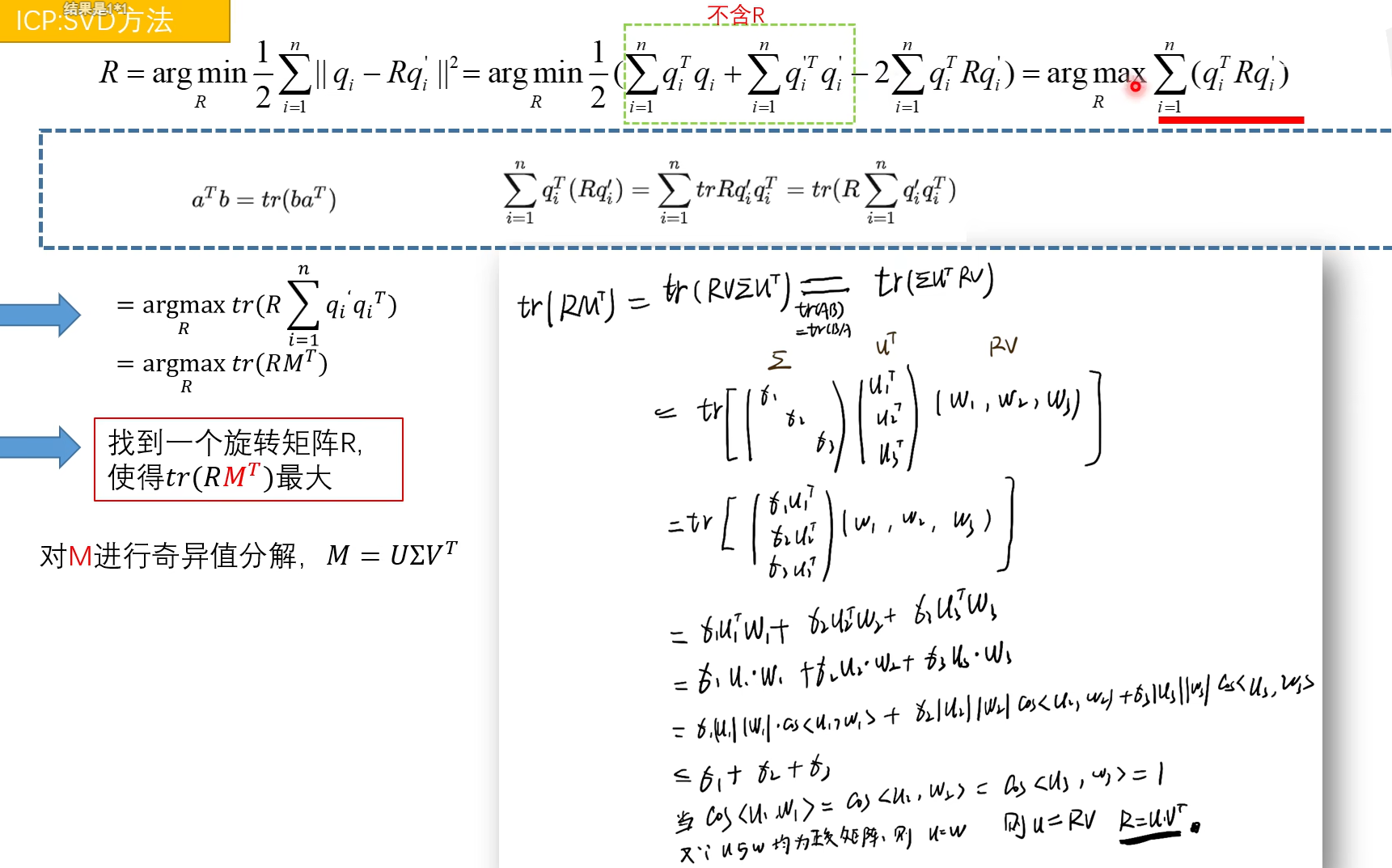

https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/447092711
slam2的LoopClosing线程中,做了Loop检测和Loop校正。
Loop是指机器人回到自己见过的场景,即机器人拍摄到了与保存在地图中的的图片B中非常相似的图片A,而对图片B,记录着一个位置姿态,就是在世界坐标系中的平移量和旋转量T0。
T1 和T0 之间,理论上存在着一定的旋转和平移。单目由于累计误差还有一个尺度误差问题
因此,我们需要根据两张图片上检测到的关键点来计算T1与T0之间的转换关系,这个转换关系里有3个量:s,R,t,
其中s 尺度量,R旋转矩阵,t平移向量。
图片A上的关键点的坐标,是在拍摄A图时的坐标系。
图片B上的关键点的坐标,是在拍摄B图时的坐标系。
也就是说,求解图片A,B上的关键点之间的变换关系,实际上是求解两个坐标系之间的变换关系。

求取的过程,先计算R,然后由R计算出s,再由 R,s计算出t.



对应的代码解释
1 /**
2 * 计算sim3
3 */
4 void Sim3Solver::ComputeSim3(cv::Mat &P1, cv::Mat &P2)
5 {
6 // Custom implementation of:
7 // Horn 1987, Closed-form solution of absolute orientataion using unit quaternions
8
9 // Step 1: Centroid and relative coordinates
10
11 cv::Mat Pr1(P1.size(),P1.type()); // Relative coordinates to centroid (set 1)
12 cv::Mat Pr2(P2.size(),P2.type()); // Relative coordinates to centroid (set 2)
13 cv::Mat O1(3,1,Pr1.type()); // Centroid of P1
14 cv::Mat O2(3,1,Pr2.type()); // Centroid of P2
15
16 // 计算点集的平均值
17 ComputeCentroid(P1,Pr1,O1);
18 ComputeCentroid(P2,Pr2,O2);
19
20 // Step 2: Compute M matrix
21
22 cv::Mat M = Pr2*Pr1.t();
23
24 // Step 3: Compute N matrix
25
26 double N11, N12, N13, N14, N22, N23, N24, N33, N34, N44;
27
28 cv::Mat N(4,4,P1.type());
29
30 N11 = M.at<float>(0,0)+M.at<float>(1,1)+M.at<float>(2,2);
31 N12 = M.at<float>(1,2)-M.at<float>(2,1);
32 N13 = M.at<float>(2,0)-M.at<float>(0,2);
33 N14 = M.at<float>(0,1)-M.at<float>(1,0);
34 N22 = M.at<float>(0,0)-M.at<float>(1,1)-M.at<float>(2,2);
35 N23 = M.at<float>(0,1)+M.at<float>(1,0);
36 N24 = M.at<float>(2,0)+M.at<float>(0,2);
37 N33 = -M.at<float>(0,0)+M.at<float>(1,1)-M.at<float>(2,2);
38 N34 = M.at<float>(1,2)+M.at<float>(2,1);
39 N44 = -M.at<float>(0,0)-M.at<float>(1,1)+M.at<float>(2,2);
40
41 N = (cv::Mat_<float>(4,4) << N11, N12, N13, N14,
42 N12, N22, N23, N24,
43 N13, N23, N33, N34,
44 N14, N24, N34, N44);
45
46
47 // Step 4: Eigenvector of the highest eigenvalue
48
49 cv::Mat eval, evec;
50
51 cv::eigen(N,eval,evec); //evec[0] is the quaternion of the desired rotation
52
53 cv::Mat vec(1,3,evec.type());
54 (evec.row(0).colRange(1,4)).copyTo(vec); //extract imaginary part of the quaternion (sin*axis)
55
56 // Rotation angle. sin is the norm of the imaginary part, cos is the real part
57 double ang=atan2(norm(vec),evec.at<float>(0,0));
58
59 vec = 2*ang*vec/norm(vec); //Angle-axis representation. quaternion angle is the half
60
61 mR12i.create(3,3,P1.type());
62
63 cv::Rodrigues(vec,mR12i); // computes the rotation matrix from angle-axis
64
65 // Step 5: Rotate set 2
66
67 cv::Mat P3 = mR12i*Pr2;
68
69 // Step 6: Scale
70
71 if(!mbFixScale)
72 {
73 double nom = Pr1.dot(P3);
74 cv::Mat aux_P3(P3.size(),P3.type());
75 aux_P3=P3;
76 cv::pow(P3,2,aux_P3);
77 double den = 0;
78
79 for(int i=0; i<aux_P3.rows; i++)
80 {
81 for(int j=0; j<aux_P3.cols; j++)
82 {
83 den+=aux_P3.at<float>(i,j);
84 }
85 }
86
87 ms12i = nom/den;
88 }
89 else
90 ms12i = 1.0f;
91
92 // Step 7: Translation
93
94 mt12i.create(1,3,P1.type());
95 mt12i = O1 - ms12i*mR12i*O2;
96
97 // Step 8: Transformation
98
99 // Step 8.1 T12
100 mT12i = cv::Mat::eye(4,4,P1.type());
101
102 cv::Mat sR = ms12i*mR12i;
103
104 sR.copyTo(mT12i.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3));
105 mt12i.copyTo(mT12i.rowRange(0,3).col(3));
106
107 // Step 8.2 T21
108
109 mT21i = cv::Mat::eye(4,4,P1.type());
110
111 cv::Mat sRinv = (1.0/ms12i)*mR12i.t();
112
113 sRinv.copyTo(mT21i.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3));
114 cv::Mat tinv = -sRinv*mt12i;
115 tinv.copyTo(mT21i.rowRange(0,3).col(3));
116 }
代码中,
11行止14行,P1,P2就是我们的左点,右点。
P1r,P2r对应于公式中的r_ri',r_li',相对坐标的意思,相对于点集平均点的相对坐标。
O1,O2就是两个点集的中心点了。
63行之前都是用四元组去求解R的,在63行,把R这个旋转矩阵存在了mR12i中,到此,我们就得到R矩阵了,后面就要求取s和t了。
求s:
s的值,我们使用推导中的公式3来求取,如下:





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号