https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/42383070
很多问题最终归结为一个最小二乘问题,如SLAM算法中的Bundle Adjustment,位姿图优化等等。求解最小二乘的方法有很多,高斯-牛顿法就是其中之一。


手动推导



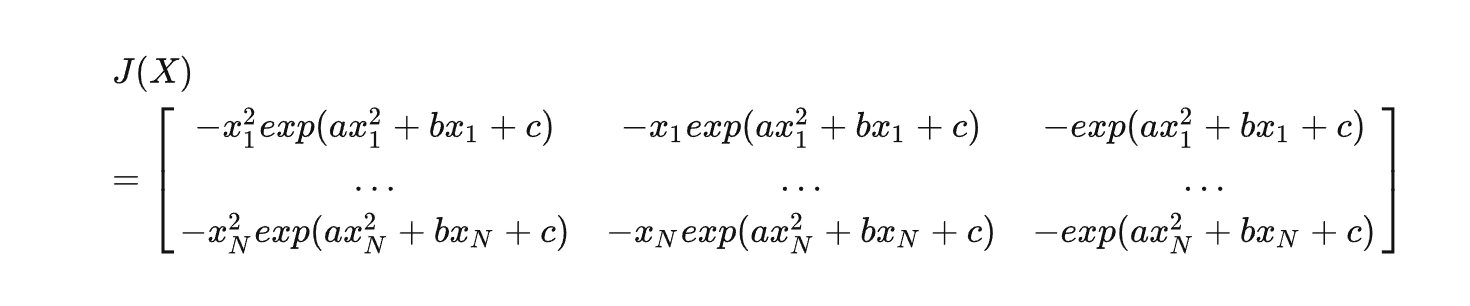
/**
* This file is part of Gauss-Newton Solver.
*
* Copyright (C) 2018-2020 Dongsheng Yang <ydsf16@buaa.edu.cn> (Beihang University)
* For more information see <https://github.com/ydsf16/Gauss_Newton_solver>
*
* Gauss_Newton_solver is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* Gauss_Newton_solver is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with Gauss_Newton_solver. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Cholesky>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/QR>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/SVD>
#include <chrono>
/* 计时类 */
class Runtimer{
public:
inline void start()
{
t_s_ = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
}
inline void stop()
{
t_e_ = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
}
inline double duration()
{
return std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<double>>(t_e_ - t_s_).count() * 1000.0;
}
private:
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point t_s_; //start time ponit
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point t_e_; //stop time point
};
/* 优化方程 */
class CostFunction{
public:
CostFunction(double* a, double* b, double* c, int max_iter, double min_step, bool is_out):
a_(a), b_(b), c_(c), max_iter_(max_iter), min_step_(min_step), is_out_(is_out)
{}
void addObservation(double x, double y)
{
std::vector<double> ob;
ob.push_back(x);
ob.push_back(y);
obs_.push_back(ob);
}
void calcJ_fx()
{
J_ .resize(obs_.size(), 3);
fx_.resize(obs_.size(), 1);
for ( size_t i = 0; i < obs_.size(); i ++)
{
std::vector<double>& ob = obs_.at(i);
double& x = ob.at(0);
double& y = ob.at(1);
double j1 = -x*x*exp(*a_ * x*x + *b_*x + *c_);
double j2 = -x*exp(*a_ * x*x + *b_*x + *c_);
double j3 = -exp(*a_ * x*x + *b_*x + *c_);
J_(i, 0 ) = j1;
J_(i, 1) = j2;
J_(i, 2) = j3;
fx_(i, 0) = y - exp( *a_ *x*x + *b_*x +*c_);
}
}
void calcH_b()
{
H_ = J_.transpose() * J_;
B_ = -J_.transpose() * fx_;
}
void calcDeltax()
{
deltax_ = H_.ldlt().solve(B_);
}
void updateX()
{
*a_ += deltax_(0);
*b_ += deltax_(1);
*c_ += deltax_(2);
}
double getCost()
{
Eigen::MatrixXd cost= fx_.transpose() * fx_;
return cost(0,0);
}
void solveByGaussNewton()
{
double sumt =0;
bool is_conv = false;
for( size_t i = 0; i < max_iter_; i ++)
{
Runtimer t;
t.start();
calcJ_fx();
calcH_b();
calcDeltax();
double delta = deltax_.transpose() * deltax_;
t.stop();
if( is_out_ )
{
std::cout << "Iter: " << std::left <<std::setw(3) << i << " Result: "<< std::left <<std::setw(10) << *a_ << " " << std::left <<std::setw(10) << *b_ << " " << std::left <<std::setw(10) << *c_ <<
" step: " << std::left <<std::setw(14) << delta << " cost: "<< std::left <<std::setw(14) << getCost() << " time: " << std::left <<std::setw(14) << t.duration() <<
" total_time: "<< std::left <<std::setw(14) << (sumt += t.duration()) << std::endl;
}
if( delta < min_step_)
{
is_conv = true;
break;
}
updateX();
}
if( is_conv == true)
std::cout << "\nConverged\n";
else
std::cout << "\nDiverged\n\n";
}
Eigen::MatrixXd fx_;
Eigen::MatrixXd J_; // 雅克比矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3d H_; // H矩阵
Eigen::Vector3d B_;
Eigen::Vector3d deltax_;
std::vector< std::vector<double> > obs_; // 观测
double* a_, *b_, *c_;
int max_iter_;
double min_step_;
bool is_out_;
};//class CostFunction
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
const double aa = 0.1, bb = 0.5, cc = 2; // 实际方程的参数
double a =0.0, b=0.0, c=0.0; // 初值
/* 构造问题 */
CostFunction cost_func(&a, &b, &c, 50, 1e-10, true);
/* 制造数据 */
const size_t N = 100; //数据个数
cv::RNG rng(cv::getTickCount());
for( size_t i = 0; i < N; i ++)
{
/* 生产带有高斯噪声的数据 */
double x = rng.uniform(0.0, 1.0) ;
double y = exp(aa*x*x + bb*x + cc) + rng.gaussian(0.05);
/* 添加到观测中 */
cost_func.addObservation(x, y);
}
/* 用高斯牛顿法求解 */
cost_func.solveByGaussNewton();
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号