C++ stl 学习8-- map
<map>头文件包含map和multimap
map,multimap 和set, multiset一样,底层都是用红黑树实现的,其中set可以看做是value等于key的map
和set一样,map中元素都是默认 < 排序的
map中key不能重复不能修改,multimap中key可以重复不能修改。
与set不同的是map可以用“下标”获取value的值
Map
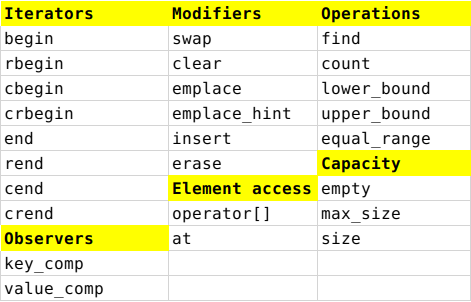
operator[] // k能与map中元素匹配时获取value,如果不能匹配这表示插入元素
mapped_type& operator[] (const key_type& k);
mapped_type& operator[] (key_type&& k);
A call to this function is equivalent to:(*((this->insert(make_pair(k,mapped_type()))).first)).second
at() // 获取map中元素,key值不在map中时抛出异常
剩下的成员函数和set相同
#include <iostream> #include <map> using namespace std; int main() { map<int,int> a{{1,9},{2,8},{3,7},{4,6},{5,5}}; // 默认小于排序 cout << a[1] << endl; // 9; 1存在所以是获取值 pair<map<int, int>::iterator, bool> it = a.insert(make_pair<int,int>(6, 4)); // it.first指向{6,4} it = a.emplace(pair<int,int>(7,3)); // it.first指向{7,3} it = a.insert({8,2}); // it.first指向{8,2} auto itor = a.find(5); // itor指向{5,5} itor = a.erase(itor); // 删除{5, 5}后itor指向{6,4} cout << itor->first << endl; // 6 for (auto& it : a) { cout << it.first << " " << it.second << endl; } itor = a.lower_bound(3); // itor 指向3 cout << itor->first << endl; itor = a.upper_bound(4); // itor指向6 cout << itor->first << endl; return 0; }
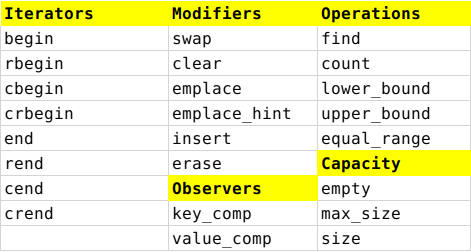
Multimap
multimap与map的最大区别就是key可以重复,所以没有operator[ ]和at成员函数
#include <iostream> #include <map> using namespace std; int main() { multimap<int,int> a{{1,1},{1,2},{1,1},{1,2},{2,1},{2,2},{4,5}}; // 默认小于排序 multimap<int,int>::iterator it = a.insert(make_pair<int,int>(6, 4)); // it指向{6,4} it = a.emplace(pair<int,int>(7,3)); // it.first指向{7,3} it = a.insert({8,2}); // it指向{8,2} it = a.find(1); // it指向{1,1} 找到第一个就不找了,it下一个元素是1,2 int num = a.erase(1); //num等于4 所有的key等于1的都删除了 for (auto& itt : a) { cout << itt.first << " " << itt.second << endl; } it = a.lower_bound(3); // itor 指向4 cout << it->first << endl; it = a.upper_bound(4); // itor指向6 cout << it->first << endl; return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号