C++ stl 学习7-- stack 和queue
<stack>头文件包含stack
<queue>头文件包含queue和priority_queue
stack
容器适配器的一种,LIFO(last-in first-out),一般是用deque实现的。
一般来说作为底层实现容器要支持empty(), size(), back(), push_back(),pop_back()
The underlying container may be any of the standard container class templates or some other specifically designed container class. The container shall support the following operations:
empty size back push_back pop_back
The standard container classes vector, deque and list fulfill these requirements. By default, if no container class is specified for a particular stack class instantiation, the standard container deque is used.
queue
容器适配器的一种, FIFO (first-in first-out),从一端进入,另一端退出,一般是用deque底层实现的,也可以用list实现
一般来说作为底层实现的容器必须支持这些操作empty(), size(), front(), back(), push_back(),pop_front()
The underlying container may be one of the standard container class template or some other specifically designed container class. This underlying container shall support at least the following operations:
empty size front back push_back pop_front
The standard container classes deque and list fulfill these requirements. By default, if no container class is specified for a particular queue class instantiation, the standard container deque is used.
priority_queue
容器适配器的一种,从一端进入,另一端退出,退出的总是按照规则而已最大的元素。不同的是里面的数据都是按照某种规则排序的,而不是按照进入的顺序。一般是用vector底层实现的,也可以用deque实现。
一般来说作为底层实现的容器必须支持这些操作empty() size() front() push_back() pop_back()且支持随机访问
Priority queues are a type of container adaptors, specifically designed such that its first element is always the greatest of the elements it contains, according to some strict weak ordering criterion
The underlying container may be any of the standard container class templates or some other specifically designed container class. The container shall be accessible through random access iterators and support the following operations:
empty() size() front() push_back() pop_back()
The standard container classes vector and deque fulfill these requirements. By default, if no container class is specified for a particular priority_queue class instantiation, the standard container vector is used.
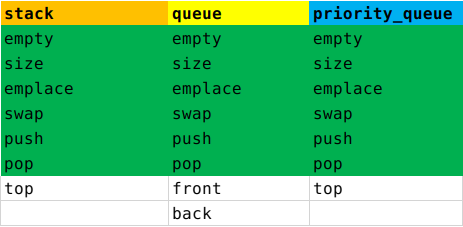
front() // 返回当前剩余元素中最先进入队列的元素
Returns a reference to the next element in the queue.
The next element is the "oldest" element in the queue and the same element that is popped out from the queue when queue::pop is called.
This member function effectively calls member front of the underlying container object.
back() // 返回最后进入的元素
Returns a reference to the last element in the queue. This is the "newest" element in the queue (i.e. the last element pushed into the queue).
This member function effectively calls member back of the underlying container object.
push() // 插入元素,根据是栈,队列还是优先队列选择合适的插入方式
pop() // 弹出元素,栈返回的是最后进入的,队列返回的是最先进入的,优先队列返回的是优先级最高的
top() // 栈返回的是最后进入的元素,优先队列返回当前优先级最高的元素
emplace() // 和push差不多,唯一区别是emplace是在对应位置直接构造元素。push则需要构造加复制(移动)
#include <iostream> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; int main() { stack<int> s; s.push(1); s.push(4); s.push(2); s.push(8); s.push(5); s.push(7); cout << s.top() << endl; // 7 s.pop(); cout << s.top() << endl; // 5 queue<int> a; a.push(1); a.push(4); a.push(2); a.push(8); a.push(5); a.push(7); cout << a.front() << endl; // 1 cout << a.back() << endl; // 7 a.pop(); // 1被弹出 cout << a.front() << endl; // 4 priority_queue<int> b; // 默认< 排序,所以最大的值优先级最大 b.push(1); b.push(4); b.push(2); b.push(8); b.push(5); b.push(7); cout << b.top() << endl; // 8 b.pop(); // 8被弹出 cout << b.top() << endl; // 7 return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号