微调 FLAN-T5 以进行聊天和对话摘要
在这个博客中,您将学习如何微调google/flan-t5-xl用于聊天和对话摘要,使用Hugging Face Transformers。如果您已经了解T5,FLAN-T5在各方面都更出色。对于相同数量的参数,这些模型在超过1000个附加任务上进行了微调,涵盖更多的语言。
在这个例子中,我们将使用samsum数据集,这是一组大约16k带有总结的类似消息的对话。这些对话是由精通英语的 linguists 创建和编写的。
你将学习如何:
快速介绍:FLAN-T5,只是更好的T5
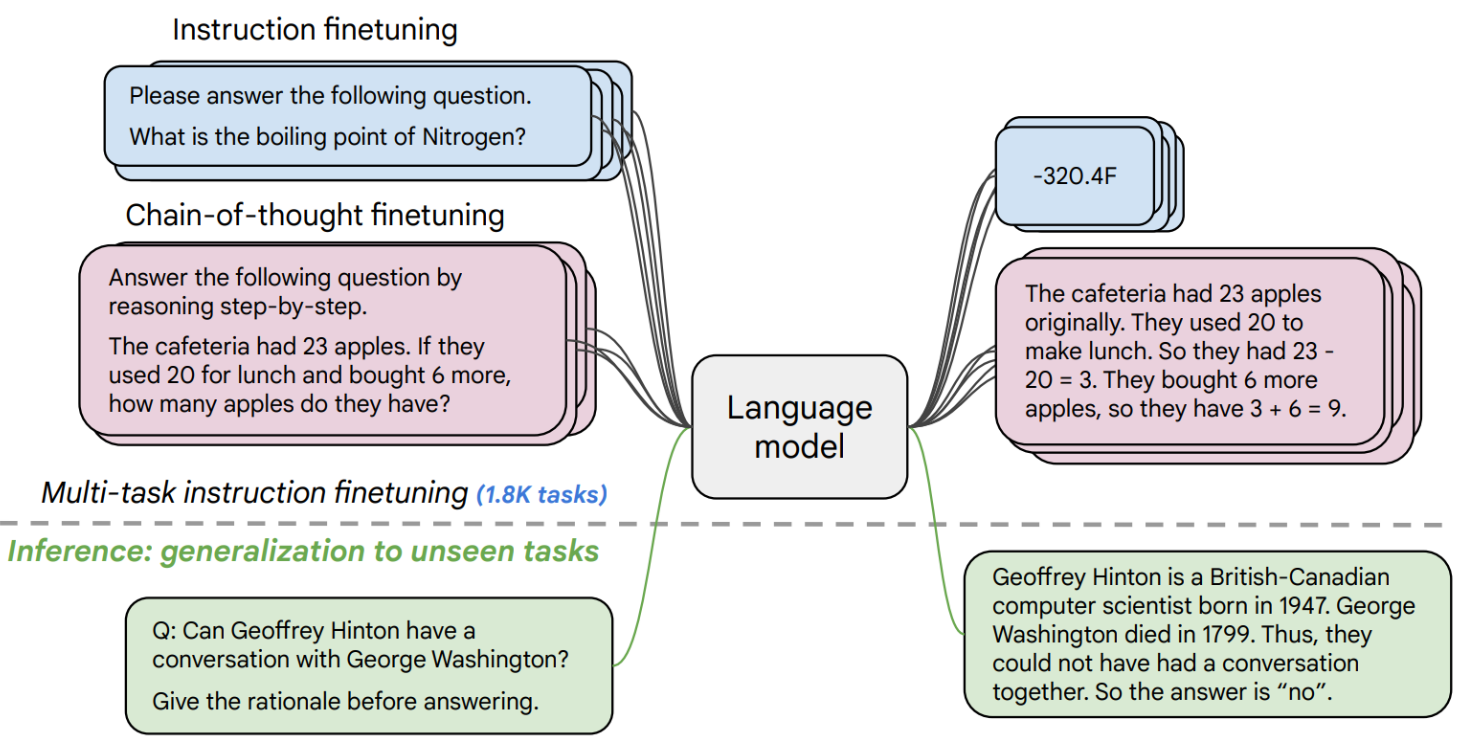
FLAN-T5随 Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models 纸张发布,是T5的增强版本,已经在混合任务中进行了微调。该论文探讨了指令微调,特别关注(1)增加任务数量,(2)扩大模型规模,以及(3)在思维链数据上进行微调。该论文发现,总体而言,指令微调是提高预训练语言模型性能和可用性的通用方法。
现在我们知道FLAN-T5是什么了,让我们开始吧。🚀
注意:本教程是在包含NVIDIA T4的g4dn.xlarge AWS EC2实例上创建和运行的。
1. 设置开发环境
我们的第一步是安装Hugging Face库,包括transformers和datasets。运行以下单元格将安装所有所需的包。
# python !pip install pytesseract transformers datasets rouge-score nltk tensorboard py7zr --upgrade
2. 加载并准备三星数据集
我们将使用samsum数据集,这是一个包含约16k条消息式对话的集合,并附有摘要。这些对话由精通英语的 linguists 创建和编写。
{
"id":"13818513",
"summary":"Amanda做了饼干,明天会带给Jerry一些。",
"dialogue":"Amanda: 我做了饼干。你要一些吗?
Jerry: 当然!
Amanda: 我明天会带给你的 :-)"
}
加载samsum数据集,我们使用来自🤗 Datasets库的load_dataset()方法。
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset_id = "knkarthick/samsum"
# Load dataset from the hub
dataset = load_dataset(dataset_id)
# 使用filter函数过滤掉包含Null值的样本
def filter_nulls(examples):
# 保留"dialogue"不为Null的样本
return [d is not None for d in examples["dialogue"]]
dataset = dataset.filter(filter_nulls, batched=True)
print(f"Train dataset size: {len(dataset['train'])}")
print(f"Test dataset size: {len(dataset['test'])}")
# Train dataset size: 14732
# Test dataset size: 819
Train dataset size: 14731
Test dataset size: 819
让我们查看一下数据集的一个例子。
from random import randrange
sample = dataset['train'][randrange(len(dataset["train"]))]
print(f"dialogue: \n{sample['dialogue']}\n---------------")
print(f"summary: \n{sample['summary']}\n---------------")
dialogue: David: The new movie of Jonhy English has come out, have you seen it? Patricia: No but I have been meaning to go tough. I heard it's hilarious. David: Rowan Atkison is just awesome, love that guy! In Mr. Bean I would just laugh so hard ahaha Patricia: Me too 😂 I couldn't watch some scenes sometimes cause they would make me nervous from all the constant crap he did ahhaha David: ahahaa xD Anyway.. wanna go to the 21:40 session today? I ain't got much going on so.. Patricia: Sure! Where are you having dinner? David: Was thinking of just ordering a pizza, you have any ideas? Patricia: There's a new Mexican place and they do take out's, want me to grab something and meet you at your place? David: Oh that's what I'm talking about! Bring me 2 chicken burritos and nachoooos with guacamole. Patricia: Anything else for the little boy? ahaha xD David: While you're at it a coke would do 😂 Patricia: Jesus.. x) Leaving my place now, cya in a bit. --------------- summary: Patricia and David are going to watch Johnny English new movie. They are having Mexican takeaway at David's before the session. ---------------
为了训练我们的模型,我们需要将输入(文本)转换为标记 ID。这是通过 🤗 Transformers Tokenizer 实现的。如果你不确定这意味着什么,请查看 Hugging Face 课程的第 6 章。
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM model_id="google/flan-t5-base" # Load tokenizer of FLAN-t5-base tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
在我们开始训练之前,我们需要预处理我们的数据。自抽象总结是一个文本到文本生成任务。这意味着我们的模型将接受一个文本作为输入,并生成一个摘要作为输出。为此,我们需要了解输入和输出的长度,以便高效地批量处理数据。
from datasets import concatenate_datasets # The maximum total input sequence length after tokenization. # Sequences longer than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded. tokenized_inputs = concatenate_datasets([dataset["train"], dataset["test"]]).map(lambda x: tokenizer(x["dialogue"], truncation=True), batched=True, remove_columns=["dialogue", "summary"]) max_source_length = max([len(x) for x in tokenized_inputs["input_ids"]]) print(f"Max source length: {max_source_length}") # The maximum total sequence length for target text after tokenization. # Sequences longer than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded." tokenized_targets = concatenate_datasets([dataset["train"], dataset["test"]]).map(lambda x: tokenizer(x["summary"], truncation=True), batched=True, remove_columns=["dialogue", "summary"]) max_target_length = max([len(x) for x in tokenized_targets["input_ids"]]) print(f"Max target length: {max_target_length}")
Max source length: 512
Max target length: 95
def preprocess_function(sample,padding="max_length"): # add prefix to the input for t5 inputs = ["summarize: " + item for item in sample["dialogue"]] # tokenize inputs model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs, max_length=max_source_length, padding=padding, truncation=True) # Tokenize targets with the `text_target` keyword argument labels = tokenizer(text_target=sample["summary"], max_length=max_target_length, padding=padding, truncation=True) # If we are padding here, replace all tokenizer.pad_token_id in the labels by -100 when we want to ignore # padding in the loss. if padding == "max_length": labels["input_ids"] = [ [(l if l != tokenizer.pad_token_id else -100) for l in label] for label in labels["input_ids"] ] model_inputs["labels"] = labels["input_ids"] return model_inputs tokenized_dataset = dataset.map(preprocess_function, batched=True, remove_columns=["dialogue", "summary", "id"]) print(f"Keys of tokenized dataset: {list(tokenized_dataset['train'].features)}")
Keys of tokenized dataset: ['input_ids', 'attention_mask', 'labels']
3. 调优和评估FLAN-T5
在我们处理完数据集后,就可以开始训练我们的模型。因此,我们首先需要从Hugging Face Hub加载我们的FLAN-T5。在示例中,我们使用了一台NVIDIA V100的实例,这意味着我们将微调base版本的模型。 我计划在后续文章中介绍如何使用Deepspeed微调xxl版本的模型。
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM # huggingface hub model id model_id="google/flan-t5-base" # load model from the hub model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
我们在训练期间想要评估我们的模型。 Trainer 通过提供一个 compute_metrics 来支持训练期间的评估。
评估摘要任务最常用的指标是 rogue_score,这是Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation的缩写。这个指标不像标准的准确率:它会将生成的摘要与一组参考摘要进行比较
我们将使用evaluate库来评估rogue分数。
import evaluate import nltk import numpy as np from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize # nltk.download("punkt") nltk.download('punkt_tab') # Metric metric = evaluate.load("rouge") # helper function to postprocess text def postprocess_text(preds, labels): preds = [pred.strip() for pred in preds] labels = [label.strip() for label in labels] # rougeLSum expects newline after each sentence preds = ["\n".join(sent_tokenize(pred)) for pred in preds] labels = ["\n".join(sent_tokenize(label)) for label in labels] return preds, labels def compute_metrics(eval_preds): preds, labels = eval_preds if isinstance(preds, tuple): preds = preds[0] decoded_preds = tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True) # Replace -100 in the labels as we can't decode them. labels = np.where(labels != -100, labels, tokenizer.pad_token_id) decoded_labels = tokenizer.batch_decode(labels, skip_special_tokens=True) # Some simple post-processing decoded_preds, decoded_labels = postprocess_text(decoded_preds, decoded_labels) result = metric.compute(predictions=decoded_preds, references=decoded_labels, use_stemmer=True) result = {k: round(v * 100, 4) for k, v in result.items()} prediction_lens = [np.count_nonzero(pred != tokenizer.pad_token_id) for pred in preds] result["gen_len"] = np.mean(prediction_lens) return result
[nltk_data] Downloading package punkt_tab to /root/nltk_data... [nltk_data] Package punkt_tab is already up-to-date!
在我们开始训练之前,需要创建一个DataCollator,它将处理我们的输入和标签的填充。我们将使用DataCollatorForSeq2Seq来自🤗 Transformers库。
from transformers import DataCollatorForSeq2Seq # we want to ignore tokenizer pad token in the loss label_pad_token_id = -100 # Data collator data_collator = DataCollatorForSeq2Seq( tokenizer, model=model, label_pad_token_id=label_pad_token_id, pad_to_multiple_of=8 )
最后一步是定义我们要用于训练的超参数 (TrainingArguments)。我们正在利用 Hugging Face Hub 的 Trainer 集成,自动将训练过程中的检查点、日志和指标推送到一个仓库中。
from huggingface_hub import HfFolder from transformers import Seq2SeqTrainer, Seq2SeqTrainingArguments # Hugging Face repository id repository_id = "flan-t5-base-samsum" # Define training args training_args = Seq2SeqTrainingArguments( output_dir=repository_id, per_device_train_batch_size=8, per_device_eval_batch_size=8, predict_with_generate=True, fp16=False, # Overflows with fp16 learning_rate=1e-5, num_train_epochs=5, # logging & evaluation strategies logging_dir=f"{repository_id}/logs", logging_strategy="steps", logging_steps=500, eval_strategy="epoch", save_strategy="epoch", save_total_limit=2, load_best_model_at_end=True, # metric_for_best_model="overall_f1", # push to hub parameters report_to="tensorboard", # push_to_hub=False, hub_strategy="every_save", hub_model_id=repository_id, hub_token=HfFolder.get_token(), ) # Create Trainer instance trainer = Seq2SeqTrainer( model=model, args=training_args, data_collator=data_collator, train_dataset=tokenized_dataset["train"], eval_dataset=tokenized_dataset["test"], compute_metrics=compute_metrics, )
我们可以使用 train 的 Trainer 来开始我们的训练。
# Start training trainer.train()
 [9210/9210 1:06:01, Epoch 5/5]
[9210/9210 1:06:01, Epoch 5/5]
Epoch Training Loss Validation Loss Rouge1 Rouge2 Rougel Rougelsum Gen Len
1 1.449900 1.402620 47.207300 23.331700 39.304300 43.478400 17.825397
2 1.423900 1.392744 47.544600 23.821400 39.900300 43.766600 17.952381
3 1.390700 1.389776 47.575800 23.675200 39.859300 43.965000 17.881563
4 1.390300 1.389634 47.248000 23.317800 39.590100 43.632800 17.986569
5 1.384800 1.388537 47.318000 23.437400 39.619900 43.692400 17.890110
很好,我们已经训练好了模型。🎉 让我们再次在测试集上运行评估最佳模型。
trainer.evaluate()
 [103/103 01:06]
[103/103 01:06]
{'eval_loss': 1.388536810874939,
'eval_rouge1': 47.318,
'eval_rouge2': 23.4374,
'eval_rougeL': 39.6199,
'eval_rougeLsum': 43.6924,
'eval_gen_len': 17.89010989010989,
'eval_runtime': 68.485,
'eval_samples_per_second': 11.959,
'eval_steps_per_second': 1.504,
'epoch': 5.0}
我们取得的最高分是rouge1 分。47.318
让我们将我们的结果和分词器保存到Hugging Face Hub,并创建一个模型卡。
# Save our tokenizer and create model card tokenizer.save_pretrained(repository_id) # trainer.create_model_card()
('flan-t5-base-samsum/tokenizer_config.json', 'flan-t5-base-samsum/special_tokens_map.json', 'flan-t5-base-samsum/tokenizer.json')
4. 运行推理
现在我们有一个训练好的模型,我们可以用它来运行推理。我们将使用pipeline transformers 的 API 和一个test 我们数据集中的示例。
from transformers import pipeline from random import randrange # load model and tokenizer from huggingface hub with pipeline summarizer = pipeline("summarization", model="philschmid/flan-t5-base-samsum", device=0) # select a random test sample sample = dataset['test'][randrange(len(dataset["test"]))] print(f"dialogue: \n{sample['dialogue']}\n---------------") # summarize dialogue res = summarizer(sample["dialogue"]) print(f"flan-t5-base summary:\n{res[0]['summary_text']}")
Device set to use cuda:0 Your max_length is set to 200, but your input_length is only 127. Since this is a summarization task, where outputs shorter than the input are typically wanted, you might consider decreasing max_length manually, e.g. summarizer('...', max_length=63) dialogue: Richie: Pogba Clay: Pogboom Richie: what a s strike yoh! Clay: was off the seat the moment he chopped the ball back to his right foot Richie: me too dude Clay: hope his form lasts Richie: This season he's more mature Clay: Yeah, Jose has his trust in him Richie: everyone does Clay: yeah, he really deserved to score after his first 60 minutes Richie: reward Clay: yeah man Richie: cool then Clay: cool --------------- flan-t5-base summary: Pogba scored a strike after his first 60 minutes. Richie and Clay hope his form lasts this season and he's more mature.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号