Vue 3.0 体验
并不是按照正常项目流程来体验,而是挑拣官方发布区别于之前版本的版块
基于版本: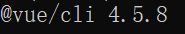
选项式 => 组合式
起步:通过脚手架 vue-cli 安装:首先全局更新最新版的 Vue CLI,4.5.0以上版本支持 Vue3
npm install -g @vue/cli # OR yarn global add @vue/cli vue create hello-vue3 # select vue 3 preset
1.查看入口文件
Vue 2 main.js:
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' new Vue({ render: h => h(App), }).$mount('#app')
Vue 3 main.js:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
createApp(App).mount('#app')
main.js 中创建Vue实例的代码替换成新引入的 createApp方法
2.创建路由
首先在/src/views 目录下创建 demo.vue:
<template> <div class="demo"> <p>烟迷楚驿,月冷蓝桥</p> </div> </template> <script> export default { } </script> <style lang="less" scoped>
</style>
然后在/src/router/index.js 中创建路由配置:
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/demo',
name: 'Demo',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "demo" */ '../views/demo.vue')
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes
})
export default router
相比较之前创建路由:
import Vue from 'vue' import Router from 'vue-router' Vue.use(Router) const router = new Router({ mode: 'history', base: process.env.VUE_APP_API_PUBLIC_PATH, routes: [] }) export default router
3.使用Composition api的位置被称为setup==>状态和事件绑定
setup组件
setup 组件选项在创建组件之前执行,一旦 props 被解析,并充当合成 API 的入口点。
注意:由于在执行 setup 时尚未创建组件实例,因此在 setup 选项中没有 this。这意味着,除了 props 之外,你将无法访问组件中声明的任何属性——本地状态、计算属性或方法。
// src/components/UserRepositories.vue `setup` function import { fetchUserRepositories } from '@/api/repositories' import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue' // in our component export default { setup (props) { const repositories = ref([]) // 定义一个变量 const getUserRepositories = async () => { // 定义一个方法 repositories.value = await fetchUserRepositories(props.user) } onMounted(getUserRepositories) // 生命周期钩子 当实例mounted后调用getUserRepositories方法 return { repositories, // 返回一个data getUserRepositories // 返回一个method } } }
以上的repositories相当于2.0data中的响应式数据,在我们的demo.vue中写:
<template>
<div class="demo">
<p>烟迷楚驿,月冷蓝桥</p>
<h1>test count: {{count}}</h1>
<button @click="add">add</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
export default {
setup () {
const count = ref(0)
const add = () => {
count.value++
}
return {
count,
add
}
}
}
//以上count看起来的效果和2.0data中定义的数据并没有什么不同。
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
</style>
4.计算属性和监听器
Vue 3.0 中计算属性和监听器的实现依旧依赖 computed 和 watch 方法:
<template>
<div class="demo">
<p>烟迷楚驿,月冷蓝桥</p>
<h1>test count: {{count}}</h1>
<div>count * 2 = {{doubleCount}}</div>
<button @click="add">add</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref,watch, computed} from 'vue'
export default {
setup () {
const count = ref(0)
const add = () => {
count.value++
}
watch(() => count.value, val => {
console.log(`count is ${val}`)
})
const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2)
return {
count,
doubleCount,
add
}
}
}
//以上count看起来的效果和2.0data中定义的数据并没有什么不同。
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
</style>
//监听器 watch 同样是一个方法,它包含 2 个参数,2 个参数都是 function,第一个参数是监听的值,count.value 表示当 count.value
发生变化就会触发监听器的回调函数,即第二个参数,第二个参数可以执行监听时候的回调
//如果是两个以上的监听:
watch( [refA, () => refB.value], ([a, b], [prevA, prevB]) => { console.log(`a is: ${a}`) console.log(`b is: ${b}`) } )
//计算属性 computed 是一个方法,里面需要包含一个回调函数,当我们访问计算属性返回结果时,会自动获取回调函数的值
5.组件内获取路由实例<script> import { getCurrentInstance } from 'vue' export default { setup () { const { ctx } = getCurrentInstance() console.log(ctx.$router.currentRoute.value) } } </script>
Vue 3.0 中通过 getCurrentInstance 方法获取当前组件的实例,然后通过 ctx 属性获得当前上下文,
ctx.$router 是 Vue Router 实例,里面包含了 currentRoute 可以获取到当前的路由信息
vue3.0数据都写在setup里,以前的所有数据状态都写在data里,
所有方法都写在methods里,而现在可以根据功能模块把状态和方法等划分在一起,更利于模块化。
摘录:=====================================================================>
受影响的API:
- Vue.nextTick
- Vue.observable (用Vue.reactive替换)
- Vue.version
- Vue.compile
- Vue.set
- Vue.delete
import { nextTick } from 'vue'
nextTick(() => {
// 一些和DOM有关的东西
})
生命周期的变化
Vue2 -> Vue3beforeCreate -> setupcreated -> setupbeforeMount -> onBeforeMountmounted -> onMountedbeforeUpdate -> onBeforeUpdateupdated -> onUpdatedbeforeDestroy -> onBeforeUnmountdestroyed -> onUnmountedactivated -> onActivateddeactivated -> onDeactivatederrorCaptured -> onErrorCapturedrenderTracked -> onRenderTrackedrenderTriggered -> onRenderTriggered
在这里主要是增加了setup这个生命周期,而其他的生命周期都是以API的形式调用,实际上随着Composition API (setup)的引入,我们访问这些钩子函数的方式已经
改变,我们所有的生命周期都应该写在setup中,此方法我们应该实现大多数组件代码,并处理响应式,生命周期钩子函数等。
import { onBeforeMount, onMounted, onBeforeUpdate, onUpdated, onBeforeUnmount, onUnmounted, onActivated, onDeactivated, onErrorCaptured, onRenderTracked, onRenderTriggered } from "vue"; export default { setup() { onBeforeMount(() => { // ... }) onMounted(() => { // ... }) onBeforeUpdate(() => { // ... }) onUpdated(() => { // ... }) onBeforeUnmount(() => { // ... }) onUnmounted(() => { // ... }) onActivated(() => { // ... }) onDeactivated(() => { // ... }) onErrorCaptured(() => { // ... }) onRenderTracked(() => { // ... }) onRenderTriggered(() => { // ... }) } }
使用proxy代替defineProperty
Vue2是通过数据劫持的方式来实现响应式的,其中最核心的方法便是通过Object.defineProperty()来实现对属性的劫持,该方法允许精确地添加或修改对象的属性,
对数据添加属性描述符中的getter与setter存取描述符实现劫持。Vue2之所以只能兼容到IE8主要就是因为defineProperty无法兼容IE8,其他浏览器也会存在轻微兼容问题。
var obj = { __x: 1 }; Object.defineProperty(obj, "x", { set: function(x){ console.log("watch"); this.__x = x; }, get: function(){ return this.__x; } }); obj.x = 11; // watch console.log(obj.x); // 11
Vue3使用Proxy实现数据劫持,Object.defineProperty只能监听属性,而Proxy能监听整个对象,通过调用new Proxy(),可以创建一个代理用来替代另一个对象被称
为目标,这个代理对目标对象进行了虚拟,因此该代理与该目标对象表面上可以被当作同一个对象来对待。代理允许拦截在目标对象上的底层操作,而这原本是Js引
擎的内部能力,拦截行为使用了一个能够响应特定操作的函数,即通过Proxy去对一个对象进行代理之后,我们将得到一个和被代理对象几乎完全一样的对象,并且
可以从底层实现对这个对象进行完全的监控。Proxy对象是ES6引入的新特性,Vue3放弃使用了Object.defineProperty,而选择了使用更快的原生Proxy,即是在兼容
性方面更偏向于现代浏览器。
var target = {a: 1}; var proxy = new Proxy(target, { set: function(target, key, value, receiver){ console.log("watch"); return Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver); }, get: function(target, key, receiver){ return target[key]; } }); proxy.a = 11; // watch console.log(target); // { a: 11 }
diff算法的更新
首先,在DOM树级别,我们注意到,在没有动态改变节点结构的模板指令(例如v-if和v-for)的情况下,节点结构保持完全静态,如果我们将一个模板分成由这些结构指
令分隔的嵌套块,则每个块中的节点结构将再次完全静态,当我们更新块中的节点时,我们不再需要递归遍历DOM树,该块内的动态绑定可以在一个平面数组中跟踪,
这种优化通过将需要执行的树遍历量减少一个数量级来规避虚拟DOM的大部分开销。
其次,编译器积极地检测模板中的静态节点、子树甚至数据对象,并在生成的代码中将它们提升到渲染函数之外,这样可以避免在每次渲染时重新创建这些对象,从而
大大提高内存使用率并减少垃圾回收的频率。
第三,在元素级别,编译器还根据需要执行的更新类型,为每个具有动态绑定的元素生成一个优化标志,例如具有动态类绑定和许多静态属性的元素将收到一个标志,
提示只需要进行类检查,运行时将获取这些提示并采用专用的快速路径。
Vue3.0 是如何变快的?
-
diff 算法优化
- Vue2 中的虚拟dom 是进行全量对比
- Vue3 新增静态标记
-
hoistStatic 静态提升
- Vue2 中无论元素是否参与更新,每次都会重新创建,然后在渲染
- Vue3 中对于不参与更新的元素,会做静态提升,只被创建一次,在渲染时直接复用即可
-
cacheHandlers 事件侦听器缓存
- 默认情况下默认情况下onClick会被视为动态绑定,所以每次都会去追踪它的变化,但是因为是同一个函数,所以没有追踪变化,直接缓存起来复用即可
-
ssr 渲染
- 当有大量静态的内容的时候,这些内容会被当作纯字符串推进一个buffer里面,即使存在动态的绑定,
- 会通过模版插值嵌入进去,这样会比通过虚拟dom来渲染的快上很多很多
- 当静态内容大到一定量级的时候,会用_createStaticVNode方法在客户端去生成一个static node。
- 这些静态node,会被直接innerHtml,就不需要创建对象,然后根据对象渲染。
emmmm..算了,不搬了,怕惹了大佬不开心,附上大佬链接!=============================================>
https://www.cnblogs.com/WindrunnerMax/p/14394440.html
http://www.sanrenyan.com/?p=2710



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号