CSS中的定位 - position
css中的position是个很重要的属性,这里介绍常见的四种定位方式。
| 定位方式 | ||
| static | 静态定位 | 默认定位,标准流, 不配合方位属性移动 |
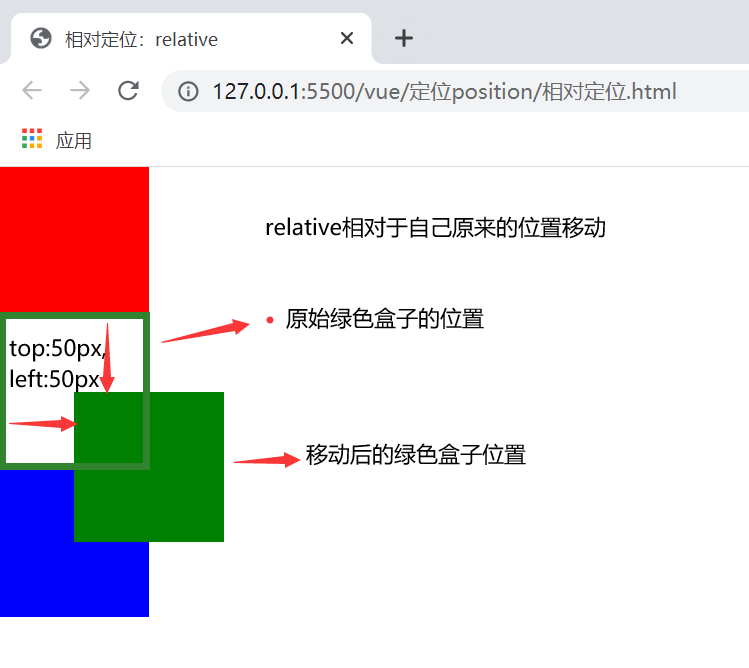
| relative | 相对定位 | 相对自己之前的位置进行移动,没有脱标 |
| absolute | 绝对定位 |
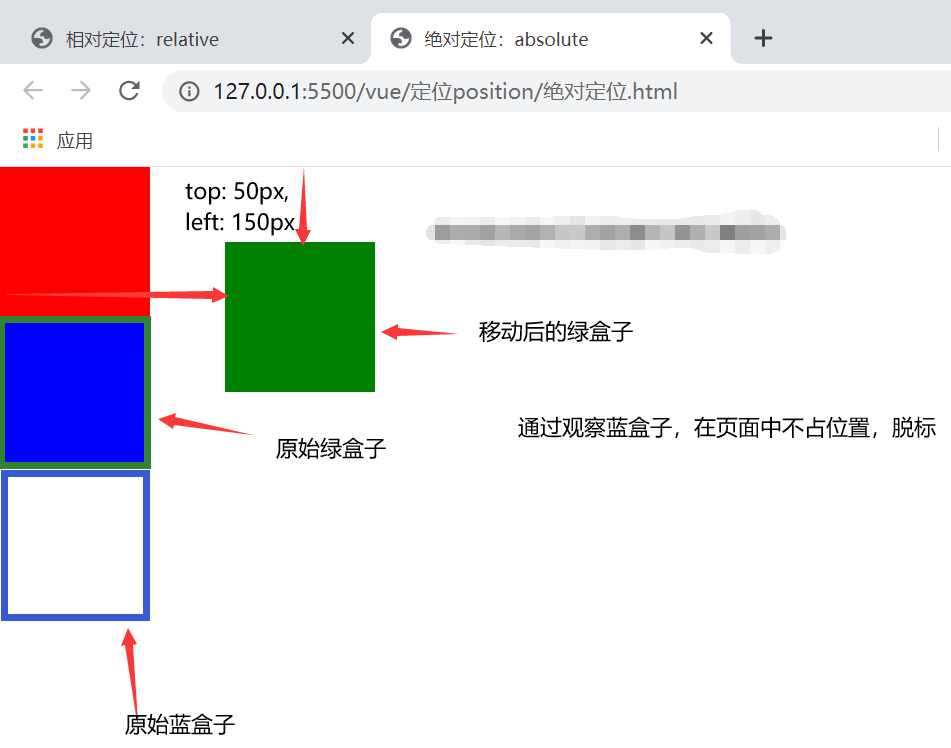
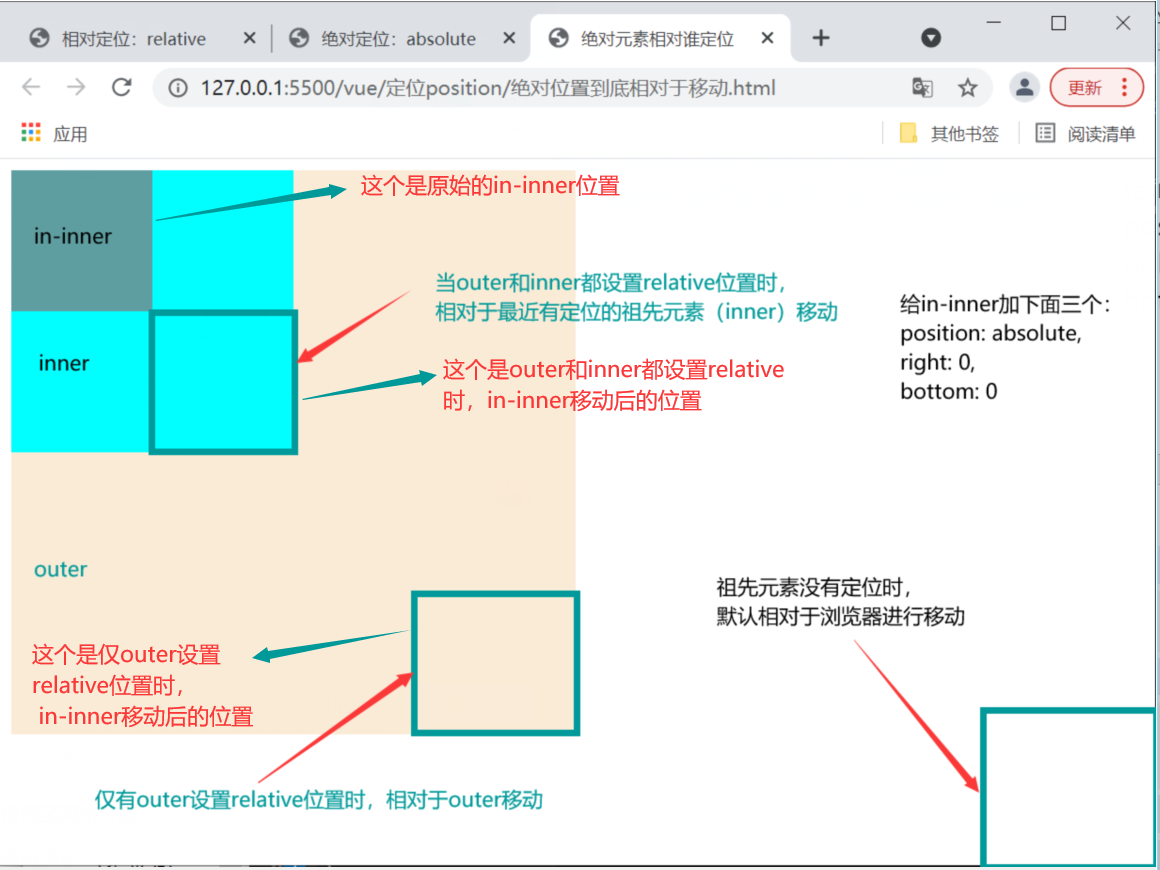
脱标。相对于除静态定位的父元素定位移动,有两种情况 (1)如果祖先元素没有定位,则默认相对于浏览器移动 (2)如果祖先元素有定位,则相对于最近的有定位的祖先元素移动 |
| fixed | 固定定位 | 脱标。相对于浏览器定位移动,应用场景主要是让盒子固定在屏幕的某个位置 |
知道常见的四种定位方式后,来看看使用定位的步骤。
步骤一:根据需求设置定位方式。
步骤二:设置偏移量(水平或者垂直偏移量),设置偏移量使用就近原则
偏移量包括:水平偏移量---right, left。垂直偏移量---top,bottom
下面图形介绍了相对定位、绝对定位
1、相对定位
2、绝对定位(祖先元素没有设置定位)
3、绝对定位(相对谁移动问题)
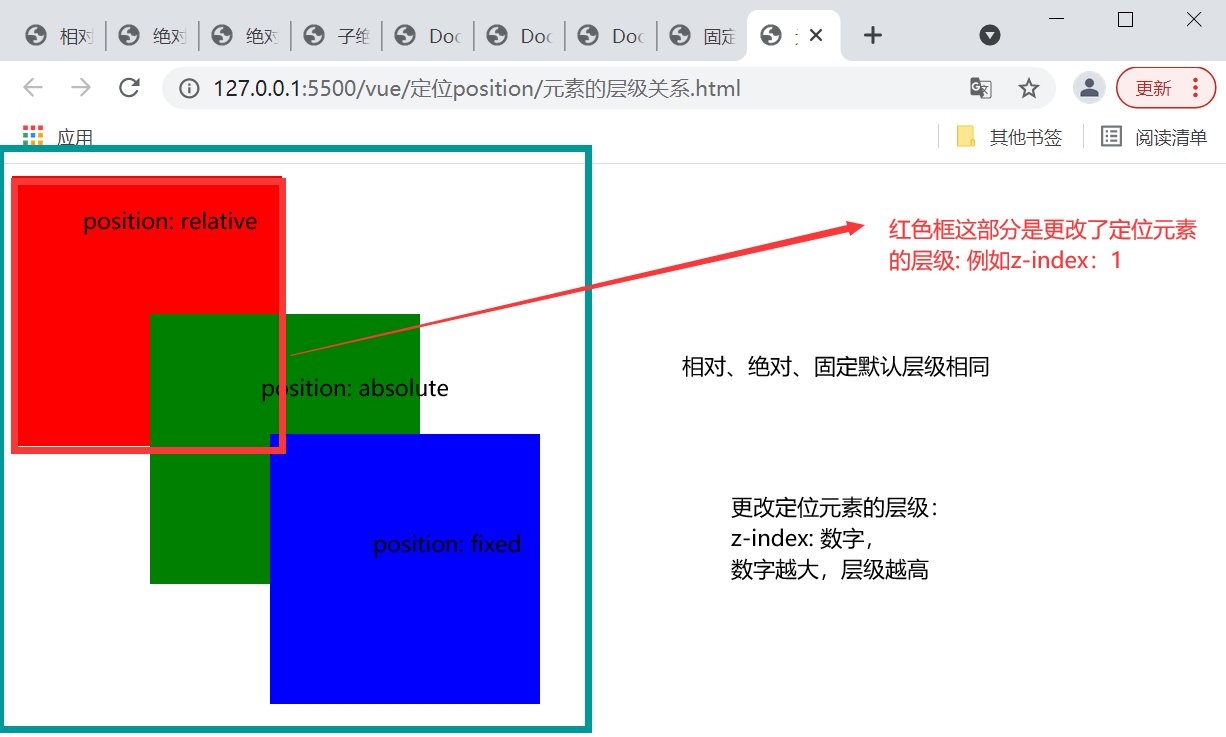
接着,介绍下如何通过z-index更改定位元素的层级,z-index的值为数字,数字越大,表示层级越高。
最后, 给个子绝父相的案例

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>子绝父相</title>
<style>
.outer {
/* position: relative; */
position: relative;
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
background-color:antiquewhite;
}
.inner {
position: absolute;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.other {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color:cadetblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>
<div class="other"></div>
</body>
</html>




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号