
package net.elaina.BigIntegerTest;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Random;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
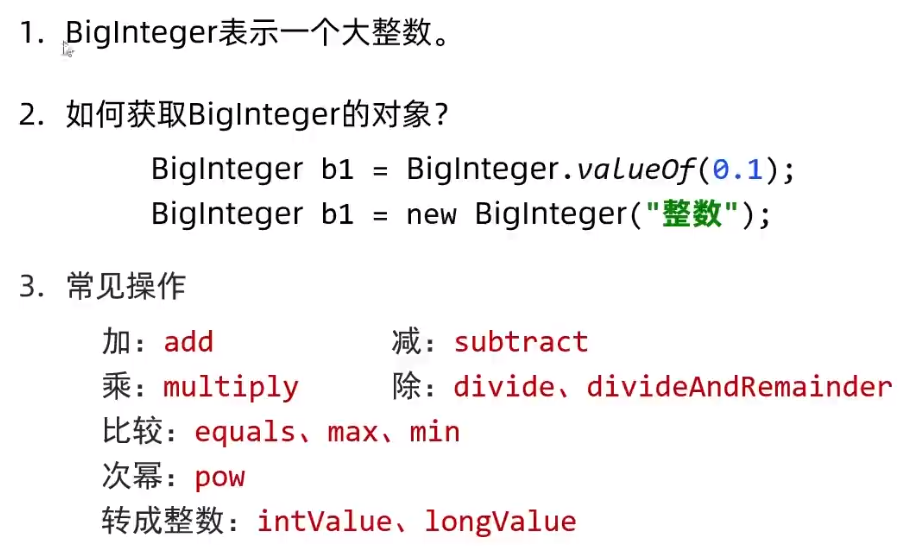
public BigInteger(int num, Random rnd) 获取随机大整数,范围:[e ~ 2的num次方-1]
public BigInteger(String val) 获取指定的大整数
public BigInteger(String val, int radix) 获取指定进制的大整数
public static BigInteger valueof(long val) 静态方法获取BigInteger的对象,内部有优化
细节:
对象一旦创建里面的数据不能发生改变。
*/
//1.获取一个随机大整数
BigInteger bd1 = new BigInteger(4,new Random()); // 2的4次方减1
System.out.println(bd1); //[0 - 15]
//2.获取一个指定的大整数
//细节:字符串中必须是整数,否则会报错
BigInteger bd2 = new BigInteger("100");
System.out.println(bd2);
//3.获取指定进制的大整数
//细节:
//1.字符串中的数字必须是整数
//2.字符串中的数字必须要跟进制吻合。
//比如二进制中,那么只能写0和1,写其他的就报错。
BigInteger bd3 = new BigInteger("100",2);
System.out.println(bd3);
//4.静态方法获取BigInteger的对象,内部有优化
//细节:
//1.能表示范围比较小,只能在long的取值范围之类,如果超出1ong的范围就不行了。
//2.在内部对常用的数字:-16~16进行了优化。
// 提前把-16~16先创建好BigInteger的对象,如果多次获取不会重新创建新的。
BigInteger bd5 = BigInteger.valueOf(100);
System.out.println(bd5);
System.out.println(Long.MAX_VALUE);
BigInteger bd6 = BigInteger.valueOf(16);
BigInteger bd7 = BigInteger.valueOf(16);
System.out.println(bd6 == bd7); // true
BigInteger bd8 = BigInteger.valueOf(17);
BigInteger bd9 = BigInteger.valueOf(17);
System.out.println(bd8 == bd9); // false
//5.对象一旦创建里面的数据不能发生改变
BigInteger bd10 = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
BigInteger bd11 = BigInteger.valueOf(2);
// 1 + 2
BigInteger result = bd10.add(bd11);
System.out.println(result);
//此时,不会修改参与计算的BigInteger对象中的值,而是产生了一个新的BigInteger对象记录3
}
}


package net.elaina.BigIntegerTest;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
public BigInteger add(BigInteger val) 加法
public BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) 减法
public BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) 乘法
public BigInteger divide(BigInteger val) 除法,获取商
public BigInteger[] divideAndRemainder(BigInteger val) 除法,获取商和余数
public boolean equals(object x) 比较是否相同
public BigInteger pow(int exponent) 次幂
public BigInteger max/min(BigInteger val) 返回较大值/较小值
public int intValue(BigInteger val) 转为int类型整数,超出范围数据有误
*/
//1.创建两个BigInteger对象
BigInteger bd1 = BigInteger.valueOf(10);
BigInteger bd2 = BigInteger.valueOf(5);
//2.加法
BigInteger bd3 = bd1.add(bd2);
System.out.println(bd3);
//3.除法,获取商和余数
BigInteger[] arr = bd1.divideAndRemainder(bd2);
System.out.println(arr[0]); //商
System.out.println(arr[1]); //余数
//4.比较是否相同
boolean result = bd1.equals(bd2);
System.out.println(result);
//5.次幂
BigInteger bd4 = bd1.pow(2);
System.out.println(bd4);
//6.max
BigInteger bd5 = bd1.max(bd2);
System.out.println(bd5);
//7. 转为int类型整数,超出范围数据有误
BigInteger bd6 = BigInteger.valueOf(1000);
int i = bd6.intValue();
System.out.println(i);
}
}







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号