c: thread in Ubuntu 22.04
/**
* @file helloworld.c
* @author your name (geovindu@163.com)
* @brief thread
* @version 0.1
* @date 2023-10-24
* ide: vscode c11,c17 Ubuntu 22.04
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2023 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants 2023
*
*/
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<threads.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<unistd.h> //Header file for sleep(). man 3 sleep for details.
#include<pthread.h>
#include "include/CheckTieck.h"
#include "include/TakeNumber.h"
#define threadcout 5
//
//
thrd_t threadId[threadcout];
mtx_t task_mtx;
struct timespec duration={.tv_sec=1,.tv_nsec=0};
size_t task=0;
/**
* @brief 线程
*
* @param agr
* @return int
*/
int execrteTask(void *agr)
{
mtx_lock(&task_mtx);
size_t local_task = ++task;
mtx_unlock(&task_mtx);
// mtx_lock(&task_mtx); // mutex lock - blocks until acquired
// printf_s("Task %zd started.\n", ++task);
printf("Task %zd started.\n", local_task);
thrd_sleep(&duration, NULL); // Just to make things take longer...
double x = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i< 1000000000 ; ++i)
x = sqrt(3.1415926);
printf(" Task %zd finished\n", local_task);
// printf_s(" Task %zd finished\n", task);
// mtx_unlock(&task_mtx); // mutex unlock - for use by other threads
return 0;
}
// 定义一个结构体,用于存储函数的参数和返回值
typedef struct {
int x; // 输入参数
int y; // 返回值
} data_t;
// 定义一个函数,接受一个指向data_t结构体的指针,打印该结构体中的x值的平方,并将该值加一存入y中
void *square_and_add_one(void *arg) {
data_t *data = (data_t *)arg;
printf("The square of %d is %d\n", data->x, data->x * data->x);
data->y = data->x + 1;
return NULL;
}
/**
* @brief
*
* @param argc
* @param argv
* @return int
*/
int main(void)
{
int argc;
char *argv;//[]={'\0'};
char ddd[11]="The hello world";
argv=ddd;
argc=2;
// 检查命令行参数的个数,至少需要一个参数
if (argc < 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <number>\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
// 将第一个参数转换为整数
printf("%s",&argv[1]);
int thdnum = atoi(&argv[1]);
// 创建一个data_t结构体,并初始化其x值为num
data_t data;
data.x = thdnum;
// 创建一个线程,并传入square_and_add_one函数和data结构体的地址
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, square_and_add_one, &data);
// 等待线程结束,并打印其返回值
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
printf("The thread returned %d\n", data.y);
if(thrd_error == mtx_init(&task_mtx, mtx_timed))
{
//int ret = vfprintf(stdout, fmt, vl);
fprintf(stderr, "Mutex creation failed.\n"); //stderr
thrd_exit(-2);
}
// Create the threads to carry out the tasks concurrently
for(size_t i = 0 ; i<threadcout ; ++i)
if(thrd_error == thrd_create(&(threadId[i]), execrteTask, NULL))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Thread creation failed.\n");
thrd_exit(-1);
}
// Join the additional threads to the main thread
for(size_t j = 0 ; j <threadcout ; ++j)
thrd_join(threadId[j], NULL);
pid_t pid;
int status;
pid = fork(); // 创建一个新进程
if (pid < 0) { // 如果创建失败,输出错误信息
fprintf(stderr, "Fork Failed");
return 1;
} else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程
printf("I am the child %d\n",pid);
execl("/bin/ls", "ls", NULL); // 在子进程中执行 /bin/ls 程序
printf("I am the child %d, and execl failed\n",pid); // 如果 execl 返回,那么说明出错
} else { // 父进程
wait(&status); // 等待子进程结束
printf("I am the parent %d, and my child has ended\n",pid);
}
printf("hello wolrd, c launguage! weblcome geovindu!涂聚文");
QueueCalling *queue1;
char select='1';
//int num=1;//顾客序号
int num=0; //叫号编号
queue1=QueueInit(); //初始化队列
if(queue1==NULL)
{
printf("创建队列时出错!\n");
//getch();
getchar();
return 0;
}
do{
//这里处理,列表不会显示两次
if(select=='1' || select=='2')
{
printf("\n请选择具体操作:\n");
printf("1.新到顾客\n");
printf("2.下一个顾客\n");
printf("0.退出\n") ;
fflush(stdin);
}
select=getchar();//getch();
switch(select)
{
case '1':
add(queue1);
printf("\n现在共有%d位顾客在等候!\n",QueueLen(queue1));
break;
case '2':
next(queue1);
printf("\n现在共有%d位顾客在等候!\n",QueueLen(queue1));
break;
case '0':
break;
}
}while(select!='0');
QueueFree(queue1); //释放队列
//getch();
getchar();
return 0;
}
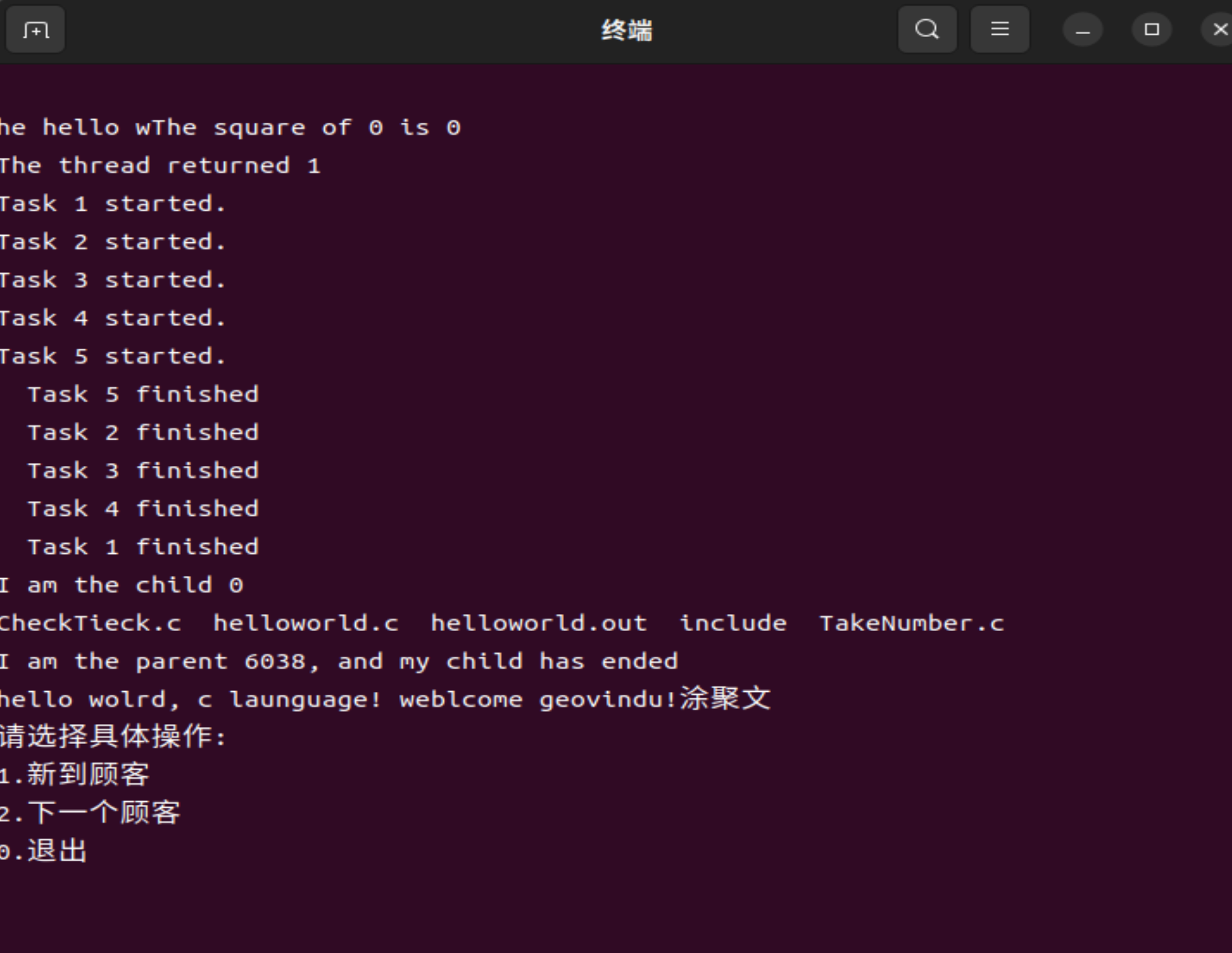
输出:
/**
* @file helloworld.c
* @author your name (geovindu@163.com)
* @brief thread
* @version 0.1
* @date 2023-10-24
* ide: vscode c11,c17 Ubuntu 22.04
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2023 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants 2023
*
*/
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<threads.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<unistd.h> //Header file for sleep(). man 3 sleep for details.
#include<pthread.h>
#include "include/CheckTieck.h"
#include "include/TakeNumber.h"
#include "include/twoDimensional.h"
#define threadcout 5
//
//
thrd_t threadId[threadcout];
mtx_t task_mtx;
struct timespec duration={.tv_sec=1,.tv_nsec=0};
size_t task=0;
/**
* @brief 线程
*
* @param agr
* @return int
*/
int execrteTask(void *agr)
{
mtx_lock(&task_mtx);
size_t local_task = ++task;
mtx_unlock(&task_mtx);
// mtx_lock(&task_mtx); // mutex lock - blocks until acquired
// printf_s("Task %zd started.\n", ++task);
printf("Task %zd started.\n", local_task);
thrd_sleep(&duration, NULL); // Just to make things take longer...
double x = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i< 1000000000 ; ++i)
x = sqrt(3.1415926);
printf(" Task %zd finished\n", local_task);
// printf_s(" Task %zd finished\n", task);
// mtx_unlock(&task_mtx); // mutex unlock - for use by other threads
return 0;
}
// 定义一个结构体,用于存储函数的参数和返回值
typedef struct {
int x; // 输入参数
int y; // 返回值
} data_t;
// 定义一个函数,接受一个指向data_t结构体的指针,打印该结构体中的x值的平方,并将该值加一存入y中
void *square_and_add_one(void *arg) {
data_t *data = (data_t *)arg;
printf("The square of %d is %d\n", data->x, data->x * data->x);
data->y = data->x + 1;
return NULL;
}
/**
* @brief
*
* @param argc
* @param argv
* @return int
*/
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
int status;
pid = fork(); // 创建一个新进程
if (pid < 0) { // 如果创建失败,输出错误信息
fprintf(stderr, "Fork Failed");
return 1;
} else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程
printf("I am the child %d\n",pid);
//execl("/bin/ls", "ls", NULL); // 在子进程中执行 /bin/ls 程序
//execl("/usr/bin/env", "env", NULL, NULL); //OK打印环境变量
//execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c","echo 'Hello!' >> test.txt",(char *) NULL); //OK 添加到文件文尾
execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c","echo 'Hello!' > test.txt",(char *) NULL); //OK 只有hello的字符
//execle("/bin/ls","ls","./",NULL); // ok显示文件夹的文件
//execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", "/bin/cat > test.txt", (char *) NULL); //ok 创建文件,并可以输入内容,关闭即保存
//execl("/bin/cat","cat","1.txt","2.txt",NULL);//显示了两个文件内容
//execl("/bin/cat", "cat", "-n", "1.js", NULL);//ok 读文件显示号
//execl("/bin/cat", "cat", "-n", "1.txt", NULL); //ok 读文件显示号
printf("I am the child %d, and execl failed\n",pid); // 如果 execl 返回,那么说明出错
} else { // 父进程
wait(&status); // 等待子进程结束
printf("I am the parent %d, and my child has ended\n",pid);
}
return 0;
}
如何在程序里使用这些内存。
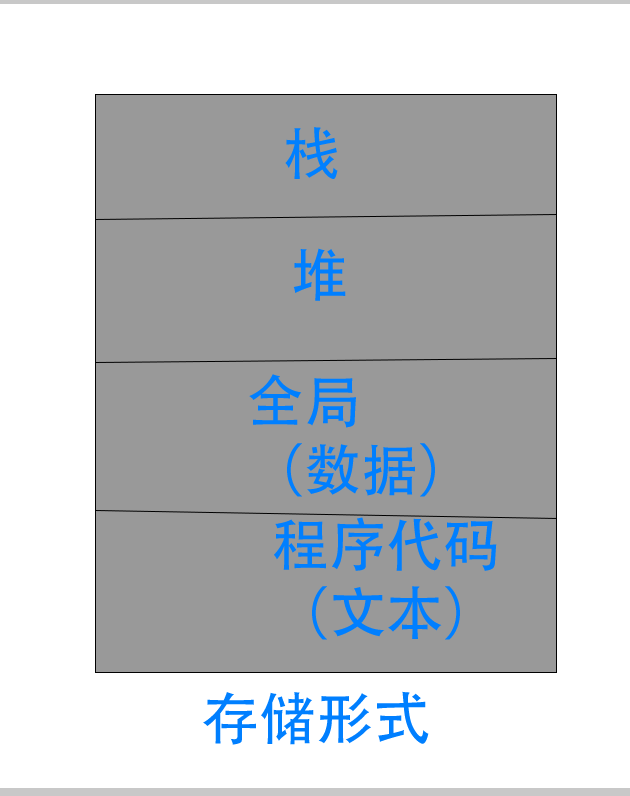
C的存储结构是非常重要的,C的存储结构主要由堆区、栈区、全局常量区、程序代码区组成。其中重要的是堆和栈,它们都属于RAM; 因此,它们是个稳定的,并且在运行时经常会改变。
函数的局部变量是在栈中创建的;同时,在堆中指针是需要你的程序手动处理的(malloc/free),堆的作用域是在程序被运行时。
栈存储变量的空间比堆的小,其原理是为了让栈存储那些只需要短暂的变量。
另一方面,堆可以处理内存需求更大的变量,堆是动态分配的。当然,堆的访问速度取决于每个段的访问对象。堆由开发人员手动处理。也就是说,有可能出现内存泄漏。堆中的变量是全局的,可以通过指针访问。
栈是一个后进先出(last-in-first-out,LIFO)的结构,这对于递归函数非常有用。每次声明一个变量,它将被在于该段的顶部(这就是一个使用pust-pop函数的后进先出结构的栈)。
输入输出格式说明符:
输出格式说明符
printf
printf_s
sprintf
sprintf_s
snprintf
snprintf_s
fprintf
fprintf_s
vfprintf
vsprintf
vprintf
vsnprintf
vfprintf_s
vprintf_s
vsnprintf_s
vsprintf_s
输入格式说明符
scanf
scanf_s
vscanf
vscanf_s
sscanf
sscanf_s
vsscanf
vsscanf_s
fscanf
fscanf_s
vfscanf
vfscanf_s
来源: Beginnin C: From Beginner to Pro, Sixth Edition
https://github.com/Apress/beginning-c-6e
https://www.demo2s.com/c/c-execl-bin-ls-ls-a-l-null.html
#include <unistd.h>
extern char **environ;
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg0, ... /*, (char *)0 */);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg0, ... /*,
(char *)0, char *const envp[]*/);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg0, ... /*, (char *)0 */);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execve(const char *path, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int fexecve(int fd, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
execl("/bin/cat","cat","1.js",">","2.js",NULL);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号