Spark Transformation 算子简介
1 Transformation 算子
RDD的操作算子分为两类:
- Transformation。用来对RDD进行转化,这个操作时延迟执行的(或者说是 Lazy 的);返回一个新的RDD
- Action。用来触发RDD的计算;得到相关计算结果 或者 将结果保存的外部系统 中;返回结果int、double、集合(不会返回新的RDD)
每一次 Transformation 操作都会产生新的RDD,供给下一个“转换”使用; 转换得到的RDD是惰性求值的。也就是说,整个转换过程只是记录了转换的轨迹, 并不会发生真正的计算,只有遇到 Action 操作时,才会发生真正的计算,开始从血 缘关系(lineage)源头开始,进行物理的转换操作;
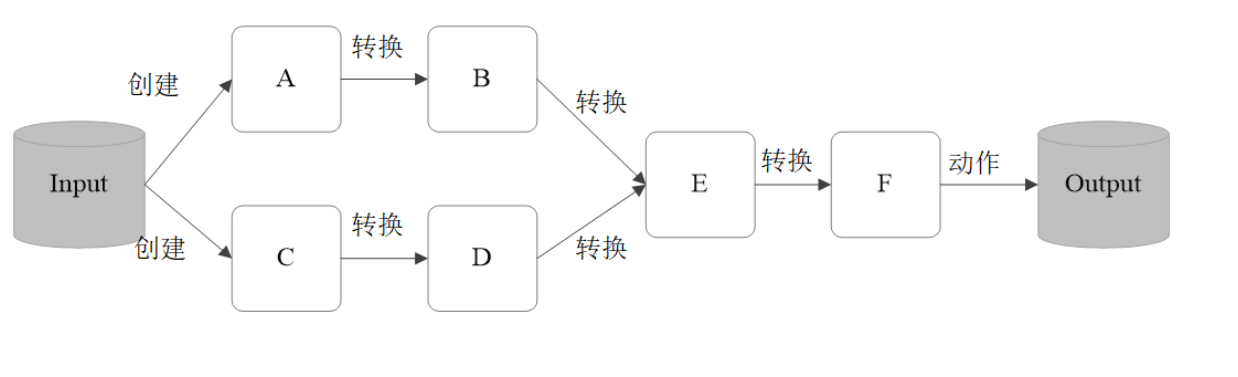
1.1 常见的 Transformation 算子,
map(func):对数据集中的每个元素都使用func,然后返回一个新的RDD
scala> val rdd3 = rdd.map(_*2)
scala> rdd3.collect
res3: Array[Int] = Array(2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 48, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58, 60, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80, 82, 84, 86, 88, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 100, 102, 104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 122, 124, 126, 128, 130, 132, 134, 136, 138, 140, 142, 144, 146, 148, 150, 152, 154, 156, 158, 160, 162, 164, 166, 168, 170, 172, 174, 176, 178, 180, 182, 184, 186, 188, 190, 192, 194, 196, 198, 200)
filter(func):对数据集中的每个元素都使用func,然后返回一个包含使func为true 的元素构成的RDD
scala> val rdd3 = rdd.filter(_ %2 == 1)
scala> rdd3.collect
res4: Array[Int] = Array(1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39, 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 55, 57, 59, 61, 63, 65, 67, 69, 71, 73, 75, 77, 79, 81, 83, 85, 87, 89, 91, 93, 95, 97, 99)
flatMap(func):与 map 类似,每个输入元素被映射为0或多个输出元素
scala> val rdd4 = sc.textFile("/data/wc.txt")
scala> val rdd5 = rdd4.flatMap(_.split(" "))
rdd5: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[String] = MapPartitionsRDD[7] at flatMap at <console>:25
scala> rdd5.collect
res5: Array[String] = Array(ffer, fe, qwsa, 123, dfsd, fsdgrt, jhnr, nrty, re)
mapPartitions(func):和map很像,但是map是将func作用在每个元素上,而 mapPartitions是func作用在整个分区上。假设一个RDD有N个元素,M个分区(N >> M),那么map的函数将被调用N次,而mapPartitions中的函数仅被调用M次, 一次处理一个分区中的所有元素
scala> rdd.mapPartitions(it => Iterator(it.toArray.mkString("-"))).collect
res6: Array[String] = Array(1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8, 9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16, 17-18-19-20-21-22-23-24-25, 26-27-28-29-30-31-32-33, 34-35-36-37-38-39-40-41, 42-43-44-45-46-47-48-49-50, 51-52-53-54-55-56-57-58, 59-60-61-62-63-64-65-66, 67-68-69-70-71-72-73-74-75, 76-77-78-79-80-81-82-83, 84-85-86-87-88-89-90-91, 92-93-94-95-96-97-98-99-100)
mapPartitionsWithIndex(func):与 mapPartitions 类似,多了分区索引值信息
scala> rdd.mapPartitionsWithIndex((index,it) => Iterator(index + "$" + it.toArray.mkString("-"))).collect
res7: Array[String] = Array(0$1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8, 1$9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16, 2$17-18-19-20-21-22-23-24-25, 3$26-27-28-29-30-31-32-33, 4$34-35-36-37-38-39-40-41, 5$42-43-44-45-46-47-48-49-50, 6$51-52-53-54-55-56-57-58, 7$59-60-61-62-63-64-65-66, 8$67-68-69-70-71-72-73-74-75, 9$76-77-78-79-80-81-82-83, 10$84-85-86-87-88-89-90-91, 11$92-93-94-95-96-97-98-99-100)
以上全部是窄依赖算子
groupBy(func):按照传入函数的返回值进行分组。将key相同的值放入一个迭代器
scala> val rdd = sc.parallelize(1 to 30)
scala> rdd.groupBy(_ % 4).collect
res8: Array[(Int, Iterable[Int])] = Array((0,CompactBuffer(28, 8, 16, 24, 4, 12, 20)), (1,CompactBuffer(13, 21, 29, 5, 1, 9, 17, 25)), (2,CompactBuffer(18, 26, 6, 14, 22, 30, 2, 10)), (3,CompactBuffer(7, 15, 3, 11, 19, 27, 23)))
glom():将每一个分区形成一个数组,形成新的RDD类型 RDD[Array[T]]
scala> rdd.getNumPartitions
res9: Int = 12
scala> rdd.glom.collect
res10: Array[Array[Int]] = Array(Array(1, 2), Array(3, 4, 5), Array(6, 7), Array(8, 9, 10), Array(11, 12), Array(13, 14, 15), Array(16, 17), Array(18, 19, 20), Array(21, 22), Array(23, 24, 25), Array(26, 27), Array(28, 29, 30))
sample(withReplacement, fraction, seed):采样算子。以指定的随机种子 (seed)随机抽样出数量为fraction的数据,withReplacement表示是抽出的数据是否 放回,true为有放回的抽样,false为无放回的抽样
scala> rdd.sample(true, 0.1, 10).collect
res15: Array[Int] = Array(2, 6, 22)
distinct([numTasks])):对RDD元素去重后,返回一个新的RDD。可传入 numTasks参数改变RDD分区数
scala> val rdd2 = sc.parallelize(1 to 5)
rdd2: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Int] = ParallelCollectionRDD[23] at parallelize at <console>:24
scala> val rdd3 = rdd2.union(rdd2)
rdd3: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Int] = UnionRDD[24] at union at <console>:25
scala> rdd3.collect
res18: Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
scala> rdd3.distinct.collect
res19: Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
coalesce(numPartitions):缩减分区数,无shuffle
scala> rdd1.getNumPartitions
res24: Int = 12
scala> val rdd2 = rdd1.coalesce(6)
rdd2: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Int] = CoalescedRDD[29] at coalesce at <console>:25
scala> rdd2.getNumPartitions
res25: Int = 6
### 增大无效
coalesce(numPartitions):缩减/增加分区数,无shuffle
scala> val rdd2 = rdd1.repartition(6)
rdd2: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Int] = MapPartitionsRDD[33] at repartition at <console>:25
scala> rdd2.getNumPartitions
res26: Int = 6
scala> val rdd2 = rdd1.repartition(8)
rdd2: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Int] = MapPartitionsRDD[37] at repartition at <console>:25
scala> rdd2.getNumPartitions
res27: Int = 8
sortBy(func, [ascending], [numTasks]):使用 func 对数据进行处理,对处理后 的结果进行排序
scala> rdd3.collect
res30: Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
scala> rdd3.sortBy(x => x).collect
collect collectAsync
scala> rdd3.sortBy(x => x).collect
res31: Array[Int] = Array(1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5)
scala> rdd3.sortBy(x => x, false).collect
res32: Array[Int] = Array(5, 5, 4, 4, 3, 3, 2, 2, 1, 1)
宽依赖的算子(shuffle):groupBy、distinct、repartition、sortBy
1.2 常见算子2
-
RDD之间的交 intersection(otherRDD) 宽依赖
scala> val rdd1 = sc.range(1, 21) rdd1: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Long] = MapPartitionsRDD[49] at range at <console>:24 scala> val rdd2 = sc.range(10, 31) rdd2: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Long] = MapPartitionsRDD[51] at range at <console>:24 scala> rdd1.intersection(rdd2).sortBy(x => x).collect collect collectAsync scala> rdd1.intersection(rdd2).sortBy(x => x).collect res33: Array[Long] = Array(10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20) -
并 union(otherRDD) 窄依赖 分区数为两个rdd分区数之和
scala> rdd1.union(rdd2).sortBy(x => x).collect res34: Array[Long] = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 10, 11, 11, 12, 12, 13, 13, 14, 14, 15, 15, 16, 16, 17, 17, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30) -
差 subtract (otherRDD) 宽依赖
scala> rdd1.subtract(rdd2).sortBy(x => x).collect res35: Array[Long] = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) -
cartesian(otherRDD):笛卡尔积 窄依赖 分区数为 两个rdd分区数乘积
scala> val rdd1 = sc.range(1, 5) rdd1: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Long] = MapPartitionsRDD[79] at range at <console>:24 scala> val rdd2 = sc.range(6, 10) rdd2: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[Long] = MapPartitionsRDD[81] at range at <console>:24 scala> rdd1.cartesian(rdd2).collect res36: Array[(Long, Long)] = Array((1,6), (1,7), (1,8), (1,9), (2,6), (2,7), (2,8), (2,9), (3,6), (3,7), (3,8), (3,9), (4,6), (4,7), (4,8), (4,9)) -
zip(otherRDD):将两个RDD组合成 key-value 形式的RDD,默认两个RDD的 partition数量以及元素数量都相同,否则会抛出异常。
scala> rdd1.zip(rdd2).collect res37: Array[(Long, Long)] = Array((1,6), (2,7), (3,8), (4,9))



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号