【洛谷】哈希表实战:5 道经典算法题(unordered_map/set 应用 + 避坑指南) - 详解
学籍管理
题目描述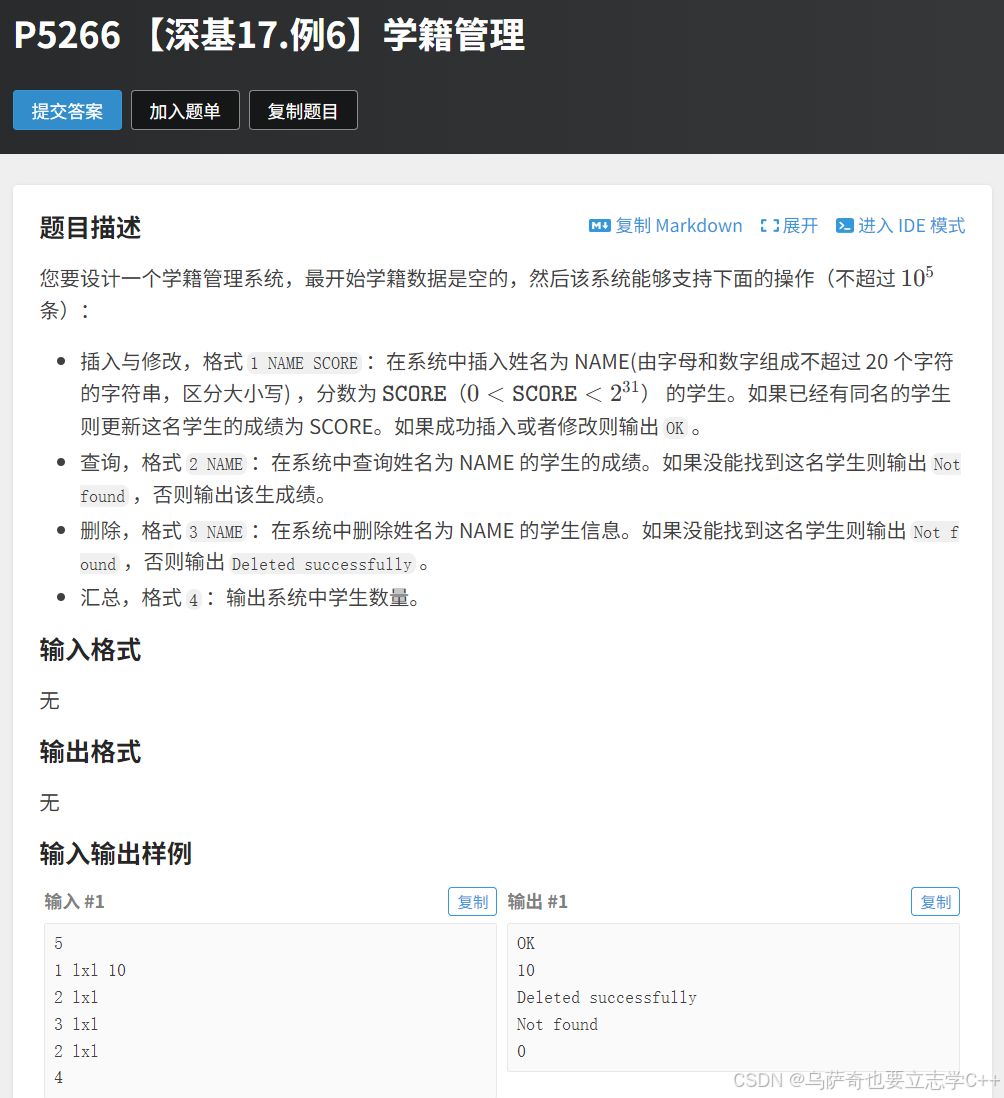
题目解析
本题比较简单,map和unordered_map都可以,unordered_map更优。主要是需要注意相关接口的使用。
(unordered_map与map的选择依据:题目仅需 “增删改查 + 统计大小”,无需有序性,unordered_map的哈希表实现(O (1) 查询)比map的红黑树实现(O (logn) 查询)更高效,)
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//操作次数,操作数,分数
int n, op, sc;
cin >> n;
unordered_map<string, int> m;
string name;
while (n--)
{
cin >> op;
if (op == 4)
{
cout << m.size() << endl;
}
else if (op == 1)
{
cin >> name >> sc;
//插入+修改
m[name] = sc;
cout << "OK" << endl;
}
else if (op == 2)
{
cin >> name;
if (m.count(name))
{
cout << m[name] << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Not found" << endl;
}
}
else
{
cin >> name;
if (m.count(name))
{
m.erase(name);
cout << "Deleted successfully" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Not found" << endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}不重复数字
题目描述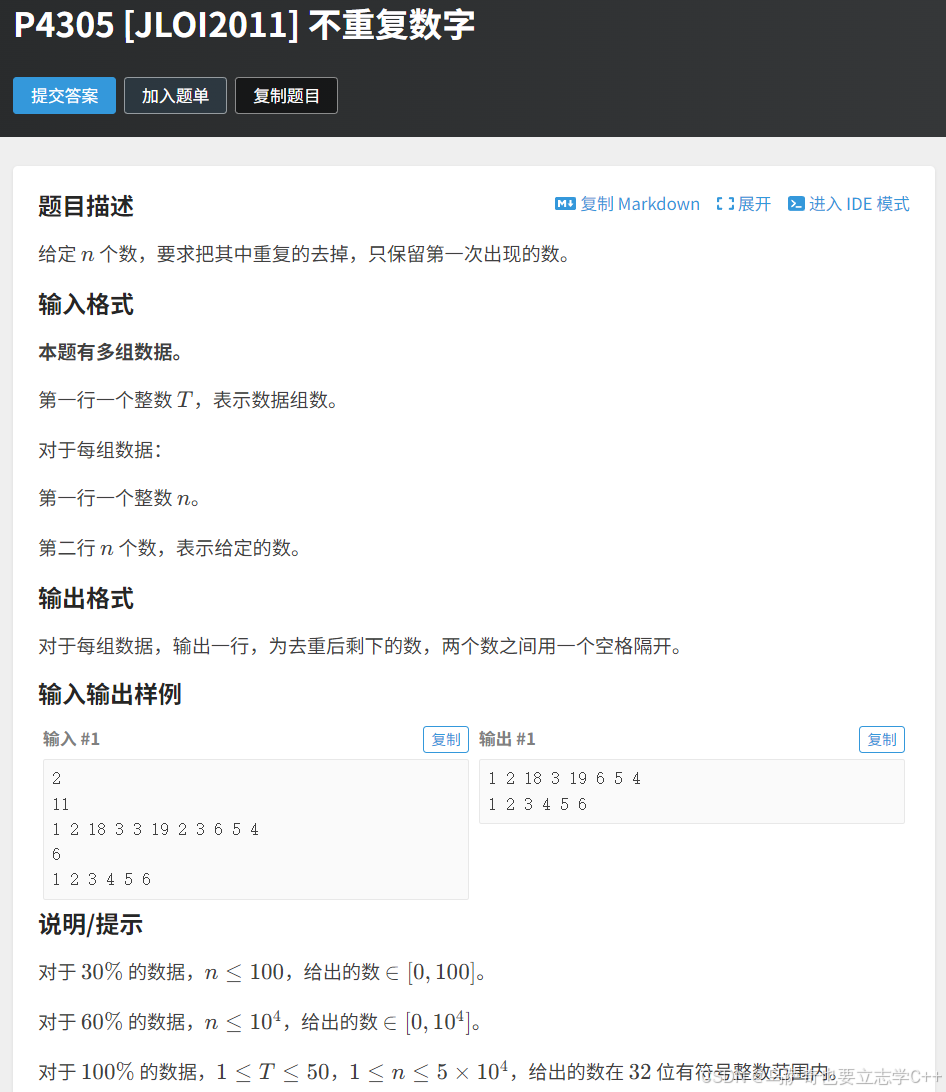
题目解析
本题思路很简单,创建一个unordered_set,读取一个数据先判断它在不在unordered_set中,如果不在则把它插入unordered_set并输出。
但是本题需要注意可能超时,cout 本身带有缓冲,但 “多次小批量输出” 的开销远大于 “一次大批量输出”。所以我们可以先把数据存入数组中,再一次性输出,或者用scanf、printf。
(unordered_set的选择逻辑:题目仅需 “去重” 无需有序,unordered_set(O (1) 插入 / 查询)比set(O (logn))更优)
代码
//1、用scanf、printf替换cin、cout
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//组数、每组数据数、元素数据
int T, n, a;
//cin >> T;
scanf("%d", &T);
//输入
while (T--)
{
unordered_set<int> s;
//cin >> n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n--)
{
//cin >> a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (s.count(a))
{
//已有数据,直接continue
continue;
}
printf("%d ", a);
s.insert(a);
}
//cout << endl;
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}//2、批量输出
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//组数、每组数据数、元素数据
int T, n, a;
cin >> T;
unordered_set<int> s;
vector<int> retv;
//输入
while (T--)
{
//每组数据输入前先清空set、vector
s.clear();
retv.clear();
cin >> n;
while (n--)
{
cin >> a;
if (s.count(a))
{
//已有数据,直接continue
continue;
}
retv.push_back(a);
s.insert(a);
}
//输出
for (auto e : retv)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}阅读理解
题目描述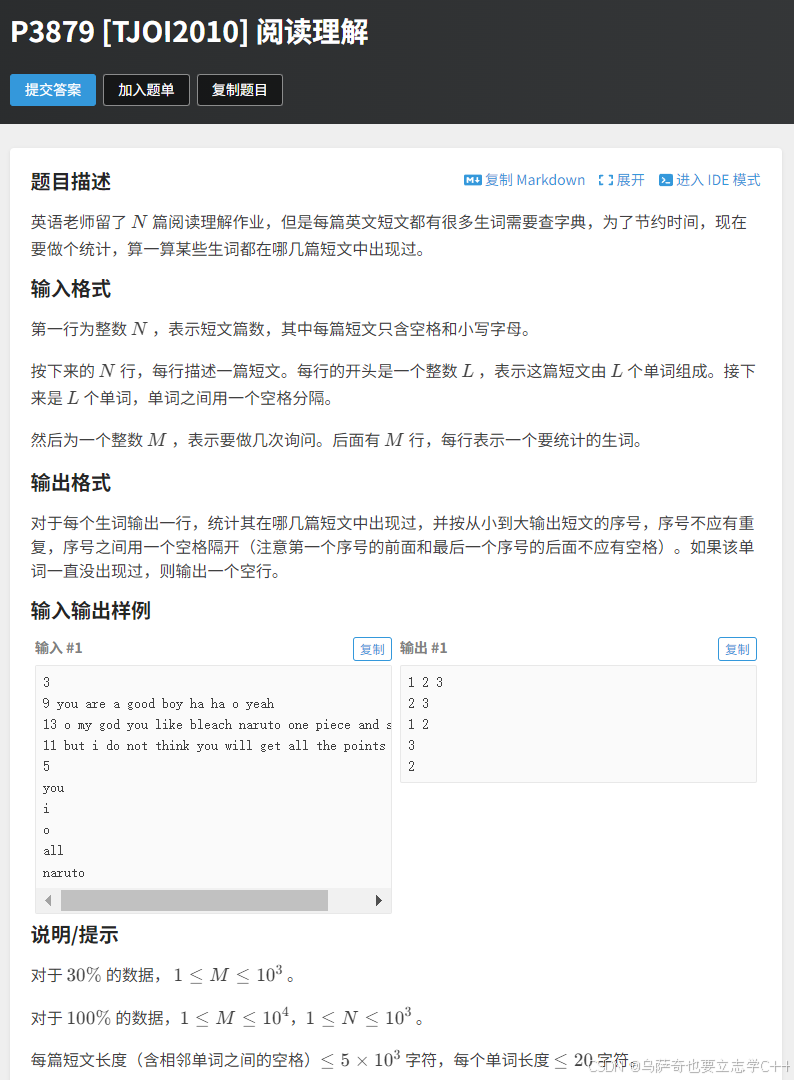
题目解析
本题需要活用我们学习过的容器,用一个unordered_map<string, set< int >>可以很高效地解决本题,首先unordered_map存储单词和在哪些文章中出现过的键值对,单词和在哪些文章中出现过用set存储,set自带去重和排升序的功能(unordered_set无排升序功能故选用set),所以最后直接范围for输出查找单词所对于的set就行了。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//读取短文
int N;
cin >> N;
unordered_map<string, set<int>> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
int L;
cin >> L;
while (L--)
{
string word;
cin >> word;
//m[word]返回set类型变量,i表示第几篇文章
m[word].insert(i);
}
}
//查询每篇短文生词出现数目
int M;
cin >> M;
while (M--)
{
string fword;
cin >> fword;
//查询某个单词在哪些文章中出现过
//m[fword]中的元素自动升序排序,所以直接范围for遍历整个m[fword]就行了
for (auto e : m[fword])
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}A-B数对
题目描述
题目解析
本题思路是把枚举转化成查找。题目要求是满足A - B = C的数对个数,转化一下相当于求满足A = C + B的数对个数。
思路是首先遍历全部数据统计出每个数出现的次数,用unorder_map存储<数,每个数出现的次数>。然后再遍历全部数据,把遍历的每一个数当作B,unorder_map中的C + B的值出现的次数就是题目要求是A-B数对的个数(比如题目示例B为2,C为1,C + B = 3,3这个数出现过一次(在unorder_map中存在,且value为1),所以数对个数加1),unorder_map[C + B]的返回值就是每一个C + B的值出现的次数。
本题返回值ret需要用long long存储,因为极端情况比如:
假设数组所有元素都相同(比如全是 5),且C = 0。
此时对每个 B(共 2e5 个)来说,A = 0 + 5,而 A 的出现次数是 2e5 次(因为所有元素都是 5)。
总对数 = 每个 B 对应的 A 次数之和 = 2e5 * 2e5 = 4e10 超过了int的上限2e9。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N]; //用于存储每一个输入的数值
int main()
{
int n, c;
cin >> n >> c;
// <数,每个数出现的次数>
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
//统计每个数出现的次数
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
mp[a[i]]++;
}
// A = C + B,B = a[i]
// 遍历全部数据作为B,统计C + a[i]出现的次数
LL ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ret += mp[c + a[i]];
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}CitiesandStatesS
题目描述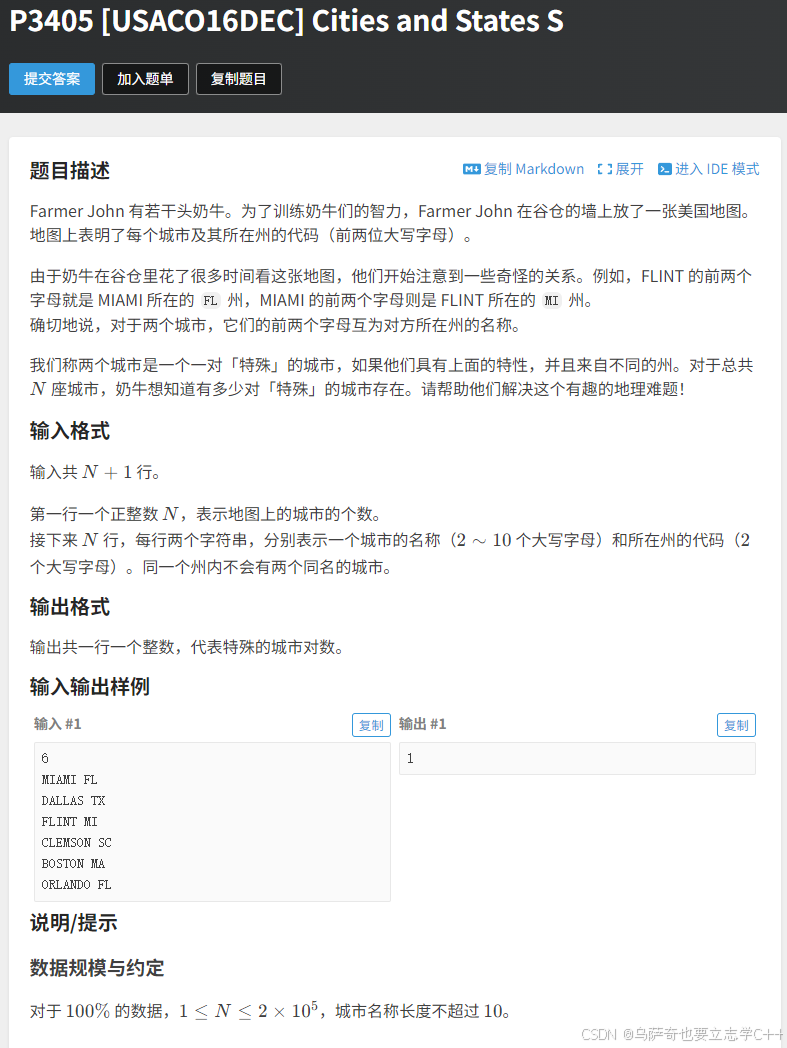
题目解析
本题思路是找反向对应关系,当出现ab对应xy的数据时,需要找历史xy对应ab出现过的次数,每来一个数据都把统计的该次数加上,次数总和就是所有满足题目要求的特殊城市对数。这种对应关系我们用字符串拼接的方式来实现,把abxy拼成一个字符串存入unordered_map的key,value记录该字符串出现的次数。截取字符串用 substr实现,拼接字符串用string的operator+实现。
substr是截取子串接口,从pos位置开始截取len个字符。

本题还有一个条件:特殊城市需要来自不同的州,所以对于形如 ab_ _ _ -> ab 这样的数据不能统计,所以遇到城市名前两个字符和州名相同的数据时直接跳过,不参与统计。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
unordered_map<string, int> mp;
int ret = 0;
while (n--)
{
string a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
//<城市前两个字符拼接州名, 出现次数>
//截取城市名前两个字符
a = a.substr(0, 2);
if (a == b)
{
//城市前两个字符和城市所在州名相同
//不符合题目规定“来自不同的州”直接continue
continue;
}
//一对统计一次,只有在一对符合要求的第二个出现的数据才统计
//先查后存,避免当前数据与自身匹配
ret += mp[b + a];
mp[a + b]++;
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}以上就是小编分享的全部内容了,如果觉得不错还请留下免费的赞和收藏
如果有建议欢迎通过评论区或私信留言,感谢您的大力支持。
一键三连好运连连哦~~





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号