Data Manipulation with dplyr in R
目录
Data Manipulation with dplyr in R
select
select(data,变量名)
The filter and arrange verbs
arrange
counties_selected <- counties %>%
select(state, county, population, private_work, public_work, self_employed)
# Add a verb to sort in descending order of public_work
counties_selected %>%arrange(desc(public_work))
filter
counties_selected <- counties %>%
select(state, county, population)
# Filter for counties in the state of California that have a population above 1000000
counties_selected %>%
filter(state == "California",
population > 1000000)
#筛选多个变量
filter(id %in% c("a","b","c"...)) 存在
filter(id %in% c("a","b","c"...)) 不存在
fct_relevel
Reorder factor levels by hand
排序,order不好使的时候
f <- factor(c("a", "b", "c", "d"), levels = c("b", "c", "d", "a"))
fct_relevel(f)
fct_relevel(f, "a")
fct_relevel(f, "b", "a")
# Move to the third position
fct_relevel(f, "a", after = 2)
# Relevel to the end
fct_relevel(f, "a", after = Inf)
fct_relevel(f, "a", after = 3)
# Revel with a function
fct_relevel(f, sort)
fct_relevel(f, sample)
fct_relevel(f, rev)
Filtering and arranging
counties_selected <- counties %>%
select(state, county, population, private_work, public_work, self_employed)
>
> # Filter for Texas and more than 10000 people; sort in descending order of private_work
> counties_selected %>%filter(state=='Texas',population>10000)%>%arrange(desc(private_work))
# A tibble: 169 x 6
state county population private_work public_work self_employed
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Texas Gregg 123178 84.7 9.8 5.4
2 Texas Collin 862215 84.1 10 5.8
3 Texas Dallas 2485003 83.9 9.5 6.4
4 Texas Harris 4356362 83.4 10.1 6.3
5 Texas Andrews 16775 83.1 9.6 6.8
6 Texas Tarrant 1914526 83.1 11.4 5.4
7 Texas Titus 32553 82.5 10 7.4
8 Texas Denton 731851 82.2 11.9 5.7
9 Texas Ector 149557 82 11.2 6.7
10 Texas Moore 22281 82 11.7 5.9
# ... with 159 more rows
Mutate
counties_selected <- counties %>%
select(state, county, population, public_work)
# Sort in descending order of the public_workers column
counties_selected %>%
mutate(public_workers = public_work * population / 100) %>%arrange(desc(public_workers))
counties %>%
# Select the five columns
select(state, county, population, men, women) %>%
# Add the proportion_men variable
mutate(proportion_men = men / population) %>%
# Filter for population of at least 10,000
filter(population >= 10000) %>%
# Arrange proportion of men in descending order
arrange(desc(proportion_men))
The count verb
counties_selected %>%count(region,sort=TRUE)
counties_selected %>%count(state,wt=citizens,sort=TRUE)
Summarizing
# Summarize to find minimum population, maximum unemployment, and average income
counties_selected %>%summarize(
min_population=min(population),
max_unemployment=max(unemployment),
average_income=mean(income)
)
# Add a density column, then sort in descending order
counties_selected %>%
group_by(state) %>%
summarize(total_area = sum(land_area),
total_population = sum(population),
density=total_population/total_area) %>%arrange(desc(density))
发现了,归根到底是一种函数关系,看看该怎样处理这个函数比较简单,如果写不出来,可能和小学的时候应用题写不出来有关系
top_n
按照优先级来筛选
# Extract the most populated row for each state
counties_selected %>%
group_by(state, metro) %>%
summarize(total_pop = sum(population)) %>%
top_n(1, total_pop)
Selecting
Using the select verb, we can answer interesting questions about our dataset by focusing in on related groups of verbs.
The colon (😃 is useful for getting many columns at a time.
In the video you learned about the select helper starts_with(). Another select helper is ends_with(), which finds the columns that end with a particular string.
counties %>%
# Select the state, county, population, and those ending with "work"
select(state, county, population, ends_with("work")) %>%
# Filter for counties that have at least 50% of people engaged in public work
filter(public_work >= 50)
我觉得这种简单的逻辑关系不应该出错,但是老是出错。。是我真的不太适合做编程这一行嘛?
rename
rename()进行重命名
# Rename the n column to num_counties
counties %>%
count(state)%>%rename(num_counties=n)
也可以在select的时候直接重命名
# Select state, county, and poverty as poverty_rate
> counties %>%select(state,county,poverty_rate=poverty)
# A tibble: 3,138 x 3
state county poverty_rate
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Alabama Autauga 12.9
2 Alabama Baldwin 13.4
3 Alabama Barbour 26.7
4 Alabama Bibb 16.8
5 Alabama Blount 16.7
6 Alabama Bullock 24.6
7 Alabama Butler 25.4
8 Alabama Calhoun 20.5
9 Alabama Chambers 21.6
10 Alabama Cherokee 19.2
# ... with 3,128 more rows
transmute
combination select & mutate
类似于mutate,添加新列但是只保留新列,删掉旧列
官方解释: use to calculate new columns while dropping other columns
counties %>%
# Keep the state, county, and populations columns, and add a density column
transmute(state, county, population, density = population / land_area) %>%
# Filter for counties with a population greater than one million
filter(population > 1000000) %>%
# Sort density in ascending order
arrange(density
这个解释挺好的
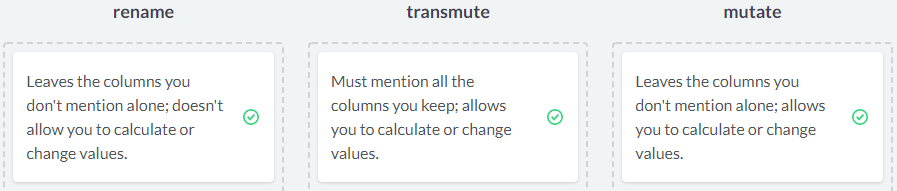
给出一个综合的例子
> # Change the name of the unemployment column
> counties %>%
rename(unemployment_rate = unemployment)
# A tibble: 3,138 x 40
census_id state county region metro population men women hispanic white
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1001 Alab~ Autau~ South Metro 55221 26745 28476 2.6 75.8
2 1003 Alab~ Baldw~ South Metro 195121 95314 99807 4.5 83.1
3 1005 Alab~ Barbo~ South Nonm~ 26932 14497 12435 4.6 46.2
4 1007 Alab~ Bibb South Metro 22604 12073 10531 2.2 74.5
5 1009 Alab~ Blount South Metro 57710 28512 29198 8.6 87.9
6 1011 Alab~ Bullo~ South Nonm~ 10678 5660 5018 4.4 22.2
7 1013 Alab~ Butler South Nonm~ 20354 9502 10852 1.2 53.3
8 1015 Alab~ Calho~ South Metro 116648 56274 60374 3.5 73
9 1017 Alab~ Chamb~ South Nonm~ 34079 16258 17821 0.4 57.3
10 1019 Alab~ Chero~ South Nonm~ 26008 12975 13033 1.5 91.7
# ... with 3,128 more rows, and 30 more variables: black <dbl>, native <dbl>,
# asian <dbl>, pacific <dbl>, citizens <dbl>, income <dbl>, income_err <dbl>,
# income_per_cap <dbl>, income_per_cap_err <dbl>, poverty <dbl>,
# child_poverty <dbl>, professional <dbl>, service <dbl>, office <dbl>,
# construction <dbl>, production <dbl>, drive <dbl>, carpool <dbl>,
# transit <dbl>, walk <dbl>, other_transp <dbl>, work_at_home <dbl>,
# mean_commute <dbl>, employed <dbl>, private_work <dbl>, public_work <dbl>,
# self_employed <dbl>, family_work <dbl>, unemployment_rate <dbl>,
# land_area <dbl>
>
> # Keep the state and county columns, and the columns containing poverty
> counties %>%
select(state, county, contains("poverty"))
# A tibble: 3,138 x 4
state county poverty child_poverty
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Alabama Autauga 12.9 18.6
2 Alabama Baldwin 13.4 19.2
3 Alabama Barbour 26.7 45.3
4 Alabama Bibb 16.8 27.9
5 Alabama Blount 16.7 27.2
6 Alabama Bullock 24.6 38.4
7 Alabama Butler 25.4 39.2
8 Alabama Calhoun 20.5 31.6
9 Alabama Chambers 21.6 37.2
10 Alabama Cherokee 19.2 30.1
# ... with 3,128 more rows
>
> # Calculate the fraction_women column without dropping the other columns
> counties %>%
mutate(fraction_women = women / population)
# A tibble: 3,138 x 41
census_id state county region metro population men women hispanic white
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1001 Alab~ Autau~ South Metro 55221 26745 28476 2.6 75.8
2 1003 Alab~ Baldw~ South Metro 195121 95314 99807 4.5 83.1
3 1005 Alab~ Barbo~ South Nonm~ 26932 14497 12435 4.6 46.2
4 1007 Alab~ Bibb South Metro 22604 12073 10531 2.2 74.5
5 1009 Alab~ Blount South Metro 57710 28512 29198 8.6 87.9
6 1011 Alab~ Bullo~ South Nonm~ 10678 5660 5018 4.4 22.2
7 1013 Alab~ Butler South Nonm~ 20354 9502 10852 1.2 53.3
8 1015 Alab~ Calho~ South Metro 116648 56274 60374 3.5 73
9 1017 Alab~ Chamb~ South Nonm~ 34079 16258 17821 0.4 57.3
10 1019 Alab~ Chero~ South Nonm~ 26008 12975 13033 1.5 91.7
# ... with 3,128 more rows, and 31 more variables: black <dbl>, native <dbl>,
# asian <dbl>, pacific <dbl>, citizens <dbl>, income <dbl>, income_err <dbl>,
# income_per_cap <dbl>, income_per_cap_err <dbl>, poverty <dbl>,
# child_poverty <dbl>, professional <dbl>, service <dbl>, office <dbl>,
# construction <dbl>, production <dbl>, drive <dbl>, carpool <dbl>,
# transit <dbl>, walk <dbl>, other_transp <dbl>, work_at_home <dbl>,
# mean_commute <dbl>, employed <dbl>, private_work <dbl>, public_work <dbl>,
# self_employed <dbl>, family_work <dbl>, unemployment <dbl>,
# land_area <dbl>, fraction_women <dbl>
>
> # Keep only the state, county, and employment_rate columns
> counties %>%
transmute(state, county, employment_rate = employed / population)
# A tibble: 3,138 x 3
state county employment_rate
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Alabama Autauga 0.434
2 Alabama Baldwin 0.441
3 Alabama Barbour 0.319
4 Alabama Bibb 0.367
5 Alabama Blount 0.384
6 Alabama Bullock 0.362
7 Alabama Butler 0.384
8 Alabama Calhoun 0.406
9 Alabama Chambers 0.402
10 Alabama Cherokee 0.390
# ... with 3,128 more rows
貌似忘记%in%符号的使用了,复习一下啊
# Filter for the names Steven, Thomas, and Matthew
selected_names <- babynames %>%
filter(name %in% c("Steven", "Thomas", "Matthew"))
Grouped mutates
这个就是两两组合之前的例子中有的


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号