注解和反射学习笔记
注解和反射学习笔记
笔记地址:https://github.com/userwusir/study-notes
学习地址:https://space.bilibili.com/95256449
初识注解--如何写
import java.lang.annotation.*;
//注解可以显示赋值,如果没有默认值,我们必须给注解赋值
@MyAnnotation(id = 1)
public class AnnotationTest01 {
@MyAnnotation(id = 1)
public void test() {
}
//默认value可以省略
@MyAnnotation2("123")
public void test2() {
}
}
//定义一个注解
//Target表示我们的注解可以用在哪些地方
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
//Retention 表示我们的注解在什么地方有效
//Retention>class>sources
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//说明该注释将被包含在javadoc中
@Documented
//Inherited说明子类可以继承父类中的该注解
@Inherited
@interface MyAnnotation {
//注解的参数:参数类型 + 参数名() ;
String name() default "";
int id();
String[] schools() default {"哔哩哔哩大学"};
}
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation2 {
String value();
}
初识反射--什么叫反射


//什么叫反射
public class ReflectionTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//通过反射获取类的class对象
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("com.wll.reflection.User");
System.out.println(c1);
//一个类在内存中只有一个Class对象
//一个类被加载后,类的整个结构都会被封装在Class对象中
Class<?> c2 = Class.forName("com.wll.reflection.User");
Class<?> c3 = Class.forName("com.wll.reflection.User");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
}
}
//实体类pojo,entity
class User {
public String sex;
private String name;
private int id;
private int age;
private void test() {
}
public User() {
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public User(String sex, String name, int id, int age) {
this.sex = sex;
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
Class类的创建方式
//测试Class类的创建方式有哪些
public class ReflectionTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Person person = new Student();
System.out.println("This is"+person.name);
//方式一:通过对象获得
Class c1 = person.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//方式二:forName获得
Class c2 = Class.forName("com.wll.reflection.Student");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
//方式三:通过类名.class获得
Class c3 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
//方式四:基本内置类型的包装类都有一个Type属性
Class c4 = Integer.TYPE;
System.out.println(c4);
//获得父类类型
Class c5 = c1.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(c5);
}
}
class Person {
String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person() {
}
}
class Student extends Person{
public Student(){
this.name = "学生";
}
}
class Teacher extends Person{
public Teacher(){
this.name = "教师";
}
}
所有类型的Class
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
//所有类型的Class
public class ReflectionTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c1 = Object.class; //类
Class c2 = Comparable.class; //接口
Class c3 = String[].class; //一维数组
Class c4 = int[][].class; //二维数组
Class c5 = Override.class; //注解
Class c6 = ElementType.class; //枚举
Class c7 = Integer.class; //基本数据类型
Class c8 = void.class; //void
Class c9 = Class.class; //class
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
System.out.println(c4);
System.out.println(c5);
System.out.println(c6);
System.out.println(c7);
System.out.println(c8);
System.out.println(c9);
//只要元素类型与维度一样,就是同一个Class
int[] a = new int[100];
int[] b = new int[200];
System.out.println(a.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println(b.getClass().hashCode());
}
}
类加载器
public class ReflectionTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//获取系统类的加载器
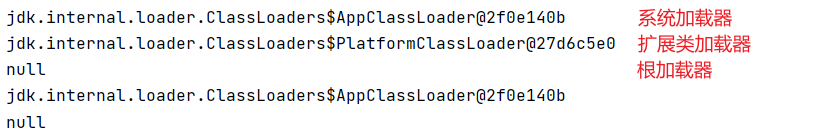
ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader);
//获取系统加载类的父类加载器-->扩展类加载器
ClassLoader parent = classLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(parent);
//获取扩展类加载器的父类加载器-->根加载器(不可直接获取)
ClassLoader parent1 = parent.getParent();
System.out.println(parent1);
//测试当前类是哪个加载器加载的
ClassLoader classLoader1 = Class.forName("com.wll.reflection.ReflectionTest04").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader1);
//测试JDK内置的类是谁加载的
classLoader1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader1);
//如何获得系统类加载器可以加载的路径
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.class.path"));
}
}
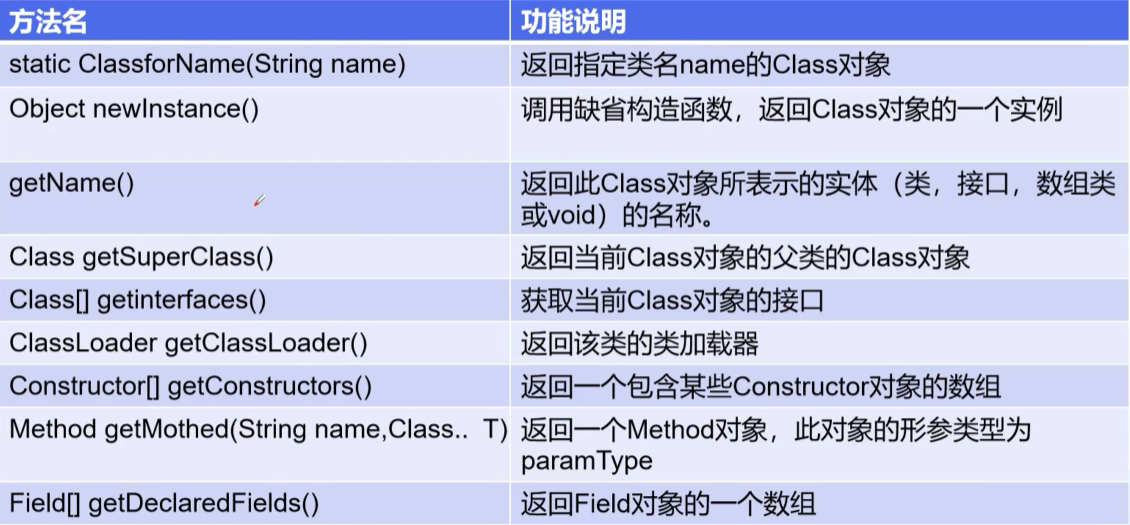
获取运行时类的完整结构
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//获得类的信息
public class ReflectionTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {
//forName获得
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.wll.reflection.User");
//获取类的名字
System.out.println(c1.getName()); //获取包名+类名
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName()); //获取类名
//获取类的属性
System.out.println("1.--------------");
Field[] fields = c1.getFields(); //只能找到public属性
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("==================");
fields = c1.getDeclaredFields(); //找到全部属性
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("2.--------------");
Field sex = c1.getField("sex"); //public属性
System.out.println(sex);
System.out.println("==================");
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name"); //所有属性
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println("3.--------------");
//获取类的方法
Method[] methods = c1.getMethods(); //获得本类及其父类的全部public方法
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
System.out.println("==================");
methods = c1.getDeclaredMethods(); //获得本类的所有方法
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
//获得指定方法
System.out.println("==================");
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null);
Method setName = c1.getMethod("setName", String.class);
System.out.println(getName);
System.out.println(setName);
//获取构造器
System.out.println("4.--------------");
Constructor[] constructors = c1.getConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
System.out.println("==================");
constructors = c1.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
//获得指定的构造器
System.out.println("==================");
Constructor declaredConstructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, String.class, int.class, int.class);
System.out.println(declaredConstructor);
//对象获得
System.out.println("5.--------------");
User user = new User();
c1 = user.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.getName()); //获取包名+类名
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName()); //获取类名
}
}
动态创建对象执行方法
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//通过反射动态的创建对象
public class ReflectionTest06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.wll.reflection.User");
//构建一个对象
User user = (User) c1.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); //调用无参构造器
System.out.println(user);
user = (User) c1.newInstance(); //本质是调用无参构造器
System.out.println(user);
Constructor declaredConstructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, String.class, int.class, int.class);
Object o = declaredConstructor.newInstance("男", "jike", 1, 18); //调用有参构造器
System.out.println(o);
//通过反射调用普通方法
Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
//invoke:激活 (对象,"方法的值")
setName.invoke(user,"jack");
System.out.println(user.getName());
//通过反射操作属性
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
//关闭程序访问安全检测,可以修改私有属性
name.setAccessible(true);
//不能直接操作私有属性,需要关闭程序的访问安全检测
name.set(user,"Jack");
System.out.println(user.getName());
}
}
获取泛型信息
package com.wll.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class ReflectionTest07 {
public void test01(Map<String, User> map, List<User> list) {
System.out.println("test01");
}
public Map<String, User> test02(){
System.out.println("test02");
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Method method = ReflectionTest07.class.getMethod("test01", Map.class, List.class);
//获取泛型类型
Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
for (Type genericParameterType : genericParameterTypes) {
System.out.println("泛型类型:" + genericParameterType);
//泛型类型是否是一种参数化类型
if (genericParameterType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericParameterType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println("真实参数信息:" + actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
method = ReflectionTest07.class.getMethod("test02", null);
//获取返回值类型
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
if (genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericReturnType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println("返回值信息:" + actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
}
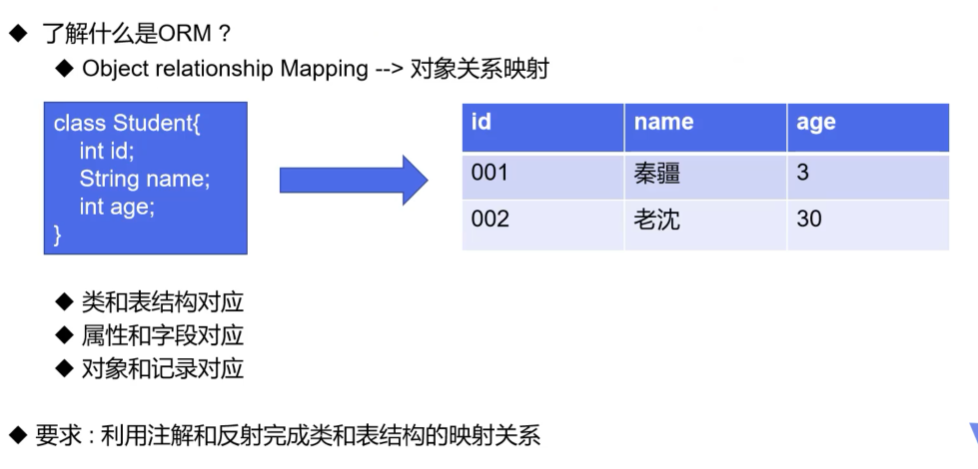
获取注解信息
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
//练习反射操作注解
public class ReflectionTest08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("com.wll.reflection.Room");
//反射获得注解
Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
//获得注解的value的值
Table table = c1.getAnnotation(Table.class);
String value = table.value();
System.out.println(value);
//获得类指定的注解
Field f = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
Filed filed = f.getAnnotation(Filed.class);
System.out.println(filed.columnName());
System.out.println(filed.type());
System.out.println(filed.length());
}
}
@Table("db_room")
class Room{
@Filed(columnName = "db_name",type = "varchar",length = 10)
private String name;
@Filed(columnName = "db_id",type = "int",length = 10)
private int id;
@Filed(columnName = "db_area",type = "int",length = 10)
private int area;
public Room() {
}
public Room(String name, int id, int area) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.area = area;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getArea() {
return area;
}
public void setArea(int area) {
this.area = area;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Room{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
", area=" + area +
'}';
}
}
//类名注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Table{
String value();
}
//属性注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Filed{
String columnName();
String type();
int length();
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号