Verilog快速入门-01基础语法
Verilog快速入门
01 基础语法
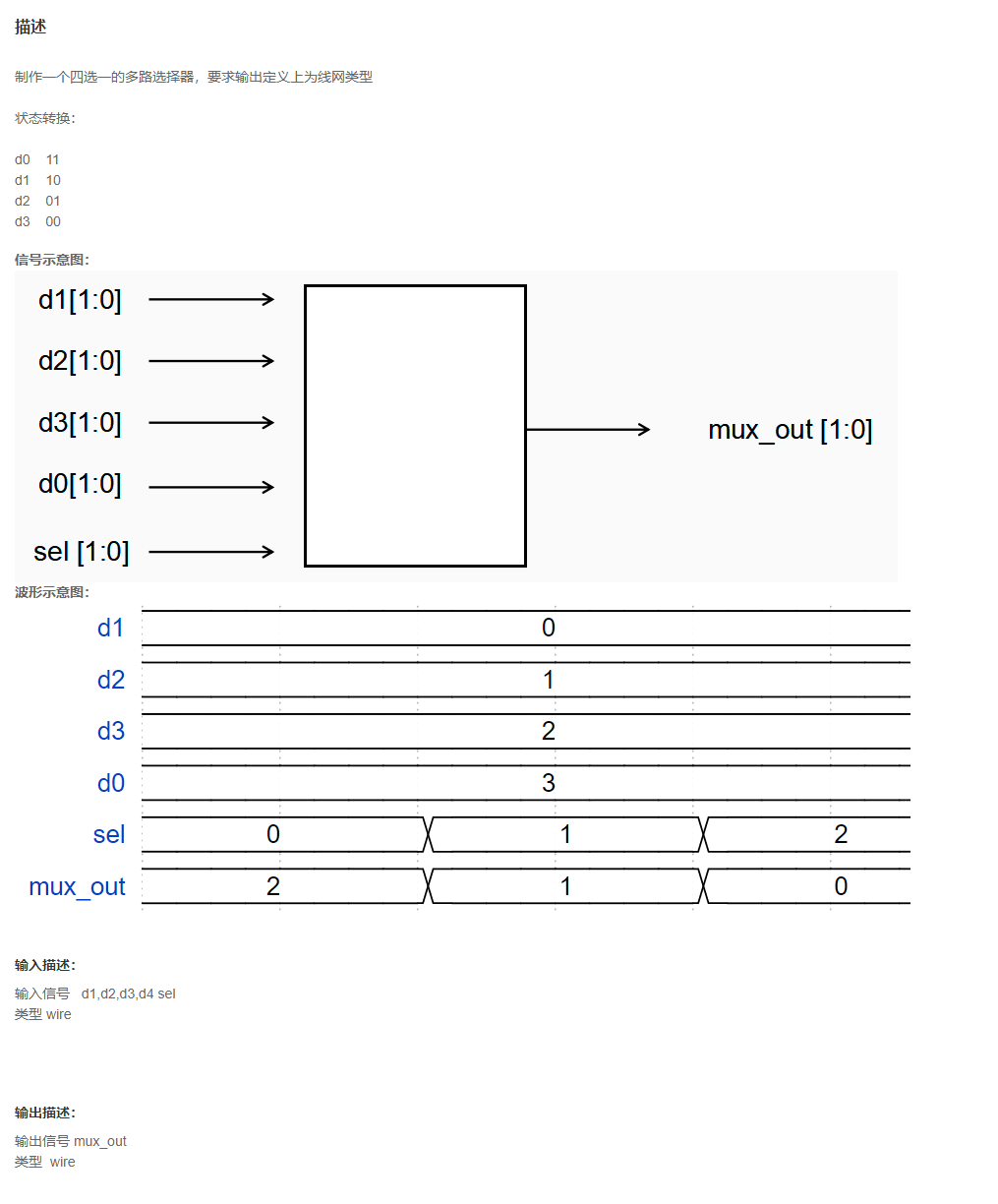
VL1 四选一多路器
题目
Code
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module mux4_1(
input [1:0]d1,d2,d3,d0,
input [1:0]sel,
output[1:0]mux_out
);
//*************code***********//
assign mux_out = (sel == 3'b11) ? d0 :
(sel == 3'b10) ? d1 :
(sel == 3'b01) ? d2 :
(sel == 3'b00) ? d3 : 2'b0;
//*************code***********//
endmodule
分析
题目要求wire类型,使用条件运算符;
也可使用中间reg变量;
// 法二
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module mux4_1(
input [1:0]d1,d2,d3,d0,
input [1:0]sel,
output[1:0]mux_out
);
//*************code***********//
reg [1:0] mux_out_tmp;
always@(*) begin
case(sel)
2'b00: mux_out_tmp = d3;
2'b01: mux_out_tmp = d2;
2'b10: mux_out_tmp = d1;
2'b11: mux_out_tmp = d0;
default: mux_out_tmp = d3;
endcase
end
assign mux_out = mux_out_tmp;
//*************code***********//
endmodule
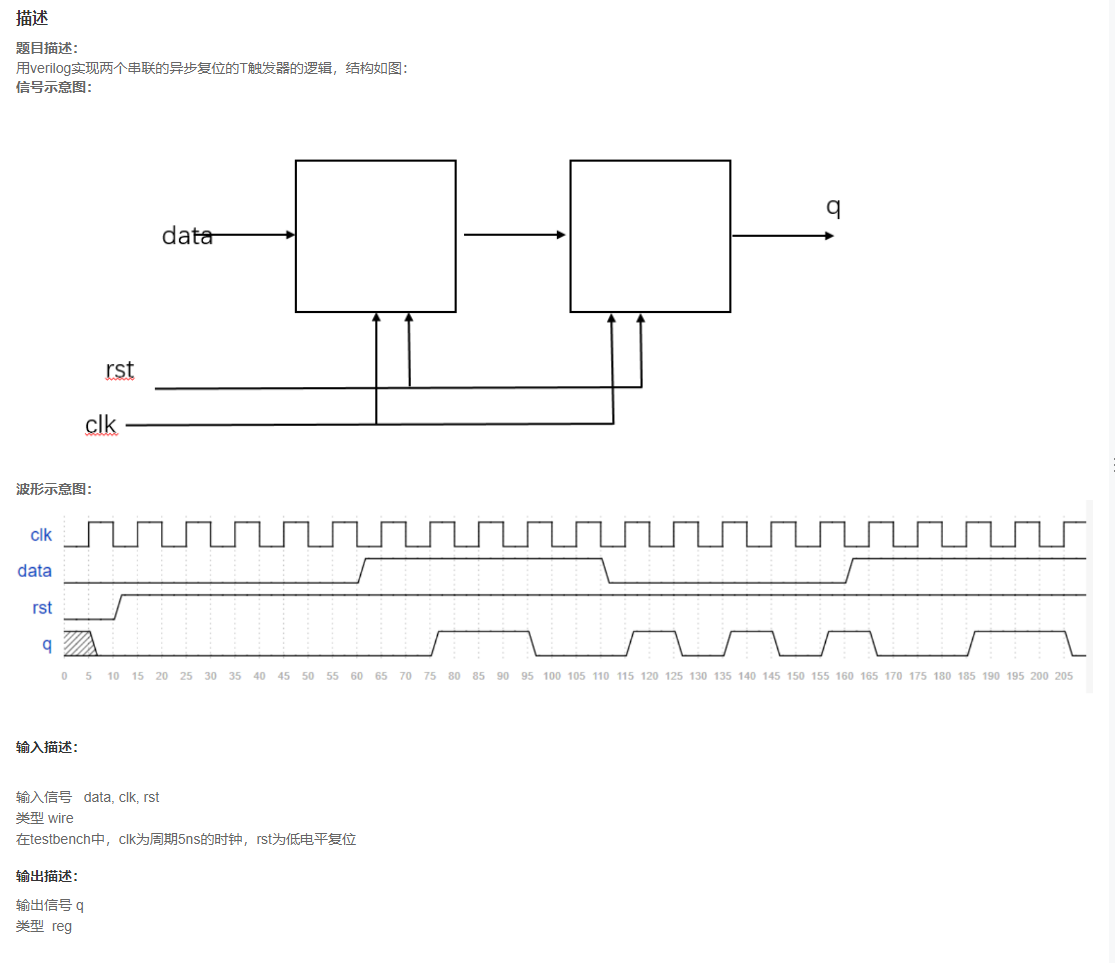
VL2 异步复位的串联T触发器
题目
code
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module Tff_2 (
input wire data, clk, rst,
output reg q
);
//*************code***********//
reg q_d1;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(rst)begin
q_d1 <= 1'b0;
q <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
q_d1 <= data;
q <= q_d1;
end
end
//*************code***********//
endmodule
分析
与D触发器不同,T触发器:当T = 0时,保持,T = 1时,翻转,这里的T就是图中触发器的输入;
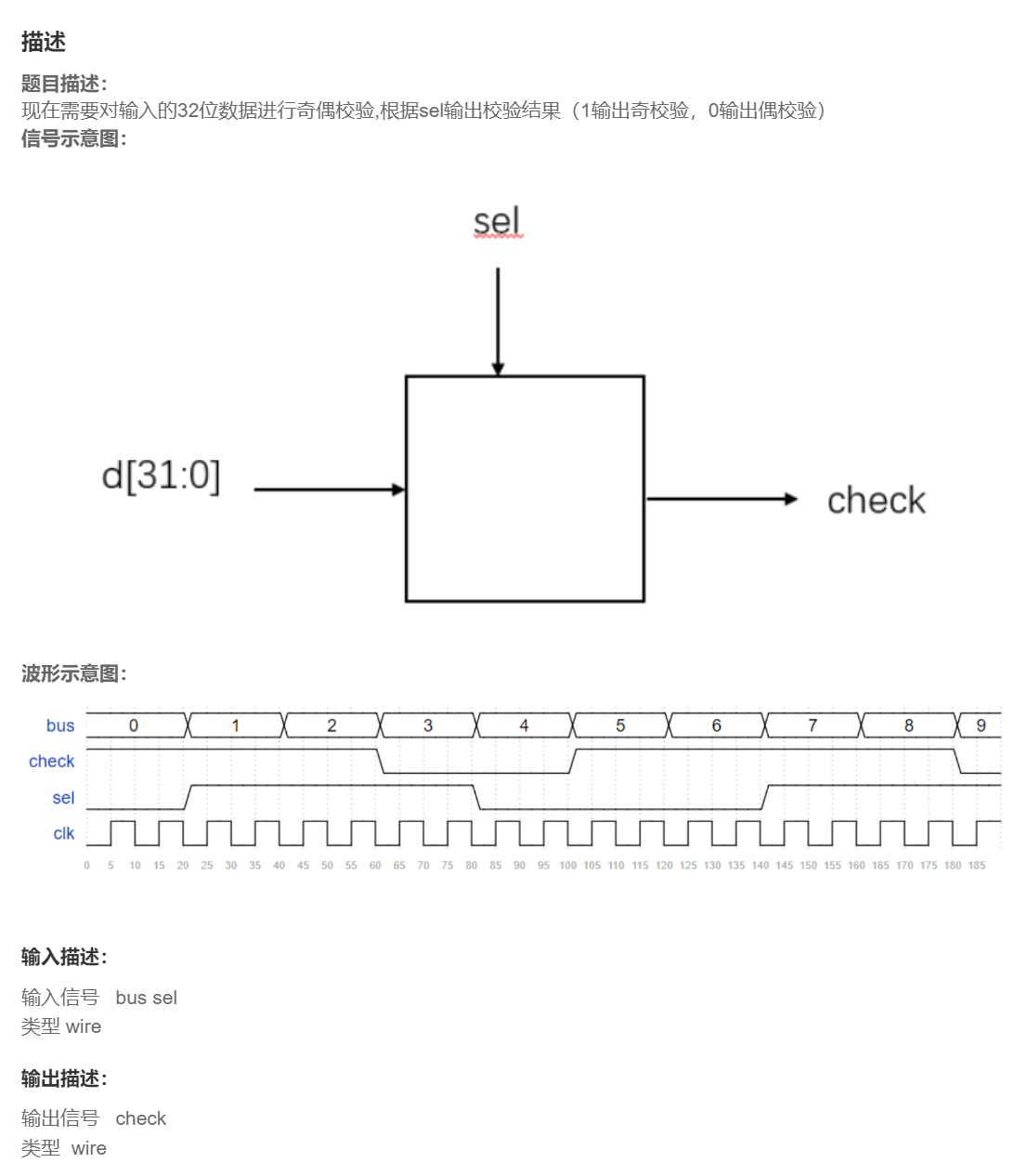
VL3 奇偶校验
题目
code
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module odd_sel(
input [31:0] bus,
input sel,
output check
);
//*************code***********//
assign check = (sel == 1) ? ^bus : ~(^bus);//sel=1 odd,sel=0 even
//*************code***********//
endmodule
分析
偶检测:输入的数据里有偶数个1就输出1;
奇检测:输入的数据里有奇数个1就输出1;
奇偶校验位选择sel,sel=1时奇校验,sel=0时偶校验
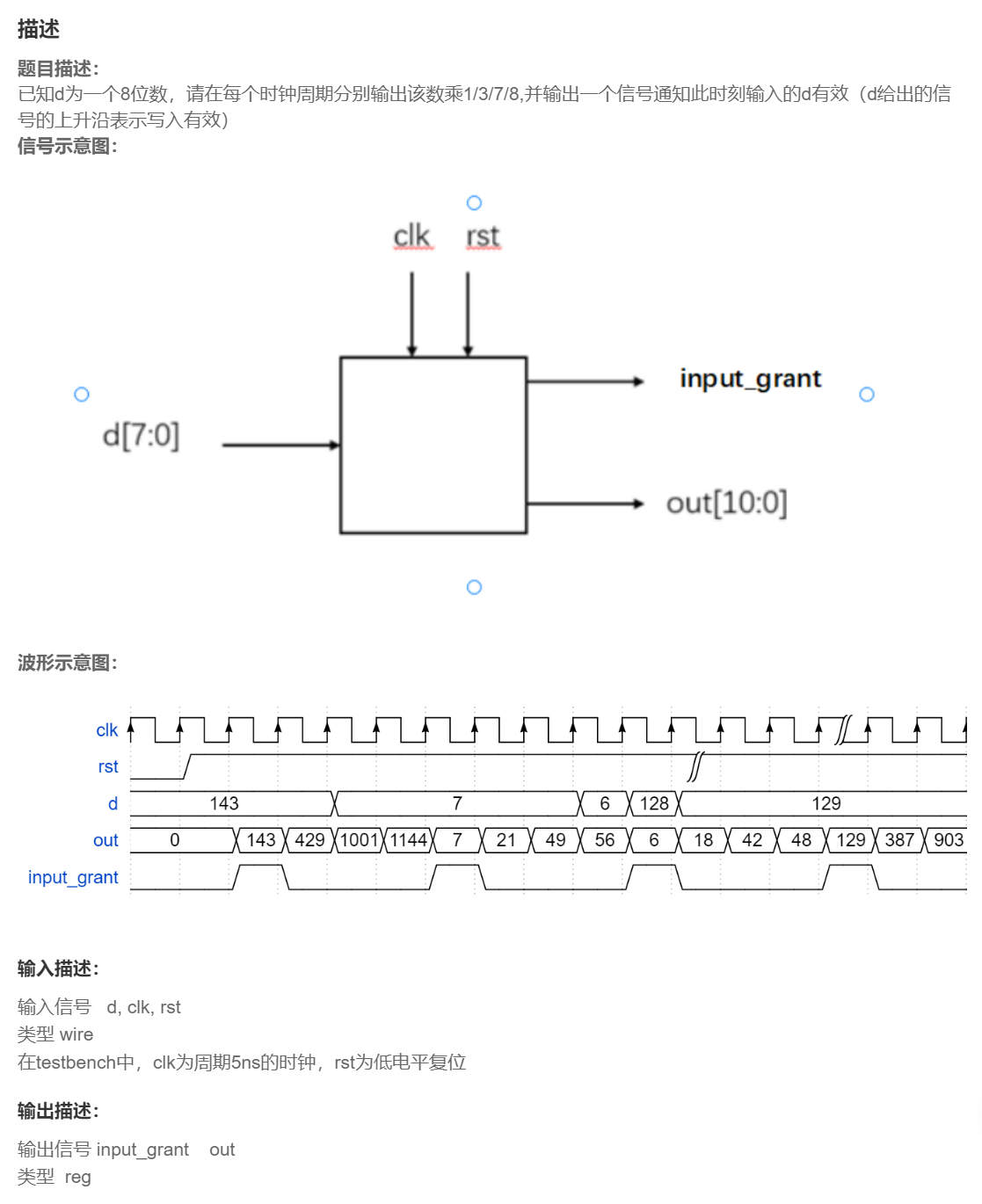
VL4 移位运算与乘法
题目
code
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module multi_sel(
input [7:0]d ,
input clk,
input rst,
output reg input_grant,
output reg [10:0]out
);
//*************code***********//
reg [1:0] cnt;
reg [7:0] data_r;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(!rst)begin
cnt <= 2'b0;
end
else if(cnt <= 2'b11)begin
cnt <= cnt + 1'b1;
end
else begin
cnt <= 2'b0;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(!rst)begin
input_grant <= 1'b0;
out <= 11'b0;
data_r <= 8'b0;
end
else begin
case(cnt)
2'b00: begin input_grant <= 1'b1;out <= d ;data_r <= d; end
2'b01: begin input_grant <= 1'b0;out <= data_r*3;data_r <= data_r; end
2'b10: begin input_grant <= 1'b0;out <= data_r*7;data_r <= data_r; end
2'b11: begin input_grant <= 1'b0;out <= data_r*8;data_r <= data_r; end
default:begin input_grant <= 1'b0;out <= 11'b0 ;data_r <= 8'b0 ; end
endcase
end
end
//*************code***********//
endmodule
分析
重要的是data_r要缓存进来的数据,不然d可能会在这一轮计算中改变值;
VL5 位拆分与运算
题目
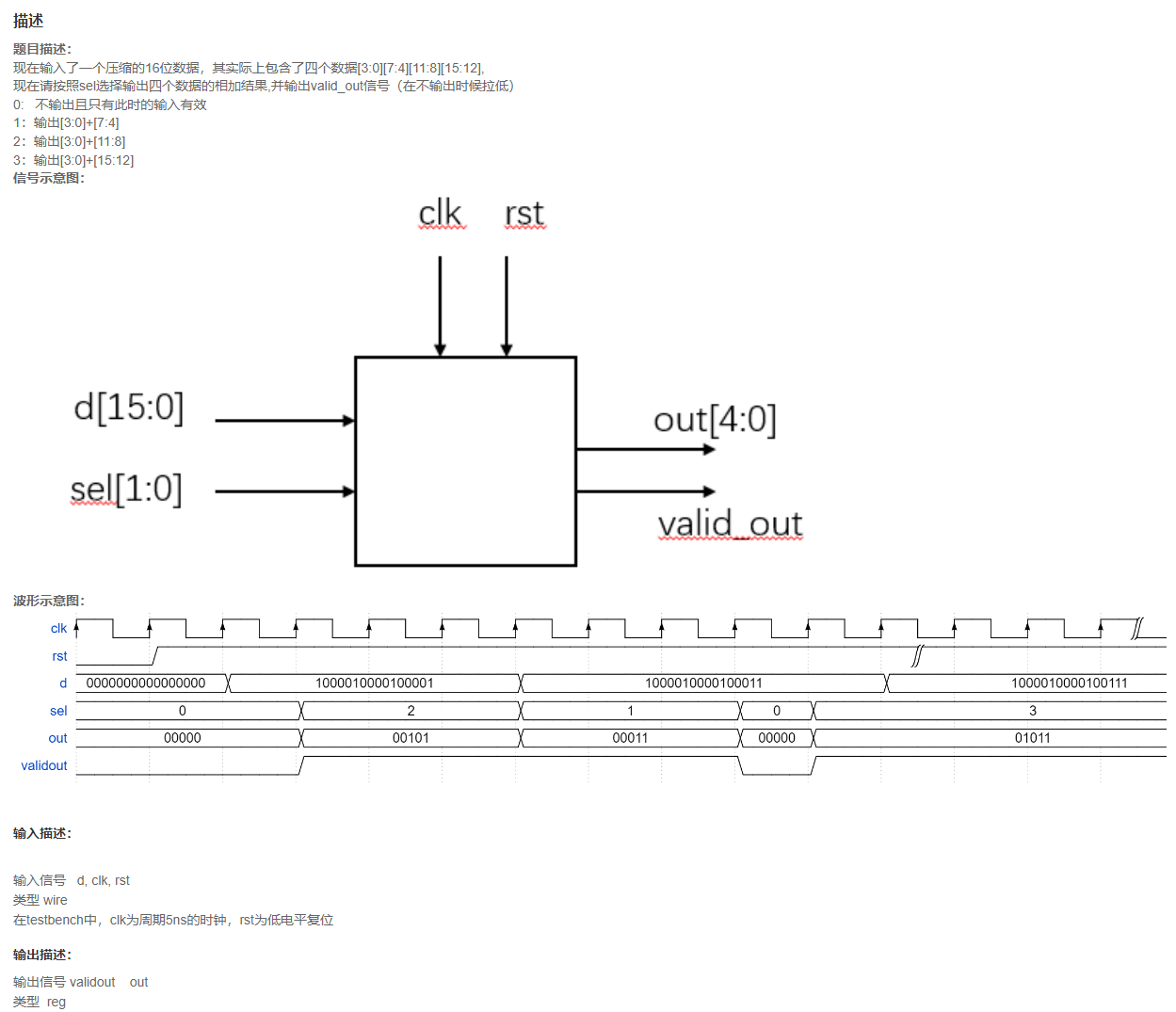
code
module data_cal(
input clk,
input rst,
input [15:0]d,
input [1:0]sel,
output reg [4:0]out,
output reg validout
);
//*************code***********//
reg [15:0]d_r;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(!rst)begin
out <= 5'b0;
validout <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
case(sel)
2'd0: begin validout <= 1'b0; d_r <= d;out <= 5'b0; end
2'd1: begin validout <= 1'b1; out <= d_r[3:0] + d_r[ 7: 4];end
2'd2: begin validout <= 1'b1; out <= d_r[3:0] + d_r[11: 8];end
2'd3: begin validout <= 1'b1; out <= d_r[3:0] + d_r[15:12];end
default:begin validout <= 1'b0; out <= 5'b0; end
endcase
end
end
//*************code***********//
endmodule
分析
注意仅在sel = 0时输入有效,所以添加寄存器缓存;
VL6 多功能数据处理器
题目

code
module data_select(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input signed[7:0]a,
input signed[7:0]b,
input [1:0]select,
output reg signed [8:0]c
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
c <= 9'b0;
end
else begin
case(select)
2'b00: begin c <= a; end
2'b01: begin c <= b; end
2'b10: begin c <= a+b; end
2'b11: begin c <= a-b; end
default:begin c <= c; end
endcase
end
end
endmodule
VL7 求两个数的差值
题目

code
module data_minus(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
output reg [8:0]c
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
c <= 9'b0;
end
else if(a>b)begin
c <= a-b;
end
else if(a<=b)begin
c <= b-a;
end
else begin
c <= 9'b0;
end
end
endmodule
分析
VL8 使用generate…for语句简化代码
题目

code
module gen_for_module(
input [7:0] data_in,
output [7:0] data_out
);
genvar i;
generate
for(i=0; i<=7; i=i+1)
begin:for_loop
assign data_out[i] = data_in[7-i];
end
endgenerate
endmodule
分析
VL9 使用子模块实现三输入数的大小比较
题目

code
module main_mod(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
input [7:0]c,
output [7:0]d
);
wire [7:0]ab_small;
wire [7:0]abc_small;
reg [7:0]c_r[1:0];
assign d = c_r[1];
comparer comparer_ab(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.a(a),
.b(b),
.c(ab_small)
);
comparer comparer_abc(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.a(ab_small),
.b(c),
.c(abc_small)
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)begin
c_r[0] <= 8'b0;
c_r[1] <= 8'b0;
end
else begin
c_r[0] <= abc_small;
c_r[1] <= c_r[0];
end
end
endmodule
module comparer(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
output [7:0]c
);
assign c = (a>=b) ? b : a;
endmodule
分析
testbench设想的是子模块使用时序逻辑,然后例化三个比较器,所以结果相对于输入是延两拍;
VL10 使用函数实现数据大小端转换
题目

code
module function_mod(
input [3:0]a,
input [3:0]b,
output [3:0]c,
output [3:0]d
);
assign c=reverse(a);
assign d=reverse(b);
function[3:0] reverse;
input [3:0] a;
begin
reverse = {a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3]};
end
endfunction
endmodule
分析
-
函数定义不得包含任何时间控制语句,即任何包含 #、@ 或 wait 的语句。
-
函数不得调用任务。
-
函数定义应至少包含一个input参数。
-
函数定义中不得有声明为output或inout的参数。
-
函数不得包含任何非阻塞赋值或过程连续赋值。
-
函数不得被任何事件触发。
-
函数定义隐含声明了一个与函数同名的函数内部变量。该变量要么默认为 1 位reg类型数据,要么与函数声明中指定的类型相同。函数定义通过将函数结果赋值给与函数同名的内部变量,来初始化函数的返回值。换句话说,在函数内部有一个隐含的变量,它的名称是函数的名称,可以在函数内部的表达式中使用。因此,在函数作用域内声明另一个与函数同名的对象是非法的。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号