java引入Elasticsearch插件
最近业务需求需要用到Es,我在百度上翻了好久没有找到一篇比较好的例子,干脆自己写点东西留着以后,万一能用到呢。
我使用的7.8版本的,下面是下载ES网盘地址 还附带了head可视化工具,有需要的自己去下载,也可以去官网下载最新版本,取舍看自己
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1r_sRsrljhSMLGyyorWqGiw
提取码:k7f9
好了 不多BB,直接进入正题,下载下来后,使用bin文件的启动文件elasticsearch.bat,双击启动即可,默认端口
引入pom文件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>7.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- elasticsearch的客户端 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.8.0</version>
</dependency>j
我觉得光写方法是不科学的,也是不利于以后发展的,现在我添加一些ES使用的技术-倒排索引
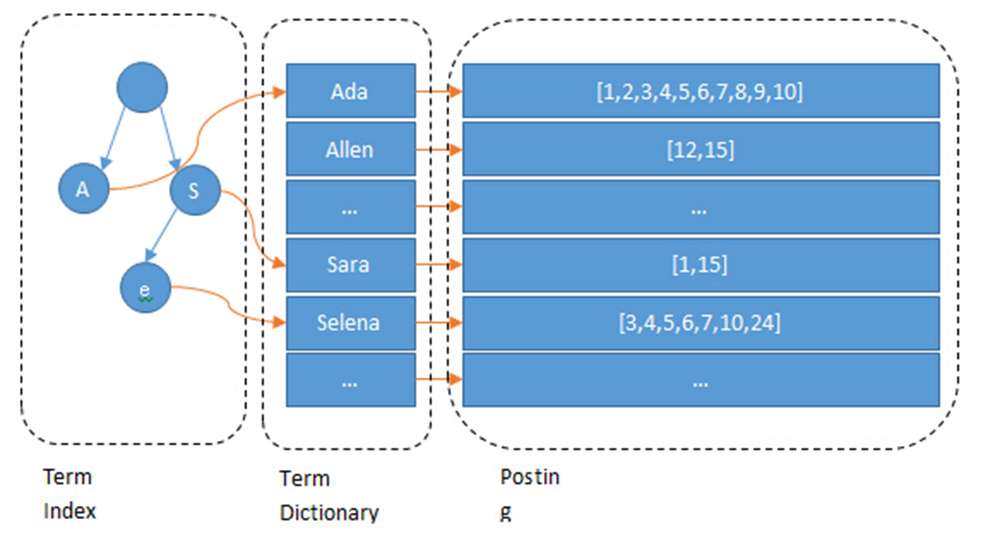
倒排索引:正向索引通过key来寻找value,类似于map,而倒排索引也叫反向索引,是通过value找key。
es为每一个field都创建了一个倒排索引term,term的集合叫做posting list,他是一个int的数组,记录了某个单词在post list的某一个位置,根据位置找到所需要的数据
Term Dictionary:
Elasticsearch为了能快速找到某个term,将所有的term排个序,二分法查找term,logN的查找效率,就像通过字典查找一样,这就是Term Dictionary。看起来,似乎和传统数据库通过B-Tree的方式类似。
Term Index:
B-Tree通过减少磁盘寻道次数来提高查询性能,Elasticsearch也是采用同样的思路,直接通过内存查找term,不读磁盘,但是如果term太多,term dictionary也会很大,放内存不现实,于是有了Term Index,就像字典里的索引页一样,A开头的有哪些term,分别在哪页,可以理解term index是一颗树,这棵树不会包含所有的term,它包含的是term的一些前缀。通过term index可以快速地定位到term dictionary的某个offset,然后从这个位置再往后顺序查找,所以term index不需要存下所有的term,而仅仅是他们的一些前缀与Term Dictionary的block之间的映射关系,再结合FST(Finite State Transducers)的压缩技术,可以使term index缓存到内存中。从term index查到对应的term dictionary的block位置之后,再去磁盘上找term,大大减少了磁盘随机读的次数。
接下来我们新建一个测试类,此处简单的贴一下代码,以后忘记的时候过来瞅瞅。(手打字是真的累)
1、链接客户端(最简单的事情)
// 创建ES客户端 RestHighLevelClient esClient = new RestHighLevelClient( RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")) ); // 关闭ES客户端 esClient.close();
2、既然链接的客户端那得做点什么事情 创建索引好了(类似于数据库中的表名)
RestHighLevelClient esClient = new RestHighLevelClient( RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")) ); // 创建索引 - 请求对象 CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("egg"); // 发送请求,获取响应 CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = esClient.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); // 响应状态 boolean acknowledged = createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged(); System.out.println("索引操作 :" + acknowledged); esClient.close();
3.创建了ES索引(表)总得添加一些数据
RestHighLevelClient esClient = new RestHighLevelClient( RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")) ); // 插入数据 IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest(); request.index("egg").id("1001"); Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("size",10); map.put("name","鸡蛋"); // 向ES插入数据,必须将数据转换位JSON格式 ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); String userJson = mapper.writeValueAsString(map); request.source(userJson, XContentType.JSON); // 插入 IndexResponse response = esClient.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); // 打印结果 System.out.println(response.getResult()); esClient.close();
4、如果单条插入太慢,那好,批量插入试一下
RestHighLevelClient esClient = new RestHighLevelClient( RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")) ); // 批量插入数据 BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest(); request.add(new IndexRequest().index("egg").id("1002").source(XContentType.JSON, "name", "狗蛋", "size",10)); request.add(new IndexRequest().index("egg").id("1003").source(XContentType.JSON, "name", "鸭蛋", "size",13)); // 批量插入 BulkResponse response = esClient.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(response.getTook()); System.out.println(response.getItems()); esClient.close();
5、今天到此为止




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号